Popular Posts
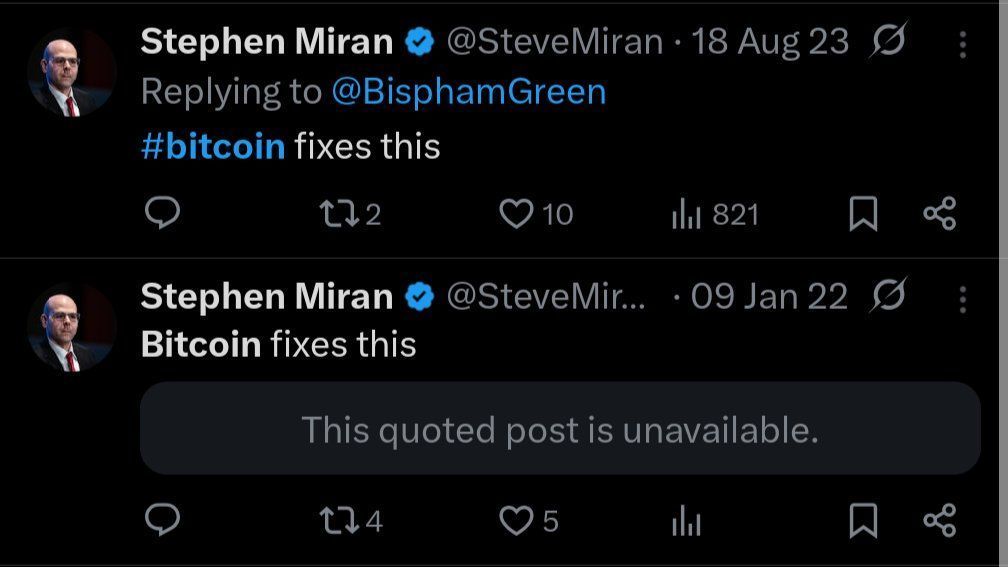
Miran est connu pour son soutien affiché à $BTC, avec son désormais culte : *“#Bitcoin fixes this”*.
Un défenseur du Web3 à la table du FOMC ? Le narratif devient réalité.
#Bitcoin #CryptoPolicy #BTC



Carmelita
2025-08-07 21:15
🚨 Trump propose Stephen Miran, économiste pro-Bitcoin, pour le poste de gouverneur à la Fed.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Polygon Labs spinout Miden secured $25M from a16z Crypto to build the world's first "edge blockchain" - moving transaction execution from validators to user devices, fundamentally solving scalability and privacy limitations!
💰 Core Breakthrough:
-
$25M seed round: a16z Crypto, 1kx, Hack VC leading
Edge execution architecture: Users execute locally, ZK proofs verify
Unlimited scalability: Eliminates network execution bottlenecks
Mainnet target: Q4 2025 launch
🎯 Technical Innovation:
-
STARK zero-knowledge proofs: No trusted setup, quantum-resistant
Actor Model architecture: Independent account operation, eliminates global state sync
Rust-native development: No specialized blockchain languages required
Hybrid public-private state: Private accounts need only 32 bytes storage
🏆 Competitive Edge:
-
Privacy by default: Private accounts transact completely off-chain
No smart contract complexity limits: Only bounded by device processing power
Enterprise-grade compliance: Selective disclosure without public transparency
Anti-MEV architecture: Order book DEXs with encrypted orders
💡 Killer Applications:
-
Corporate treasury management: Confidential multi-million dollar fund management
High-frequency trading infrastructure: Encrypted orders, strategy protection
Web3 gaming: Anti-cheat, hidden attribute items
AI/ML applications: Private data training, model parameter protection
🎮 Ecosystem Development:
-
Miden Pioneer Program: Early developer support initiative
POL holder airdrop: ~10% token distribution to Polygon community
Polygon AggLayer integration: Cross-chain liquidity hub
Direct competition with Solana, Sui, Aptos
⚠️ Technical Requirements:
-
Client-side proof generation: Smartphones support basic operations
Hardware demands: Complex contracts may need dedicated devices
Network connectivity: Periodic blockchain state synchronization
Key security: Users fully control private account management
🌟 Market Position:
-
First institutional ZK-native design: Beyond simple Ethereum compatibility
Privacy-first architecture: Programmable confidentiality for complex apps
Infinite parallelization: Multiple users execute simultaneously
Next-gen blockchain paradigm: From network execution to client proving
Revolutionary Impact: Miden transforms blockchain from "network execution + user verification" to "user execution + network verification," achieving true unlimited scalability and native privacy protection, positioning to become the next-generation blockchain infrastructure standard.
Read the complete technical analysis and application scenarios: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/miden-edge-blockchain-guide/?utm_source=blog
#Miden #EdgeBlockchain #ZeroKnowledge #STARK



JU Blog
2025-08-12 08:31
🚀 Miden Edge Blockchain Revolution: a16z-Led $25M Funding Redefines Blockchain Execution!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
⏳Countdown: 4 Days! The JuCoin Million Airdrop Invitation Boost is on!
Open the event page, click “Share” to quickly invite friends, and accelerate your reward growth.
This is your last chance to overtake — don’t miss it!
👉 Quick Share: https://bit.ly/40NWXjH
👉 Đăng ký Jucoin ngay: https://www.jucoin.com/pro/PARTNER
#JuCoin #JucoinVietnam #Airdrop


Lee Jucoin
2025-08-12 11:14
JuCoin Million Airdrop Plan🚀
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Beta and How Does It Measure Market Sensitivity?
Understanding beta is essential for investors aiming to gauge how their investments respond to overall market movements. Beta, a core concept in finance, quantifies the volatility or systematic risk of an asset relative to the broader market. This metric helps investors assess whether an asset tends to move in tandem with market trends or behaves more independently.
At its core, beta is calculated by comparing the covariance between an investment’s returns and those of a benchmark index—such as the S&P 500—to the variance of that index. A beta value provides insight into how much an asset's price might change when the market moves. For example, a beta of 1 indicates that the investment generally moves in line with the overall market. If the market rises by 10%, such an asset would typically increase by about 10%. Conversely, a beta greater than 1 suggests higher volatility; if it’s less than 1, it indicates lower sensitivity.
Why Investors Use Beta
Investors rely on beta primarily for risk assessment and portfolio diversification strategies. Stocks with high betas tend to experience larger swings during bullish or bearish markets, making them suitable for aggressive investors seeking higher returns but willing to accept increased risk. On the other hand, low-beta assets are often favored by conservative investors who prioritize stability.
Beta also plays a vital role in financial models like Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which estimates expected returns based on systematic risk factors. By understanding an asset’s beta, investors can better predict potential gains or losses relative to overall market performance.
Market Sensitivity: How Beta Reflects Response to Market Changes
Market sensitivity refers broadly to how responsive an investment is when there are shifts in economic conditions or investor sentiment affecting financial markets. A high-beta security reacts strongly—either positively or negatively—to these changes; low-beta securities tend to be more stable and less affected.
This responsiveness makes beta particularly useful during volatile periods when understanding potential risks becomes crucial for managing portfolios effectively. For instance:
- High-beta stocks may offer substantial upside during bull markets but can also lead to significant losses during downturns.
- Low-beta stocks provide steadiness but might underperform compared to more volatile assets when markets rally.
Recent Trends: Extending Beta Analysis Beyond Traditional Assets
Traditionally applied within stock markets and bonds, recent years have seen increasing interest in applying beta analysis across alternative investments—including commodities and real estate—and notably cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Cryptocurrencies exhibit unique characteristics—they are highly volatile yet increasingly correlated with traditional assets at times—making their betas valuable indicators of their market sensitivity:
- Cryptocurrency Betas: Calculated using historical price data against indices such as S&P 500 or specialized crypto benchmarks.
- High Volatility Reflection: Bitcoin's high price swings translate into elevated beta values compared with traditional assets.
- Risk Management Tool: Knowing cryptocurrency betas helps traders diversify portfolios effectively while managing exposure risks amid rapid price fluctuations.
The Rise of Crypto Market Sensitivity Analysis
As digital currencies gain mainstream acceptance, understanding their behavior relative to traditional financial instruments has become critical for both institutional and retail investors alike. The high volatility inherent in cryptocurrencies means they can dramatically influence portfolio performance depending on prevailing market conditions—a fact reflected through their calculated betas.
For example:
- During periods of heightened regulatory scrutiny or macroeconomic uncertainty, cryptocurrency betas may spike due to increased sensitivity.
- Conversely, positive developments like adoption announcements can cause sharp upward movements aligned with broader equity rallies if correlations increase temporarily.
Potential Risks from High Market Sensitivity
While leveraging knowledge about a security’s beta offers strategic advantages—such as optimizing diversification—it also exposes investors to certain risks associated with high-market sensitivity:
- Rapid Price Fluctuations*: Assets with elevated betas can experience swift gains but equally rapid declines based on minor shifts in investor sentiment or macroeconomic news.
- Regulatory Impact*: Sudden policy changes can disproportionately affect highly sensitive assets like cryptocurrencies.
- Sentiment-driven Movements*: Investor emotions often amplify responses beyond fundamental factors leading potentially unpredictable outcomes especially during turbulent times.
By monitoring these sensitivities through updated calculations of each asset'sbeta over time—and staying informed about external influences—investors improve their abilityto navigate complex markets confidently while aligning strategies accordingto individual risk tolerance levels.
How Understanding Beta Enhances Investment Decision-Making
Incorporating insights frombeta analysis allows investors not onlyto assess current risksbut also forecast future performance scenarios under differentmarket conditions.This proactive approach supports better decision-makingby enabling tailored portfolio adjustments aimed at balancing risk versus reward efficiently.For example:
- Diversifying across low-and high-beta assets accordingto one’s appetitefor volatility
- Hedging positionsin highly sensitive securitiesduring uncertain periods
- Adjusting exposurebasedon evolving macroeconomic trendsand geopolitical developments
The Role Of E-A-T In Financial Content About Beta
When discussing complex topics such asbeta measurementand its applicationin modern investing,it is vital that content demonstrates Expertise Authority Trustworthiness (E-A-T). This involves referencing reputable sources—including academic research,published studies,and industry experts—and providing accurate information groundedin current financial theoriesand practices.By doing so,the content ensures credibilityand helps readers make informed decisions rootedin reliable data ratherthan speculation.
Final Thoughts
Beta remains oneof the most fundamental metricsfor evaluatingmarket sensitivity within traditional finance.As digital assets continue gaining prominence,the importanceof understandingcryptocurrencybetas grows correspondingly.Investors who graspthe nuancesof this measurecan better managerisks,and capitalizeon opportunitiespresentedby dynamicmarkets.Furthermore,moving forward,the integrationof advanced analyticsand real-time data will likely enhance our abilityto interpretbetavaluesthroughout diverseasset classes,increasing transparencyandinformed decision-makingacross all levelsof investing activity


Lo
2025-05-14 19:05
What is Beta and how does it evaluate a strategy’s market sensitivity?
What Is Beta and How Does It Measure Market Sensitivity?
Understanding beta is essential for investors aiming to gauge how their investments respond to overall market movements. Beta, a core concept in finance, quantifies the volatility or systematic risk of an asset relative to the broader market. This metric helps investors assess whether an asset tends to move in tandem with market trends or behaves more independently.
At its core, beta is calculated by comparing the covariance between an investment’s returns and those of a benchmark index—such as the S&P 500—to the variance of that index. A beta value provides insight into how much an asset's price might change when the market moves. For example, a beta of 1 indicates that the investment generally moves in line with the overall market. If the market rises by 10%, such an asset would typically increase by about 10%. Conversely, a beta greater than 1 suggests higher volatility; if it’s less than 1, it indicates lower sensitivity.
Why Investors Use Beta
Investors rely on beta primarily for risk assessment and portfolio diversification strategies. Stocks with high betas tend to experience larger swings during bullish or bearish markets, making them suitable for aggressive investors seeking higher returns but willing to accept increased risk. On the other hand, low-beta assets are often favored by conservative investors who prioritize stability.
Beta also plays a vital role in financial models like Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which estimates expected returns based on systematic risk factors. By understanding an asset’s beta, investors can better predict potential gains or losses relative to overall market performance.
Market Sensitivity: How Beta Reflects Response to Market Changes
Market sensitivity refers broadly to how responsive an investment is when there are shifts in economic conditions or investor sentiment affecting financial markets. A high-beta security reacts strongly—either positively or negatively—to these changes; low-beta securities tend to be more stable and less affected.
This responsiveness makes beta particularly useful during volatile periods when understanding potential risks becomes crucial for managing portfolios effectively. For instance:
- High-beta stocks may offer substantial upside during bull markets but can also lead to significant losses during downturns.
- Low-beta stocks provide steadiness but might underperform compared to more volatile assets when markets rally.
Recent Trends: Extending Beta Analysis Beyond Traditional Assets
Traditionally applied within stock markets and bonds, recent years have seen increasing interest in applying beta analysis across alternative investments—including commodities and real estate—and notably cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Cryptocurrencies exhibit unique characteristics—they are highly volatile yet increasingly correlated with traditional assets at times—making their betas valuable indicators of their market sensitivity:
- Cryptocurrency Betas: Calculated using historical price data against indices such as S&P 500 or specialized crypto benchmarks.
- High Volatility Reflection: Bitcoin's high price swings translate into elevated beta values compared with traditional assets.
- Risk Management Tool: Knowing cryptocurrency betas helps traders diversify portfolios effectively while managing exposure risks amid rapid price fluctuations.
The Rise of Crypto Market Sensitivity Analysis
As digital currencies gain mainstream acceptance, understanding their behavior relative to traditional financial instruments has become critical for both institutional and retail investors alike. The high volatility inherent in cryptocurrencies means they can dramatically influence portfolio performance depending on prevailing market conditions—a fact reflected through their calculated betas.
For example:
- During periods of heightened regulatory scrutiny or macroeconomic uncertainty, cryptocurrency betas may spike due to increased sensitivity.
- Conversely, positive developments like adoption announcements can cause sharp upward movements aligned with broader equity rallies if correlations increase temporarily.
Potential Risks from High Market Sensitivity
While leveraging knowledge about a security’s beta offers strategic advantages—such as optimizing diversification—it also exposes investors to certain risks associated with high-market sensitivity:
- Rapid Price Fluctuations*: Assets with elevated betas can experience swift gains but equally rapid declines based on minor shifts in investor sentiment or macroeconomic news.
- Regulatory Impact*: Sudden policy changes can disproportionately affect highly sensitive assets like cryptocurrencies.
- Sentiment-driven Movements*: Investor emotions often amplify responses beyond fundamental factors leading potentially unpredictable outcomes especially during turbulent times.
By monitoring these sensitivities through updated calculations of each asset'sbeta over time—and staying informed about external influences—investors improve their abilityto navigate complex markets confidently while aligning strategies accordingto individual risk tolerance levels.
How Understanding Beta Enhances Investment Decision-Making
Incorporating insights frombeta analysis allows investors not onlyto assess current risksbut also forecast future performance scenarios under differentmarket conditions.This proactive approach supports better decision-makingby enabling tailored portfolio adjustments aimed at balancing risk versus reward efficiently.For example:
- Diversifying across low-and high-beta assets accordingto one’s appetitefor volatility
- Hedging positionsin highly sensitive securitiesduring uncertain periods
- Adjusting exposurebasedon evolving macroeconomic trendsand geopolitical developments
The Role Of E-A-T In Financial Content About Beta
When discussing complex topics such asbeta measurementand its applicationin modern investing,it is vital that content demonstrates Expertise Authority Trustworthiness (E-A-T). This involves referencing reputable sources—including academic research,published studies,and industry experts—and providing accurate information groundedin current financial theoriesand practices.By doing so,the content ensures credibilityand helps readers make informed decisions rootedin reliable data ratherthan speculation.
Final Thoughts
Beta remains oneof the most fundamental metricsfor evaluatingmarket sensitivity within traditional finance.As digital assets continue gaining prominence,the importanceof understandingcryptocurrencybetas grows correspondingly.Investors who graspthe nuancesof this measurecan better managerisks,and capitalizeon opportunitiespresentedby dynamicmarkets.Furthermore,moving forward,the integrationof advanced analyticsand real-time data will likely enhance our abilityto interpretbetavaluesthroughout diverseasset classes,increasing transparencyandinformed decision-makingacross all levelsof investing activity
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🔍 David Schwartz (CTO) rappelle que :
• Ripple opère moins de **1% des validateurs**
• Les évolutions de XRPL dépendent du **consensus communautaire**
• Les milliards en escrow sont **verrouillés par smart contracts**, sans accès direct
👉 Une piqûre de rappel importante sur la gouvernance réelle des protocoles.
#XRP #crypto #cryptocurrency



Carmelita
2025-08-07 14:15
🚨 Fin des fantasmes : Ripple ne contrôle pas le $XRP Ledger.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Asseto is committed to building a compliant bridge that brings traditional financial assets into the decentralized world. Through smart contracts and multi-stage approval processes, it achieves high security and liquidity, supporting tokenization of stocks, bonds, and other traditional assets. Here are the platform's core highlights:
💰 Three-Layer Architecture:
-
Off-Chain Compliance Layer: KYC/AML verification, fiat settlement, multi-sig custody for asset security
On-Chain Smart Contract Layer: Token issuance/transfer, oracle real-time pricing
Cross-Chain Bridging Layer: Support for Ethereum, BSC, and other multi-chain asset free flow
Modular Governance: Token holders vote to adjust compliance parameters and fee structures
🎯 Privacy & Security Guarantees: 1️⃣ Trusted Execution Environment (TEE): Encrypted user data storage, dedicated audit nodes 2️⃣ Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP): Verify KYC results without exposing sensitive information on-chain 3️⃣ Multi-Signature Timelock: Cross-chain asset transfers remain fully controlled 4️⃣ Third-Party Security Audits: Regular smart contract audits and penetration testing
🏆 Asset Tokenization Process:
-
Asset Custody: Regulated custodians safeguard traditional assets
Contract Minting: On-chain mint transactions generate 1:1 pegged tokens (aStock, aBond)
Cross-Chain Distribution: Bridge tokens to target networks via cross-chain bridge
Redemption & Settlement: Users burn tokens to request redemption, off-chain releases corresponding assets
💡 $ASO Token Economics (100M Total Supply):
-
Rewards & Bribes 60%: Liquidity mining, governance proposal rewards, and "bribe" mechanisms
Public Sale (LBP) 12%: Public offering, initial liquidity foundation
Core Team 11.6%: 3-month lockup, 2-year linear vesting
Protocol Growth 10%: Ecosystem incubation, partner incentives, R&D grants
Community Incentives 4%: Early user airdrops, community activity rewards
Initial Liquidity 2.4%: Trading pair depth support
🔐 Incentive Mechanisms:
-
Staking Yield: Participate in network security verification, earn base APY
Revenue Distribution: Protocol revenues buy back ASO and distribute to stakers
Liquidity Mining: Provide liquidity in designated trading pairs for additional rewards
Governance Voting: Participate in protocol governance, "bribe" mechanism increases voting power
🌟 Dual Yield Model:
-
DeFi Yield: Participate in protocol interest sharing and liquidity mining
Traditional Yield: Connect to traditional asset dividends and coupon payments
Principal Protection: Compliance fund and multi-sig custody emergency compensation mechanism
Community Governance: ASO holders decide asset types, fee adjustments
📱 Supported Asset Types:
-
Current: Stocks, corporate bonds, government bonds, money-market instruments
Planned: Fund shares, commodities expansion
🔮 Participation Process: Complete KYC/AML verification → Deposit funds to compliant custodian account → Mint asset tokens on-chain → DeFi ecosystem applications
⚡ Redemption Service:
-
Standard Redemption: 3-5 business days
Expedited Redemption: 1-2 business days (additional fees)
🛡️ Risk Prevention:
-
Multi-entity custody for risk distribution
Regular audits for transparent operations
Off-chain redundancy backup
Compliance fund emergency mechanisms
Asseto enables traditional financial assets to seamlessly access DeFi ecosystems through innovative compliance architecture, providing investors with "fiat + crypto" composite yields while maintaining regulatory compliance, potentially accelerating traditional asset digitization.
Read the complete compliance mechanism analysis: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/asseto-defi-compliance/?utm_source=blog
#Asseto #ASO #CrossChain #KYC



JU Blog
2025-08-05 10:34
🏦 Asseto: Compliant Bridge Between Traditional Assets and DeFi Revolution!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can Machine Learning Algorithms Classify Chart Patterns?
Machine learning has transformed many industries, and financial markets are no exception. One of the most promising applications is in classifying chart patterns—visual representations of price movements that traders rely on for decision-making. Understanding how machine learning algorithms can identify and categorize these patterns offers insights into the future of automated trading and technical analysis.
What Are Chart Pattern Classifications?
Chart pattern classification involves using advanced algorithms to analyze financial charts—such as candlestick or line graphs—and automatically recognize specific formations like head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, flags, or triangles. These patterns often signal potential trend reversals or continuations, guiding traders on when to buy or sell assets.
Traditionally, human analysts interpret these visual cues based on experience. However, manual analysis can be subjective and time-consuming. Machine learning automates this process by training models to detect subtle features within chart data rapidly and with high accuracy.
The Role of Machine Learning in Financial Market Analysis
The integration of machine learning into finance isn't new but has gained momentum due to increased computational power and data availability. Early efforts focused on simple models; today’s deep learning techniques enable complex pattern recognition akin to image processing tasks.
In cryptocurrency markets—characterized by high volatility and rapid price changes—the need for real-time analysis makes machine learning especially valuable. Automated systems can process vast amounts of historical data quickly, providing timely signals that might be missed through manual analysis.
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms Used in Chart Pattern Recognition
Different types of machine learning approaches serve various purposes in pattern classification:
Supervised Learning: This method trains models using labeled datasets where each chart is tagged with its corresponding pattern type (e.g., bullish flag). Once trained, the model can classify new charts based on learned features.
Unsupervised Learning: Here, algorithms like clustering group similar patterns without predefined labels. This approach helps discover new or rare formations that may not fit traditional categories.
Reinforcement Learning: Models learn optimal trading strategies through trial-and-error interactions with market environments rather than static datasets. They adapt over time to maximize profits based on feedback signals.
Popular Techniques & Architectures
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Originally designed for image recognition tasks, CNNs excel at analyzing visual data such as chart images—they identify edges, shapes, and textures indicative of specific patterns.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Suitable for sequential data like time series; RNNs analyze the order-dependent nature of price movements over time.
Gradient Boosting Machines (GBMs): Ensemble methods combining multiple weak classifiers; effective for structured tabular data derived from technical indicators alongside raw chart images.
Challenges Faced by Machine Learning Models
Despite their advantages, deploying machine learning for chart pattern classification comes with hurdles:
Data Quality & Noise: Financial market data often contains noise due to random fluctuations or incomplete records which can mislead models if not properly preprocessed.
Overfitting Risks: Complex models might memorize training examples rather than generalize well across unseen data—a problem known as overfitting—which reduces predictive reliability during live trading.
Regulatory Considerations: As automated strategies become more prevalent, compliance with legal frameworks becomes critical—especially regarding transparency and fairness in algorithmic decision-making.
Recent Advances Enhancing Pattern Recognition Accuracy
Recent developments have significantly improved how effectively machines classify chart patterns:
Deep neural networks incorporating attention mechanisms allow models to focus selectively on relevant parts of a chart image or sequence.
Transformer architectures—originally popularized in natural language processing—are now being adapted for financial time-series analysis due to their ability to capture long-term dependencies within market data.
Combining multiple analytical tools such as sentiment analysis from news feeds alongside technical indicators creates more holistic trading signals driven by comprehensive AI systems.
Open-source frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch have democratized access so researchers worldwide can develop sophisticated models without starting from scratch—all contributing toward faster innovation cycles in this domain.
Impact & Future Outlook
The widespread adoption of machine learning-based classification could influence overall market efficiency by reducing information asymmetry among traders who leverage these tools extensively. While this democratization enhances transparency overall—it also raises concerns about potential market manipulation if used irresponsibly.
Automation may lead some roles traditionally performed manually by analysts becoming obsolete; however—as with any technological shift—it also opens opportunities for professionals skilled at developing advanced AI-driven strategies.
Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing algorithmic trading practices; ensuring ethical standards remain vital as AI's role expands within financial ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
- Machine learning automates identification/classification of complex chart formations
- Deep architectures like CNNs/RNNs improve detection accuracy
- Challenges include noisy datasets & overfitting risks
- Recent innovations involve attention mechanisms & transformer-based models
- Widespread use impacts market dynamics & regulatory landscape
By understanding how these intelligent systems work behind the scenes—from training neural networks on historical charts to deploying them live—you gain a clearer picture of modern technical analysis's future trajectory—and how it continues transforming investment strategies worldwide.
Semantic Keywords:
machine learning finance | stock/chart pattern recognition | deep neural networks trading | automated technical analysis | AI cryptocurrency markets | supervised vs unsupervised ML | reinforcement learning trading strategies


kai
2025-05-09 21:30
How can machine learning algorithms classify chart patterns?
How Can Machine Learning Algorithms Classify Chart Patterns?
Machine learning has transformed many industries, and financial markets are no exception. One of the most promising applications is in classifying chart patterns—visual representations of price movements that traders rely on for decision-making. Understanding how machine learning algorithms can identify and categorize these patterns offers insights into the future of automated trading and technical analysis.
What Are Chart Pattern Classifications?
Chart pattern classification involves using advanced algorithms to analyze financial charts—such as candlestick or line graphs—and automatically recognize specific formations like head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, flags, or triangles. These patterns often signal potential trend reversals or continuations, guiding traders on when to buy or sell assets.
Traditionally, human analysts interpret these visual cues based on experience. However, manual analysis can be subjective and time-consuming. Machine learning automates this process by training models to detect subtle features within chart data rapidly and with high accuracy.
The Role of Machine Learning in Financial Market Analysis
The integration of machine learning into finance isn't new but has gained momentum due to increased computational power and data availability. Early efforts focused on simple models; today’s deep learning techniques enable complex pattern recognition akin to image processing tasks.
In cryptocurrency markets—characterized by high volatility and rapid price changes—the need for real-time analysis makes machine learning especially valuable. Automated systems can process vast amounts of historical data quickly, providing timely signals that might be missed through manual analysis.
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms Used in Chart Pattern Recognition
Different types of machine learning approaches serve various purposes in pattern classification:
Supervised Learning: This method trains models using labeled datasets where each chart is tagged with its corresponding pattern type (e.g., bullish flag). Once trained, the model can classify new charts based on learned features.
Unsupervised Learning: Here, algorithms like clustering group similar patterns without predefined labels. This approach helps discover new or rare formations that may not fit traditional categories.
Reinforcement Learning: Models learn optimal trading strategies through trial-and-error interactions with market environments rather than static datasets. They adapt over time to maximize profits based on feedback signals.
Popular Techniques & Architectures
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Originally designed for image recognition tasks, CNNs excel at analyzing visual data such as chart images—they identify edges, shapes, and textures indicative of specific patterns.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Suitable for sequential data like time series; RNNs analyze the order-dependent nature of price movements over time.
Gradient Boosting Machines (GBMs): Ensemble methods combining multiple weak classifiers; effective for structured tabular data derived from technical indicators alongside raw chart images.
Challenges Faced by Machine Learning Models
Despite their advantages, deploying machine learning for chart pattern classification comes with hurdles:
Data Quality & Noise: Financial market data often contains noise due to random fluctuations or incomplete records which can mislead models if not properly preprocessed.
Overfitting Risks: Complex models might memorize training examples rather than generalize well across unseen data—a problem known as overfitting—which reduces predictive reliability during live trading.
Regulatory Considerations: As automated strategies become more prevalent, compliance with legal frameworks becomes critical—especially regarding transparency and fairness in algorithmic decision-making.
Recent Advances Enhancing Pattern Recognition Accuracy
Recent developments have significantly improved how effectively machines classify chart patterns:
Deep neural networks incorporating attention mechanisms allow models to focus selectively on relevant parts of a chart image or sequence.
Transformer architectures—originally popularized in natural language processing—are now being adapted for financial time-series analysis due to their ability to capture long-term dependencies within market data.
Combining multiple analytical tools such as sentiment analysis from news feeds alongside technical indicators creates more holistic trading signals driven by comprehensive AI systems.
Open-source frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch have democratized access so researchers worldwide can develop sophisticated models without starting from scratch—all contributing toward faster innovation cycles in this domain.
Impact & Future Outlook
The widespread adoption of machine learning-based classification could influence overall market efficiency by reducing information asymmetry among traders who leverage these tools extensively. While this democratization enhances transparency overall—it also raises concerns about potential market manipulation if used irresponsibly.
Automation may lead some roles traditionally performed manually by analysts becoming obsolete; however—as with any technological shift—it also opens opportunities for professionals skilled at developing advanced AI-driven strategies.
Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing algorithmic trading practices; ensuring ethical standards remain vital as AI's role expands within financial ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
- Machine learning automates identification/classification of complex chart formations
- Deep architectures like CNNs/RNNs improve detection accuracy
- Challenges include noisy datasets & overfitting risks
- Recent innovations involve attention mechanisms & transformer-based models
- Widespread use impacts market dynamics & regulatory landscape
By understanding how these intelligent systems work behind the scenes—from training neural networks on historical charts to deploying them live—you gain a clearer picture of modern technical analysis's future trajectory—and how it continues transforming investment strategies worldwide.
Semantic Keywords:
machine learning finance | stock/chart pattern recognition | deep neural networks trading | automated technical analysis | AI cryptocurrency markets | supervised vs unsupervised ML | reinforcement learning trading strategies
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are 3Commas Pricing Tiers?
Understanding the different pricing options available on 3Commas is essential for traders looking to optimize their cryptocurrency trading strategies. As a platform that caters to both beginners and seasoned professionals, 3Commas offers a tiered subscription model designed to meet varying needs and budgets. This article provides an in-depth overview of these tiers, their features, target audiences, and recent platform updates.
Overview of 3Commas as a Cryptocurrency Trading Platform
Founded in 2017 by Yuriy Serdyuk and Oleksandr Lutskevych, 3Commas has established itself as a leading tool in the crypto trading space. Its user-friendly interface combined with powerful automation tools has attracted traders worldwide. The platform supports multiple exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase Pro, Kraken, and others—allowing users to manage diverse portfolios seamlessly.
Key features include automated trading bots that execute trades based on predefined strategies, backtesting tools for strategy validation before live deployment, and social trading functionalities where users can follow or copy successful traders. These capabilities make it suitable for both novices exploring automated trading and professional traders seeking advanced algorithmic solutions.
The Three Main Pricing Tiers
As of now, 3Commas offers three primary subscription plans: Free, Premium (at $34/month), and Pro (at $99/month). Each tier is structured to provide increasing levels of access to features aligned with trader experience levels.
Free Plan: Entry-Level Access
The free plan serves as an excellent starting point for newcomers interested in exploring automated crypto trading without financial commitment. It includes basic functionalities such as limited access to simple trading bots—often one or two—and some backtesting capabilities. However, these are restricted compared to paid plans; users can only trade on select pairs with limited customization options.
This tier is ideal for those who want hands-on experience with minimal risk or cost before deciding whether more advanced tools are necessary. It also allows new traders to familiarize themselves with the platform’s interface while testing initial strategies.
Premium Plan: Intermediate Features at $34/Month
Designed for active traders seeking more control over their automation strategies without breaking the bank, the Premium plan unlocks full backtesting capabilities—a crucial feature for refining algorithms before deploying them live. Users gain access to a broader range of trading pairs and customizable bot settings that enable more sophisticated trade execution.
Priority customer support is another benefit here; this ensures quicker assistance when technical issues arise or strategic questions need addressing. Overall, this plan strikes a balance between affordability and functionality suitable for intermediate-level traders aiming to enhance their performance through automation.
Pro Plan: Advanced Tools at $99/Month
The most comprehensive offering from 3Commas targets professional or highly active crypto traders who require cutting-edge features. The Pro plan includes customizable algorithms powered by real-time data feeds—providing more accurate market insights—and dedicated account management services tailored toward high-frequency or large-volume trades.
Exclusive content such as premium signals and detailed market analysis further empowers users making complex decisions quickly within volatile markets. This tier demands higher investment but delivers tools suited for those operating at an institutional level or managing significant portfolios requiring personalized support.
Recent Platform Developments Enhancing User Experience
In recent months, 3Commas has focused heavily on expanding its ecosystem through several key updates:
Integration With Additional Exchanges: By partnering with new platforms like Bitfinex and Huobi Global recently integrated into its system—users now have access to even wider liquidity pools.
Enhanced Security Measures: Recognizing the importance of safeguarding user assets amid rising cyber threats in crypto space—the platform introduced two-factor authentication improvements along with stronger encryption protocols.
Community Engagement Initiatives: Active communication channels via social media forums allow users feedback-driven development cycles; this helps tailor future updates based on actual trader needs rather than assumptions alone.
These enhancements demonstrate how committed 3Commas remains towards providing secure yet innovative solutions tailored toward evolving market demands.
Potential Risks Associated With Subscription Tiers
While flexible pricing makes it accessible across various trader profiles—including beginners—the reliance on paid plans introduces certain risks:
Cost Considerations: For individual hobbyists or small-scale investors operating under tight budgets—especially those considering the Pro plan—the monthly expense might be prohibitive relative to expected gains.
Dependence On Technology & Data Feeds: Automated systems rely heavily on stable internet connections plus accurate real-time data feeds; any disruption could impact trade execution adversely.
Regulatory Environment Changes: As governments worldwide tighten regulations around cryptocurrencies—and some exchanges face restrictions—the integration capabilities offered by platforms like 3Commas could be affected unexpectedly.
Being aware of these factors helps ensure informed decision-making when choosing an appropriate subscription level aligned with personal risk tolerance and operational requirements.
Who Should Choose Which Tier?
Selecting the right plan depends largely on your experience level:
- Beginners should start with the free version—to learn how automated bots work without financial exposure—and upgrade later if needed.
- Intermediate traders aiming for better customization should consider upgrading to Premium ($34/month) once comfortable managing multiple pairs simultaneously.
- Professional operators executing high-frequency trades—or managing large portfolios—are best served by investing in Pro ($99/month), which offers advanced algorithms coupled with dedicated support services.
Final Thoughts: Making Informed Choices Based On Your Trading Goals
Understanding what each pricing tier offers enables you not only maximize your investment but also align your choice closely with your skill set — whether you're just starting out or already operating at an expert level within cryptocurrency markets.
By staying updated about recent developments like exchange integrations or security upgrades—as well as being mindful of potential risks—you can leverage platforms like 3Commas effectively while minimizing vulnerabilities associated with reliance solely on technology-driven solutions.
Keywords: cryptocurrency trading platforms | automated crypto bots | crypto exchange integration | backtesting tools | social trading | crypto portfolio management | beginner vs professional trader | subscription plans comparison


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-26 14:37
What are 3Commas pricing tiers?
What Are 3Commas Pricing Tiers?
Understanding the different pricing options available on 3Commas is essential for traders looking to optimize their cryptocurrency trading strategies. As a platform that caters to both beginners and seasoned professionals, 3Commas offers a tiered subscription model designed to meet varying needs and budgets. This article provides an in-depth overview of these tiers, their features, target audiences, and recent platform updates.
Overview of 3Commas as a Cryptocurrency Trading Platform
Founded in 2017 by Yuriy Serdyuk and Oleksandr Lutskevych, 3Commas has established itself as a leading tool in the crypto trading space. Its user-friendly interface combined with powerful automation tools has attracted traders worldwide. The platform supports multiple exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase Pro, Kraken, and others—allowing users to manage diverse portfolios seamlessly.
Key features include automated trading bots that execute trades based on predefined strategies, backtesting tools for strategy validation before live deployment, and social trading functionalities where users can follow or copy successful traders. These capabilities make it suitable for both novices exploring automated trading and professional traders seeking advanced algorithmic solutions.
The Three Main Pricing Tiers
As of now, 3Commas offers three primary subscription plans: Free, Premium (at $34/month), and Pro (at $99/month). Each tier is structured to provide increasing levels of access to features aligned with trader experience levels.
Free Plan: Entry-Level Access
The free plan serves as an excellent starting point for newcomers interested in exploring automated crypto trading without financial commitment. It includes basic functionalities such as limited access to simple trading bots—often one or two—and some backtesting capabilities. However, these are restricted compared to paid plans; users can only trade on select pairs with limited customization options.
This tier is ideal for those who want hands-on experience with minimal risk or cost before deciding whether more advanced tools are necessary. It also allows new traders to familiarize themselves with the platform’s interface while testing initial strategies.
Premium Plan: Intermediate Features at $34/Month
Designed for active traders seeking more control over their automation strategies without breaking the bank, the Premium plan unlocks full backtesting capabilities—a crucial feature for refining algorithms before deploying them live. Users gain access to a broader range of trading pairs and customizable bot settings that enable more sophisticated trade execution.
Priority customer support is another benefit here; this ensures quicker assistance when technical issues arise or strategic questions need addressing. Overall, this plan strikes a balance between affordability and functionality suitable for intermediate-level traders aiming to enhance their performance through automation.
Pro Plan: Advanced Tools at $99/Month
The most comprehensive offering from 3Commas targets professional or highly active crypto traders who require cutting-edge features. The Pro plan includes customizable algorithms powered by real-time data feeds—providing more accurate market insights—and dedicated account management services tailored toward high-frequency or large-volume trades.
Exclusive content such as premium signals and detailed market analysis further empowers users making complex decisions quickly within volatile markets. This tier demands higher investment but delivers tools suited for those operating at an institutional level or managing significant portfolios requiring personalized support.
Recent Platform Developments Enhancing User Experience
In recent months, 3Commas has focused heavily on expanding its ecosystem through several key updates:
Integration With Additional Exchanges: By partnering with new platforms like Bitfinex and Huobi Global recently integrated into its system—users now have access to even wider liquidity pools.
Enhanced Security Measures: Recognizing the importance of safeguarding user assets amid rising cyber threats in crypto space—the platform introduced two-factor authentication improvements along with stronger encryption protocols.
Community Engagement Initiatives: Active communication channels via social media forums allow users feedback-driven development cycles; this helps tailor future updates based on actual trader needs rather than assumptions alone.
These enhancements demonstrate how committed 3Commas remains towards providing secure yet innovative solutions tailored toward evolving market demands.
Potential Risks Associated With Subscription Tiers
While flexible pricing makes it accessible across various trader profiles—including beginners—the reliance on paid plans introduces certain risks:
Cost Considerations: For individual hobbyists or small-scale investors operating under tight budgets—especially those considering the Pro plan—the monthly expense might be prohibitive relative to expected gains.
Dependence On Technology & Data Feeds: Automated systems rely heavily on stable internet connections plus accurate real-time data feeds; any disruption could impact trade execution adversely.
Regulatory Environment Changes: As governments worldwide tighten regulations around cryptocurrencies—and some exchanges face restrictions—the integration capabilities offered by platforms like 3Commas could be affected unexpectedly.
Being aware of these factors helps ensure informed decision-making when choosing an appropriate subscription level aligned with personal risk tolerance and operational requirements.
Who Should Choose Which Tier?
Selecting the right plan depends largely on your experience level:
- Beginners should start with the free version—to learn how automated bots work without financial exposure—and upgrade later if needed.
- Intermediate traders aiming for better customization should consider upgrading to Premium ($34/month) once comfortable managing multiple pairs simultaneously.
- Professional operators executing high-frequency trades—or managing large portfolios—are best served by investing in Pro ($99/month), which offers advanced algorithms coupled with dedicated support services.
Final Thoughts: Making Informed Choices Based On Your Trading Goals
Understanding what each pricing tier offers enables you not only maximize your investment but also align your choice closely with your skill set — whether you're just starting out or already operating at an expert level within cryptocurrency markets.
By staying updated about recent developments like exchange integrations or security upgrades—as well as being mindful of potential risks—you can leverage platforms like 3Commas effectively while minimizing vulnerabilities associated with reliance solely on technology-driven solutions.
Keywords: cryptocurrency trading platforms | automated crypto bots | crypto exchange integration | backtesting tools | social trading | crypto portfolio management | beginner vs professional trader | subscription plans comparison
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) encompasses a set of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent the process of disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income. Money laundering typically involves three key stages: placement, layering, and integration. During placement, illicit cash is introduced into the financial system—often through banks or other financial institutions. Layering involves complex transactions that obscure the origin of the money by moving it across various accounts or jurisdictions. Finally, in the integration stage, the laundered money re-enters the economy as seemingly legitimate funds.
The primary goal of AML measures is to detect and deter these activities before they can cause widespread harm to financial systems and economies. Criminal enterprises involved in activities like drug trafficking, terrorism financing, human trafficking, or corruption rely heavily on money laundering to legitimize their profits. Therefore, effective AML policies are essential for maintaining transparency within financial markets and safeguarding against criminal exploitation.
Regulatory Frameworks for AML
Internationally recognized standards shape AML efforts worldwide. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), established in 1989 during a G7 summit, plays a pivotal role by setting global guidelines aimed at combating money laundering and terrorist financing. Countries adopt these standards into their national laws to create cohesive enforcement mechanisms.
In addition to FATF's recommendations, regional bodies such as the European Union have enacted directives like AMLD4 (2016) and AMLD6 (2023), which strengthen due diligence requirements and expand reporting obligations for financial institutions operating within their jurisdictions. In countries like the United States, agencies such as FinCEN enforce compliance with these regulations through monitoring reports from banks and other entities.
Financial Institutions' Responsibilities
Banks are at the forefront of implementing AML measures because they serve as primary gateways for illicit funds entering or leaving legal channels. Their responsibilities include verifying customer identities through Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures—collecting information about clients’ backgrounds—and continuously monitoring transactions for suspicious activity patterns.
When unusual transactions are detected—such as large cash deposits inconsistent with a customer’s profile—they must be reported promptly via Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). These reports help authorities investigate potential cases of money laundering or related crimes before significant damage occurs.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges: New Frontiers in AML
The rise of cryptocurrencies has introduced both opportunities and challenges in anti-money laundering efforts. Digital assets offer anonymity features that can facilitate illegal activities if not properly regulated; hence regulators worldwide are developing specific guidelines tailored for crypto exchanges.
For example:
- The U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has issued directives requiring cryptocurrency platforms to implement robust KYC/AML protocols.
- European regulators have also increased scrutiny over digital asset service providers under existing anti-money laundering frameworks.
Technological Innovations Enhancing Compliance
Advancements in technology play an increasingly vital role in strengthening AML compliance programs:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms analyze transaction data rapidly to identify suspicious behavior.
- Machine Learning models adapt over time based on new data patterns.
- Automated reporting tools streamline submission processes for regulatory authorities.These innovations enable institutions not only to improve detection accuracy but also reduce operational costs associated with manual oversight.
Recent Developments Shaping Future Policies
Regulatory landscapes continue evolving amid technological progress:
- In 2022, a prominent cryptocurrency exchange faced a $50 million fine from U.S authorities due to violations related to inadequate KYC/AML practices.
- The European Union’s Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD6), implemented in 2023, expanded scope by including virtual asset service providers under stricter compliance requirements.Additionally,the ongoing debate around stablecoins highlights concerns regarding their potential misuse for cross-border money laundering schemes—a topic gaining attention among policymakers like Senator Elizabeth Warren who advocate for tighter safeguards against illicit finance flows involving digital assets.
Impacts of Non-Compliance
Failure by financial institutions or crypto platforms to adhere strictly to AML regulations can lead not only to hefty fines but also severe reputational damage that may threaten long-term viability:
- Fines reaching hundreds of millions USD
- Loss of licensing privileges
- Increased scrutiny from regulatorsMoreover,non-compliance undermines public trust in financial systems overall—a critical factor considering how interconnected global markets have become today.
Historical Milestones & Ongoing Challenges
Since its inception during G7 meetings in 1970—and subsequent establishment of FATF—the fight against money laundering has seen significant milestones:
- Introduction of international standards guiding national policies
- Implementation phases across different regions
- Adoption of advanced technological solutionsDespite progress made over decades,challenges persist due mainly to evolving methods employed by criminals who exploit emerging technologies like cryptocurrencies or decentralized finance platforms—necessitating continuous updates on regulatory frameworks alongside innovative detection tools.
Why Robust Anti-Money Laundering Measures Matter?
Effective AML policies protect economies from being exploited by criminal enterprises while fostering transparency within global finance networks. They help prevent funding terrorism campaigns that threaten security worldwide; safeguard consumer interests; uphold market integrity; promote fair competition among businesses; ensure compliance with international obligations—all crucial components underpinning stable economic growth.
Key Takeaways:
Money laundering involves three stages: placement into banks/accounts → layering through complex transactions → integration into legitimate economy.
International bodies such as FATF set standards adopted globally via national legislation
Financial institutions must verify identities using KYC processes & monitor transactions actively
Emerging technologies like AI enhance detection capabilities
Cryptocurrency exchanges face increasing regulation amid concerns over anonymity features facilitating illegal activities
By understanding these core aspects—and recognizing ongoing developments—you can better appreciate why strong anti-money laundering measures remain vital components within modern financial regulation frameworks.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:
Money Laundering Prevention | Financial Crime Detection | Cryptocurrency Regulation | KYC Procedures | Suspicious Activity Reporting | Digital Asset Compliance | Global Regulatory Standards | Fintech & Anti-Money Laundering | Blockchain Transparency Measures


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-15 01:43
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) encompasses a set of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent the process of disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income. Money laundering typically involves three key stages: placement, layering, and integration. During placement, illicit cash is introduced into the financial system—often through banks or other financial institutions. Layering involves complex transactions that obscure the origin of the money by moving it across various accounts or jurisdictions. Finally, in the integration stage, the laundered money re-enters the economy as seemingly legitimate funds.
The primary goal of AML measures is to detect and deter these activities before they can cause widespread harm to financial systems and economies. Criminal enterprises involved in activities like drug trafficking, terrorism financing, human trafficking, or corruption rely heavily on money laundering to legitimize their profits. Therefore, effective AML policies are essential for maintaining transparency within financial markets and safeguarding against criminal exploitation.
Regulatory Frameworks for AML
Internationally recognized standards shape AML efforts worldwide. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), established in 1989 during a G7 summit, plays a pivotal role by setting global guidelines aimed at combating money laundering and terrorist financing. Countries adopt these standards into their national laws to create cohesive enforcement mechanisms.
In addition to FATF's recommendations, regional bodies such as the European Union have enacted directives like AMLD4 (2016) and AMLD6 (2023), which strengthen due diligence requirements and expand reporting obligations for financial institutions operating within their jurisdictions. In countries like the United States, agencies such as FinCEN enforce compliance with these regulations through monitoring reports from banks and other entities.
Financial Institutions' Responsibilities
Banks are at the forefront of implementing AML measures because they serve as primary gateways for illicit funds entering or leaving legal channels. Their responsibilities include verifying customer identities through Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures—collecting information about clients’ backgrounds—and continuously monitoring transactions for suspicious activity patterns.
When unusual transactions are detected—such as large cash deposits inconsistent with a customer’s profile—they must be reported promptly via Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). These reports help authorities investigate potential cases of money laundering or related crimes before significant damage occurs.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges: New Frontiers in AML
The rise of cryptocurrencies has introduced both opportunities and challenges in anti-money laundering efforts. Digital assets offer anonymity features that can facilitate illegal activities if not properly regulated; hence regulators worldwide are developing specific guidelines tailored for crypto exchanges.
For example:
- The U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has issued directives requiring cryptocurrency platforms to implement robust KYC/AML protocols.
- European regulators have also increased scrutiny over digital asset service providers under existing anti-money laundering frameworks.
Technological Innovations Enhancing Compliance
Advancements in technology play an increasingly vital role in strengthening AML compliance programs:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms analyze transaction data rapidly to identify suspicious behavior.
- Machine Learning models adapt over time based on new data patterns.
- Automated reporting tools streamline submission processes for regulatory authorities.These innovations enable institutions not only to improve detection accuracy but also reduce operational costs associated with manual oversight.
Recent Developments Shaping Future Policies
Regulatory landscapes continue evolving amid technological progress:
- In 2022, a prominent cryptocurrency exchange faced a $50 million fine from U.S authorities due to violations related to inadequate KYC/AML practices.
- The European Union’s Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD6), implemented in 2023, expanded scope by including virtual asset service providers under stricter compliance requirements.Additionally,the ongoing debate around stablecoins highlights concerns regarding their potential misuse for cross-border money laundering schemes—a topic gaining attention among policymakers like Senator Elizabeth Warren who advocate for tighter safeguards against illicit finance flows involving digital assets.
Impacts of Non-Compliance
Failure by financial institutions or crypto platforms to adhere strictly to AML regulations can lead not only to hefty fines but also severe reputational damage that may threaten long-term viability:
- Fines reaching hundreds of millions USD
- Loss of licensing privileges
- Increased scrutiny from regulatorsMoreover,non-compliance undermines public trust in financial systems overall—a critical factor considering how interconnected global markets have become today.
Historical Milestones & Ongoing Challenges
Since its inception during G7 meetings in 1970—and subsequent establishment of FATF—the fight against money laundering has seen significant milestones:
- Introduction of international standards guiding national policies
- Implementation phases across different regions
- Adoption of advanced technological solutionsDespite progress made over decades,challenges persist due mainly to evolving methods employed by criminals who exploit emerging technologies like cryptocurrencies or decentralized finance platforms—necessitating continuous updates on regulatory frameworks alongside innovative detection tools.
Why Robust Anti-Money Laundering Measures Matter?
Effective AML policies protect economies from being exploited by criminal enterprises while fostering transparency within global finance networks. They help prevent funding terrorism campaigns that threaten security worldwide; safeguard consumer interests; uphold market integrity; promote fair competition among businesses; ensure compliance with international obligations—all crucial components underpinning stable economic growth.
Key Takeaways:
Money laundering involves three stages: placement into banks/accounts → layering through complex transactions → integration into legitimate economy.
International bodies such as FATF set standards adopted globally via national legislation
Financial institutions must verify identities using KYC processes & monitor transactions actively
Emerging technologies like AI enhance detection capabilities
Cryptocurrency exchanges face increasing regulation amid concerns over anonymity features facilitating illegal activities
By understanding these core aspects—and recognizing ongoing developments—you can better appreciate why strong anti-money laundering measures remain vital components within modern financial regulation frameworks.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:
Money Laundering Prevention | Financial Crime Detection | Cryptocurrency Regulation | KYC Procedures | Suspicious Activity Reporting | Digital Asset Compliance | Global Regulatory Standards | Fintech & Anti-Money Laundering | Blockchain Transparency Measures
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Evaluate the Sustainability of Net Income
Understanding whether a company's net income is sustainable is essential for investors, analysts, and business leaders aiming to gauge long-term financial health. Sustainable net income indicates that a company can maintain its profitability over time without depleting resources or risking environmental and social responsibilities. This article explores key factors, recent trends, and practical methods to assess the sustainability of net income effectively.
What Does Sustainability in Net Income Mean?
Sustainability in net income refers to a company's ability to generate consistent profits over an extended period while balancing economic viability with environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Unlike short-term earnings spikes driven by one-off events or market anomalies, sustainable net income reflects underlying operational strength and strategic resilience.
Achieving this balance involves evaluating not just financial metrics but also how environmental practices and societal impacts influence long-term performance. Investors increasingly prioritize companies that demonstrate responsible management of resources alongside steady profitability.
Key Financial Indicators for Assessing Sustainability
Financial health forms the foundation of sustainable net income. Several indicators help determine whether a company's profits are likely to persist:
- Profitability Trends: Consistent or growing profit margins suggest stable operations capable of weathering market fluctuations.
- Cash Flow Stability: Positive cash flow ensures ongoing liquidity necessary for investments, debt repayment, and operational needs.
- Debt Levels: Maintaining manageable debt ratios prevents financial distress; excessive leverage can threaten future earnings stability.
Regular analysis of these metrics helps identify companies with resilient financial structures capable of supporting sustained profitability.
Economic Factors Influencing Long-Term Profitability
Beyond internal finances, external economic conditions significantly impact a company's ability to sustain its net income:
- Market Position & Competitive Advantage: Firms with strong brand recognition or unique offerings are better positioned for ongoing revenue streams.
- Revenue Diversification: Relying on multiple sources reduces vulnerability; if one segment underperforms, others can offset losses.
- Regulatory Environment Compliance: Adherence to laws minimizes legal risks and potential penalties that could erode profits.
Monitoring these factors provides insight into how well-positioned a company is within its industry landscape for enduring success.
The Role of Environmental Responsibility in Financial Sustainability
Environmental considerations are increasingly integral when assessing long-term profitability. Companies investing in green initiatives—such as renewable energy adoption or waste reduction—can lower operational costs while enhancing reputation among eco-conscious consumers.
Supply chain management also plays a crucial role; environmentally responsible sourcing mitigates risks related to resource depletion or regulatory sanctions due to unsustainable practices. Incorporating sustainability into core strategies not only benefits society but also supports stable profit generation by reducing exposure to environmental liabilities.
Recent Developments Impacting Net Income Sustainability
Recent corporate reports highlight contrasting scenarios illustrating the importance of sustainability:
In early 2025, Check Point Software Technologies showcased robust financial results exceeding expectations during Q1 2025[1]. Their strong earnings reflect effective management strategies aligned with both growth objectives and sustainability principles.
Conversely, Everest Group experienced challenges during the same period[2], reporting an increased combined ratio (102.7%), signaling potential strain on their profitability margins which could threaten future earnings stability if trends persist.
These examples underscore how current performance metrics serve as vital indicators when evaluating long-term viability — emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring beyond surface-level figures.
Risks That Threaten Net Income Longevity
Several risks can undermine efforts toward maintaining sustainable profits:
Financial Distress from High Debt Levels: Excessive borrowing hampers flexibility; interest obligations may divert funds from growth initiatives.
Regulatory Penalties & Non-compliance: Failure to meet environmental standards exposes firms to fines that directly reduce profit margins.
Environmental & Reputational Risks: Environmental damage incidents can lead not only legal consequences but also loss of customer trust impacting sales longevity.
Proactively managing these risks through strategic planning enhances resilience against unforeseen disruptions affecting long-term earnings stability.
Practical Strategies for Evaluating Net Income Sustainability
To accurately assess whether a company's profits are sustainable over time:
- Analyze historical financial statements focusing on profit consistency and cash flow patterns.
- Review industry position—market share data—and diversification strategies employed by the firm.
- Examine corporate social responsibility (CSR) reports highlighting green initiatives and supply chain ethics.
- Monitor regulatory compliance records alongside any penalties incurred historically.
- Stay updated on macroeconomic trends influencing sector-specific demand cycles or resource availability.
Combining quantitative data with qualitative insights offers a comprehensive view essential for informed decision-making regarding investment or strategic planning.
Keywords:sustainable net income | financial health | economic sustainability | environmental impact | cash flow analysis | risk assessment | corporate responsibility | long-term profitability


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-19 17:00
How to evaluate the sustainability of net income?
How to Evaluate the Sustainability of Net Income
Understanding whether a company's net income is sustainable is essential for investors, analysts, and business leaders aiming to gauge long-term financial health. Sustainable net income indicates that a company can maintain its profitability over time without depleting resources or risking environmental and social responsibilities. This article explores key factors, recent trends, and practical methods to assess the sustainability of net income effectively.
What Does Sustainability in Net Income Mean?
Sustainability in net income refers to a company's ability to generate consistent profits over an extended period while balancing economic viability with environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Unlike short-term earnings spikes driven by one-off events or market anomalies, sustainable net income reflects underlying operational strength and strategic resilience.
Achieving this balance involves evaluating not just financial metrics but also how environmental practices and societal impacts influence long-term performance. Investors increasingly prioritize companies that demonstrate responsible management of resources alongside steady profitability.
Key Financial Indicators for Assessing Sustainability
Financial health forms the foundation of sustainable net income. Several indicators help determine whether a company's profits are likely to persist:
- Profitability Trends: Consistent or growing profit margins suggest stable operations capable of weathering market fluctuations.
- Cash Flow Stability: Positive cash flow ensures ongoing liquidity necessary for investments, debt repayment, and operational needs.
- Debt Levels: Maintaining manageable debt ratios prevents financial distress; excessive leverage can threaten future earnings stability.
Regular analysis of these metrics helps identify companies with resilient financial structures capable of supporting sustained profitability.
Economic Factors Influencing Long-Term Profitability
Beyond internal finances, external economic conditions significantly impact a company's ability to sustain its net income:
- Market Position & Competitive Advantage: Firms with strong brand recognition or unique offerings are better positioned for ongoing revenue streams.
- Revenue Diversification: Relying on multiple sources reduces vulnerability; if one segment underperforms, others can offset losses.
- Regulatory Environment Compliance: Adherence to laws minimizes legal risks and potential penalties that could erode profits.
Monitoring these factors provides insight into how well-positioned a company is within its industry landscape for enduring success.
The Role of Environmental Responsibility in Financial Sustainability
Environmental considerations are increasingly integral when assessing long-term profitability. Companies investing in green initiatives—such as renewable energy adoption or waste reduction—can lower operational costs while enhancing reputation among eco-conscious consumers.
Supply chain management also plays a crucial role; environmentally responsible sourcing mitigates risks related to resource depletion or regulatory sanctions due to unsustainable practices. Incorporating sustainability into core strategies not only benefits society but also supports stable profit generation by reducing exposure to environmental liabilities.
Recent Developments Impacting Net Income Sustainability
Recent corporate reports highlight contrasting scenarios illustrating the importance of sustainability:
In early 2025, Check Point Software Technologies showcased robust financial results exceeding expectations during Q1 2025[1]. Their strong earnings reflect effective management strategies aligned with both growth objectives and sustainability principles.
Conversely, Everest Group experienced challenges during the same period[2], reporting an increased combined ratio (102.7%), signaling potential strain on their profitability margins which could threaten future earnings stability if trends persist.
These examples underscore how current performance metrics serve as vital indicators when evaluating long-term viability — emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring beyond surface-level figures.
Risks That Threaten Net Income Longevity
Several risks can undermine efforts toward maintaining sustainable profits:
Financial Distress from High Debt Levels: Excessive borrowing hampers flexibility; interest obligations may divert funds from growth initiatives.
Regulatory Penalties & Non-compliance: Failure to meet environmental standards exposes firms to fines that directly reduce profit margins.
Environmental & Reputational Risks: Environmental damage incidents can lead not only legal consequences but also loss of customer trust impacting sales longevity.
Proactively managing these risks through strategic planning enhances resilience against unforeseen disruptions affecting long-term earnings stability.
Practical Strategies for Evaluating Net Income Sustainability
To accurately assess whether a company's profits are sustainable over time:
- Analyze historical financial statements focusing on profit consistency and cash flow patterns.
- Review industry position—market share data—and diversification strategies employed by the firm.
- Examine corporate social responsibility (CSR) reports highlighting green initiatives and supply chain ethics.
- Monitor regulatory compliance records alongside any penalties incurred historically.
- Stay updated on macroeconomic trends influencing sector-specific demand cycles or resource availability.
Combining quantitative data with qualitative insights offers a comprehensive view essential for informed decision-making regarding investment or strategic planning.
Keywords:sustainable net income | financial health | economic sustainability | environmental impact | cash flow analysis | risk assessment | corporate responsibility | long-term profitability
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Proof-of-Stake (PoS)?
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain technology to validate transactions and secure the network. Unlike the traditional Proof-of-Work (PoW), which relies on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles through energy-intensive computations, PoS selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up as collateral. This approach aims to create a more efficient, scalable, and environmentally friendly way of maintaining blockchain integrity.
How Does Proof-of-Stake Work?
In a PoS system, participants known as validators are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake in the network. The more coins a validator commits, the higher their chances of being selected to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. This process involves several key steps:
- Staking: Validators lock up a specific amount of cryptocurrency as collateral.
- Validator Selection: The network randomly or deterministically selects validators based on factors like stake size and sometimes other criteria such as coin age.
- Validation: Selected validators verify transactions within proposed blocks.
- Reward & Penalties: Successful validation earns rewards; misbehavior results in penalties like slashing—where part or all of their staked coins are forfeited.
This method ensures that those with more at stake have greater incentive to act honestly since malicious activity can lead to significant financial loss.
Advantages of Proof-of-Stake
Proof-of-Stake offers several benefits over traditional PoW systems:
Energy Efficiency
One of PoS's most significant advantages is its lower energy consumption. Since it eliminates the need for computationally intensive mining operations, it reduces electricity usage drastically—making blockchain networks more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Scalability
PoS allows for faster transaction processing times and higher throughput compared to PoW networks. This scalability makes it suitable for applications requiring high-speed data validation without compromising security.
Security Features
While no system is entirely immune from attacks, well-designed PoS protocols incorporate mechanisms like slashing penalties that discourage malicious behavior. Additionally, because validators risk losing their staked assets if they act dishonestly, this creates economic incentives aligned with honest participation.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Proof-of-Stake
Despite its advantages, PoS faces certain challenges that developers and stakeholders must address:
Nothing-at-Stake Problem
In some early implementations of PoS, validators could vote for multiple conflicting chains without penalty—a situation called "nothing-at-stake." To mitigate this risk, modern protocols implement slashing conditions where misbehavior leads to penalties severe enough to deter such actions.
Centralization Concerns
Since larger stakeholders have increased influence over block creation probabilities, there's potential for wealth concentration leading to centralization risks—where power becomes concentrated among few large holders rather than distributed evenly across participants.
Security Considerations
Although generally considered secure when properly implemented, emerging attack vectors specific to staking systems require ongoing research and protocol improvements. Continuous updates help maintain resilience against threats like long-range attacks or validator collusion.
Ethereum’s Transition From Proof-of-Work To Proof-of-Stake
Ethereum’s move from proof-of-work (PoW) toward proof-of-stake (PoS) represents one of the most prominent real-world applications demonstrating this consensus mechanism's potential. Launched initially in December 2020 via its Beacon Chain upgrade—the first phase towards Ethereum 2.0—the transition aimed at addressing scalability issues while significantly reducing energy consumption associated with mining activities.
The milestone event called "The Merge," completed in 2023 after years of development effort by Ethereum developers worldwide—including extensive testing—marked Ethereum’s full switch from energy-intensive mining toward an eco-friendly staking model. This shift not only enhances sustainability but also paves the way for future upgrades focused on increasing transaction throughput through sharding techniques integrated into Eth2 architecture.
Future Outlook & Adoption Trends
As major cryptocurrencies adopt proof-of-stake mechanisms—including Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT), among others—the landscape is witnessing rapid growth driven by both technological advancements and environmental considerations. Stakeholder interest continues rising due primarily to benefits like reduced operational costs and improved scalability prospects which appeal both investors seeking returns via staking rewards—and developers aiming for robust decentralized applications capable of handling mass adoption scenarios efficiently.
However, widespread adoption also brings regulatory scrutiny; authorities worldwide are beginning scrutinizing staking practices concerning investor protections and compliance frameworks—a factor that could influence future development directions within this space significantly.
Key Takeaways About Proof-of-Stake
To summarize what makes proof-of-stake distinct:
- Validators participate by locking up tokens instead of performing resource-heavy computations.
- It offers superior energy efficiency compared with proof-of-work.
- Security relies heavily on economic incentives; misbehavior results in financial penalties.
- Major networks like Ethereum have successfully transitioned or plan transitions towards PoS models.
Understanding these core aspects helps users evaluate whether adopting or supporting proof-based blockchain projects aligns with their goals—whether it's investing safely or developing scalable decentralized solutions.
Addressing User Concerns & Trustworthiness
For users considering involvement in staking activities—or simply wanting clarity about how these systems operate—it’s crucial first understanding security measures involved such as slashing conditions designed specifically against malicious actions—and how decentralization efforts aim at preventing undue influence by large stakeholders alone.
Furthermore,
- Look into reputable platforms offering staking services,
- Review governance structures ensuring transparency,
- Stay updated about ongoing protocol improvements addressing vulnerabilities,
are essential steps toward engaging confidently within evolving proof-based ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Proof-of-stake has emerged as an innovative alternative that addresses many limitations inherent in traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms while promoting sustainability through reduced energy use—and fostering scalability necessary for mainstream adoption today’s digital economy demands increasingly efficient infrastructure solutions rooted firmly in trustworthiness backed by transparent governance models.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-11 10:39
What is proof-of-stake?
What Is Proof-of-Stake (PoS)?
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain technology to validate transactions and secure the network. Unlike the traditional Proof-of-Work (PoW), which relies on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles through energy-intensive computations, PoS selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up as collateral. This approach aims to create a more efficient, scalable, and environmentally friendly way of maintaining blockchain integrity.
How Does Proof-of-Stake Work?
In a PoS system, participants known as validators are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake in the network. The more coins a validator commits, the higher their chances of being selected to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. This process involves several key steps:
- Staking: Validators lock up a specific amount of cryptocurrency as collateral.
- Validator Selection: The network randomly or deterministically selects validators based on factors like stake size and sometimes other criteria such as coin age.
- Validation: Selected validators verify transactions within proposed blocks.
- Reward & Penalties: Successful validation earns rewards; misbehavior results in penalties like slashing—where part or all of their staked coins are forfeited.
This method ensures that those with more at stake have greater incentive to act honestly since malicious activity can lead to significant financial loss.
Advantages of Proof-of-Stake
Proof-of-Stake offers several benefits over traditional PoW systems:
Energy Efficiency
One of PoS's most significant advantages is its lower energy consumption. Since it eliminates the need for computationally intensive mining operations, it reduces electricity usage drastically—making blockchain networks more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Scalability
PoS allows for faster transaction processing times and higher throughput compared to PoW networks. This scalability makes it suitable for applications requiring high-speed data validation without compromising security.
Security Features
While no system is entirely immune from attacks, well-designed PoS protocols incorporate mechanisms like slashing penalties that discourage malicious behavior. Additionally, because validators risk losing their staked assets if they act dishonestly, this creates economic incentives aligned with honest participation.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Proof-of-Stake
Despite its advantages, PoS faces certain challenges that developers and stakeholders must address:
Nothing-at-Stake Problem
In some early implementations of PoS, validators could vote for multiple conflicting chains without penalty—a situation called "nothing-at-stake." To mitigate this risk, modern protocols implement slashing conditions where misbehavior leads to penalties severe enough to deter such actions.
Centralization Concerns
Since larger stakeholders have increased influence over block creation probabilities, there's potential for wealth concentration leading to centralization risks—where power becomes concentrated among few large holders rather than distributed evenly across participants.
Security Considerations
Although generally considered secure when properly implemented, emerging attack vectors specific to staking systems require ongoing research and protocol improvements. Continuous updates help maintain resilience against threats like long-range attacks or validator collusion.
Ethereum’s Transition From Proof-of-Work To Proof-of-Stake
Ethereum’s move from proof-of-work (PoW) toward proof-of-stake (PoS) represents one of the most prominent real-world applications demonstrating this consensus mechanism's potential. Launched initially in December 2020 via its Beacon Chain upgrade—the first phase towards Ethereum 2.0—the transition aimed at addressing scalability issues while significantly reducing energy consumption associated with mining activities.
The milestone event called "The Merge," completed in 2023 after years of development effort by Ethereum developers worldwide—including extensive testing—marked Ethereum’s full switch from energy-intensive mining toward an eco-friendly staking model. This shift not only enhances sustainability but also paves the way for future upgrades focused on increasing transaction throughput through sharding techniques integrated into Eth2 architecture.
Future Outlook & Adoption Trends
As major cryptocurrencies adopt proof-of-stake mechanisms—including Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT), among others—the landscape is witnessing rapid growth driven by both technological advancements and environmental considerations. Stakeholder interest continues rising due primarily to benefits like reduced operational costs and improved scalability prospects which appeal both investors seeking returns via staking rewards—and developers aiming for robust decentralized applications capable of handling mass adoption scenarios efficiently.
However, widespread adoption also brings regulatory scrutiny; authorities worldwide are beginning scrutinizing staking practices concerning investor protections and compliance frameworks—a factor that could influence future development directions within this space significantly.
Key Takeaways About Proof-of-Stake
To summarize what makes proof-of-stake distinct:
- Validators participate by locking up tokens instead of performing resource-heavy computations.
- It offers superior energy efficiency compared with proof-of-work.
- Security relies heavily on economic incentives; misbehavior results in financial penalties.
- Major networks like Ethereum have successfully transitioned or plan transitions towards PoS models.
Understanding these core aspects helps users evaluate whether adopting or supporting proof-based blockchain projects aligns with their goals—whether it's investing safely or developing scalable decentralized solutions.
Addressing User Concerns & Trustworthiness
For users considering involvement in staking activities—or simply wanting clarity about how these systems operate—it’s crucial first understanding security measures involved such as slashing conditions designed specifically against malicious actions—and how decentralization efforts aim at preventing undue influence by large stakeholders alone.
Furthermore,
- Look into reputable platforms offering staking services,
- Review governance structures ensuring transparency,
- Stay updated about ongoing protocol improvements addressing vulnerabilities,
are essential steps toward engaging confidently within evolving proof-based ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Proof-of-stake has emerged as an innovative alternative that addresses many limitations inherent in traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms while promoting sustainability through reduced energy use—and fostering scalability necessary for mainstream adoption today’s digital economy demands increasingly efficient infrastructure solutions rooted firmly in trustworthiness backed by transparent governance models.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Ecosystem Grants and Incentives Drive Project Growth?
Ecosystem grants and incentives have become essential tools for fostering innovation and sustainable development within the crypto and investment sectors. As blockchain technology, decentralized finance (DeFi), and emerging tech continue to evolve rapidly, these financial supports help projects overcome early-stage funding hurdles while encouraging community participation. Understanding how these grants influence project growth is key for entrepreneurs, investors, and community members alike.
What Are Ecosystem Grants in Crypto and Investment?
Ecosystem grants are financial awards provided by organizations—such as blockchain foundations, venture capital firms, or community groups—to support promising projects. These grants serve as catalysts for development by offering resources that enable teams to focus on building their solutions without the immediate pressure of fundraising. In the crypto space especially, these funds often target specific areas like blockchain infrastructure, decentralized applications (dApps), or innovative protocols.
There are generally three types of ecosystem grants:
- Crypto-specific Grants: Focused on blockchain development, smart contract creation, security audits, or DeFi innovations.
- General Ecosystem Grants: Broader in scope; they may support AI integration with fintech platforms or other emerging technologies.
- Community-driven Grants: Funded directly by user communities or organizations aligned with specific values; they emphasize social impact or grassroots initiatives.
These varied grant types reflect a strategic approach to nurturing diverse technological advancements while fostering inclusive growth within ecosystems.
How Do Ecosystem Incentives Promote Project Development?
The primary goal of ecosystem incentives is to accelerate project growth through targeted funding coupled with non-financial benefits such as mentorships, technical support, networking opportunities, and visibility within the community. These incentives motivate developers to innovate confidently because they reduce initial financial risks—a critical factor during early stages when securing traditional funding can be challenging.
By providing clear pathways for project validation—through milestones like product launches or user adoption—ecosystem incentives also encourage accountability among recipients. This structured approach ensures that funded projects align with broader ecosystem goals such as decentralization principles or interoperability standards.
Furthermore,these programs often foster collaboration among startups,established companies,and academic institutions,creating a vibrant environment conducive to knowledge sharingand joint innovation efforts.
The Impact of Funding Growth on Project Success
Recent years have seen a surge in funds allocated toward ecosystem grants globally. This increase correlates strongly with the expansion of DeFi platforms and enterprise-grade blockchain solutions seeking mainstream adoption. Larger grant pools mean more ambitious projects can get off the ground—ranging from scalable Layer 2 solutions to privacy-preserving protocols—and contribute significantly toward industry evolution.
Moreover,diversification in grant programs has broadened access across various sectors beyond pure cryptocurrency applications.For instance:
- Fintech startups integrating blockchain
- AI-powered analytics tools
- Sustainability-focused crypto initiatives
This diversification not only fuels technological progress but also attracts a wider range of talent into ecosystems previously dominated solely by core crypto developers.
Community Engagement: A Key Driver
Community-driven grants have gained prominence because they leverage collective enthusiasm around particular projects or causes. When users invest their time and resources into supporting initiatives aligned with their values—such as environmental sustainability through green tokens—they create organic momentum that sustains long-term project viability.
In addition,community engagement enhances transparencyand accountability since stakeholders directly influence decision-making processes related to fund allocation.This participatory model fosters trust between developers and users—a crucial element amid increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
Challenges Facing Ecosystem Grant Programs
Despite their benefits,ecosystem grants face several challenges that could impede long-term success:
Regulatory Uncertainty: As governments tighten regulations around cryptocurrencies and token offerings,compliance becomes complex.Grant providers must ensure programs adhere to legal frameworks to avoid reputational damage or legal repercussions.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile;the value of granted tokens can fluctuate dramatically.This volatility impacts project sustainability if revenue models depend heavily on token appreciation rather than real-world utility.
Over-reliance on External Funding: Projects overly dependent on continuous grant inflows risk stagnation once funding diminishes unless diversified revenue streams develop over time.
Navigating Future Trends in Ecosystem Incentives
Looking ahead,
the landscape will likely see increased emphasis on compliance mechanisms,
more sophisticated evaluation criteria,
and greater integration between public-private partnerships.
Additionally,
regulators may introduce clearer guidelines tailored specifically for grant programs,
ensuring transparency while protecting investor interests.
Projects should focus not only on securing initial funding but also establishing sustainable business models that leverage ecosystem support effectively over time.
Final Thoughts: Supporting Sustainable Innovation Through Strategic Incentives
Ecosystem grants play an instrumental role in shaping the future trajectory of crypto innovations by lowering barriers for new entrants while promoting collaborative growth environments. They act as accelerators—not just providing capital but also fostering community involvement vital for long-term success.
However,
stakeholders must remain vigilant about regulatory developments
and market dynamics
to maximize benefits from these incentive structures without exposing themselves unnecessarily to risks.
As this field continues evolving rapidly,
a balanced approach combining strategic funding with compliance awareness will be essential
for ensuring resilient growth across all facets of the digital economy.
Keywords: ecosystem grants crypto | investment incentives | blockchain project funding | DeFi development support | community-driven crypto projects | startup incubation crypto | regulatory challenges in crypto financing


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 02:51
How do ecosystem grants and incentives drive project growth?
How Do Ecosystem Grants and Incentives Drive Project Growth?
Ecosystem grants and incentives have become essential tools for fostering innovation and sustainable development within the crypto and investment sectors. As blockchain technology, decentralized finance (DeFi), and emerging tech continue to evolve rapidly, these financial supports help projects overcome early-stage funding hurdles while encouraging community participation. Understanding how these grants influence project growth is key for entrepreneurs, investors, and community members alike.
What Are Ecosystem Grants in Crypto and Investment?
Ecosystem grants are financial awards provided by organizations—such as blockchain foundations, venture capital firms, or community groups—to support promising projects. These grants serve as catalysts for development by offering resources that enable teams to focus on building their solutions without the immediate pressure of fundraising. In the crypto space especially, these funds often target specific areas like blockchain infrastructure, decentralized applications (dApps), or innovative protocols.
There are generally three types of ecosystem grants:
- Crypto-specific Grants: Focused on blockchain development, smart contract creation, security audits, or DeFi innovations.
- General Ecosystem Grants: Broader in scope; they may support AI integration with fintech platforms or other emerging technologies.
- Community-driven Grants: Funded directly by user communities or organizations aligned with specific values; they emphasize social impact or grassroots initiatives.
These varied grant types reflect a strategic approach to nurturing diverse technological advancements while fostering inclusive growth within ecosystems.
How Do Ecosystem Incentives Promote Project Development?
The primary goal of ecosystem incentives is to accelerate project growth through targeted funding coupled with non-financial benefits such as mentorships, technical support, networking opportunities, and visibility within the community. These incentives motivate developers to innovate confidently because they reduce initial financial risks—a critical factor during early stages when securing traditional funding can be challenging.
By providing clear pathways for project validation—through milestones like product launches or user adoption—ecosystem incentives also encourage accountability among recipients. This structured approach ensures that funded projects align with broader ecosystem goals such as decentralization principles or interoperability standards.
Furthermore,these programs often foster collaboration among startups,established companies,and academic institutions,creating a vibrant environment conducive to knowledge sharingand joint innovation efforts.
The Impact of Funding Growth on Project Success
Recent years have seen a surge in funds allocated toward ecosystem grants globally. This increase correlates strongly with the expansion of DeFi platforms and enterprise-grade blockchain solutions seeking mainstream adoption. Larger grant pools mean more ambitious projects can get off the ground—ranging from scalable Layer 2 solutions to privacy-preserving protocols—and contribute significantly toward industry evolution.
Moreover,diversification in grant programs has broadened access across various sectors beyond pure cryptocurrency applications.For instance:
- Fintech startups integrating blockchain
- AI-powered analytics tools
- Sustainability-focused crypto initiatives
This diversification not only fuels technological progress but also attracts a wider range of talent into ecosystems previously dominated solely by core crypto developers.
Community Engagement: A Key Driver
Community-driven grants have gained prominence because they leverage collective enthusiasm around particular projects or causes. When users invest their time and resources into supporting initiatives aligned with their values—such as environmental sustainability through green tokens—they create organic momentum that sustains long-term project viability.
In addition,community engagement enhances transparencyand accountability since stakeholders directly influence decision-making processes related to fund allocation.This participatory model fosters trust between developers and users—a crucial element amid increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
Challenges Facing Ecosystem Grant Programs
Despite their benefits,ecosystem grants face several challenges that could impede long-term success:
Regulatory Uncertainty: As governments tighten regulations around cryptocurrencies and token offerings,compliance becomes complex.Grant providers must ensure programs adhere to legal frameworks to avoid reputational damage or legal repercussions.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile;the value of granted tokens can fluctuate dramatically.This volatility impacts project sustainability if revenue models depend heavily on token appreciation rather than real-world utility.
Over-reliance on External Funding: Projects overly dependent on continuous grant inflows risk stagnation once funding diminishes unless diversified revenue streams develop over time.
Navigating Future Trends in Ecosystem Incentives
Looking ahead,
the landscape will likely see increased emphasis on compliance mechanisms,
more sophisticated evaluation criteria,
and greater integration between public-private partnerships.
Additionally,
regulators may introduce clearer guidelines tailored specifically for grant programs,
ensuring transparency while protecting investor interests.
Projects should focus not only on securing initial funding but also establishing sustainable business models that leverage ecosystem support effectively over time.
Final Thoughts: Supporting Sustainable Innovation Through Strategic Incentives
Ecosystem grants play an instrumental role in shaping the future trajectory of crypto innovations by lowering barriers for new entrants while promoting collaborative growth environments. They act as accelerators—not just providing capital but also fostering community involvement vital for long-term success.
However,
stakeholders must remain vigilant about regulatory developments
and market dynamics
to maximize benefits from these incentive structures without exposing themselves unnecessarily to risks.
As this field continues evolving rapidly,
a balanced approach combining strategic funding with compliance awareness will be essential
for ensuring resilient growth across all facets of the digital economy.
Keywords: ecosystem grants crypto | investment incentives | blockchain project funding | DeFi development support | community-driven crypto projects | startup incubation crypto | regulatory challenges in crypto financing
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Clustering Algorithms (e.g., K-means) Categorize Technical Indicator Patterns?
Clustering algorithms have become essential tools in analyzing financial data, especially within the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency markets. They help traders and analysts identify hidden patterns in technical indicators, which are crucial for making informed trading decisions. Among these algorithms, K-means stands out due to its simplicity and effectiveness. This article explores how clustering algorithms like K-means categorize technical indicator patterns, their applications in crypto trading, recent technological advancements, and potential challenges.
Understanding Clustering Algorithms in Financial Data Analysis
Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning technique that groups data points based on their similarities without pre-labeled outcomes. Unlike classification models that require labeled training data, clustering identifies natural groupings within the dataset itself. In finance and cryptocurrency markets—where market behavior can be complex and unpredictable—clustering helps uncover underlying structures or recurring patterns that might not be immediately obvious.
In the context of technical analysis, clustering algorithms analyze historical price movements, volume data, or derived indicators to classify different market states or pattern types. This categorization enables traders to recognize similar scenarios quickly and adapt their strategies accordingly.
How Does K-means Work for Categorizing Technical Indicators?
K-means is one of the most widely used clustering methods because of its straightforward approach:
- Initialization: The algorithm begins by randomly selecting a predefined number of centroids (K). These centroids represent initial cluster centers.
- Assignment: Each data point—such as a specific value from a moving average or candlestick pattern—is assigned to the nearest centroid based on distance metrics like Euclidean distance.
- Update: Once all points are assigned, new centroids are calculated as the mean position of all points within each cluster.
- Iteration: Steps 2 and 3 repeat until convergence criteria are met—usually when cluster assignments stabilize or after reaching a set number of iterations.
This iterative process partitions large datasets into meaningful groups where each cluster shares similar characteristics concerning selected features like price momentum or volatility measures.
Applying Clustering to Technical Indicators in Cryptocurrency Markets
Technical indicators serve as mathematical representations derived from historical price and volume data; they help traders interpret market trends more objectively than raw prices alone. Clustering algorithms can analyze these indicators across different timeframes or assets to identify commonalities:
Candlestick Pattern Grouping: Candlestick charts visually depict price action over specific periods using various formations such as doji, hammer, shooting star etc., which often signal potential reversals or continuations. By applying K-means clustering on features extracted from candlestick shapes (like body size relative to wick length), traders can group similar patterns together—making it easier to spot recurring signals across different assets.
Moving Averages Classification: Moving averages smooth out short-term fluctuations but vary depending on period lengths (e.g., 50-day vs 200-day). Clustering these averages based on their performance during trending versus consolidating phases helps identify which types tend to predict future movements more reliably under certain conditions.
Volume-Based Indicators: Volume spikes often precede significant price moves; grouping such events through clustering allows for better anticipation of breakout scenarios.
By categorizing these patterns effectively through machine learning techniques like K-means, traders gain insights into market behavior clusters rather than relying solely on individual indicator readings.
Recent Developments Enhancing Clustering Applications
The integration of advanced technologies has significantly expanded what’s possible with clustering methods:
Artificial Intelligence & Deep Learning: Combining traditional clustering with deep neural networks enhances pattern recognition capabilities — especially when dealing with high-frequency trading data where complexity increases exponentially.
Real-Time Data Processing: Modern systems now enable live analysis using streaming market feeds; this means clusters can be updated dynamically as new information arrives—a critical advantage in volatile crypto markets where timing is everything.
Blockchain Technology Integration: Blockchain's transparent ledger ensures tamper-proof datasets for analysis purposes; this fosters trustworthiness when deploying automated pattern recognition systems based on clustered technical indicators.
These innovations allow traders not only to classify existing patterns but also adapt swiftly amidst changing market conditions while maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Challenges and Risks When Using Clustering Algorithms
Despite their advantages, applying clustering techniques involves certain pitfalls:
Overfitting Risks: If parameters such as the number of clusters (K) aren’t chosen carefully—or if models overly tailor themselves to historical data—they may perform poorly when faced with new unseen scenarios.
Data Quality Concerns: Noisy datasets caused by erroneous trades or incomplete records can lead clusters astray—misleading analysts about actual market states.
Regulatory Considerations: As AI-driven analytics become more prevalent in financial markets—including cryptocurrencies—regulators scrutinize transparency standards and fairness aspects related to automated decision-making processes involving sensitive financial information.
Addressing these issues requires rigorous validation procedures alongside continuous monitoring during deployment phases.
By leveraging sophisticated clustering algorithms like K-means within technical analysis frameworks—and staying aware of emerging technological trends—traders can enhance their ability to recognize meaningful chart patterns efficiently. However, understanding inherent limitations ensures responsible use aligned with best practices for risk management and compliance standards across evolving financial landscapes.
Key Takeaways:
- Unsupervised learning via clustering uncovers hidden structures in complex crypto-market datasets
- Techniques like K-means categorize candlestick formations & moving averages effectively
- Recent tech advances improve real-time adaptability & security via blockchain integration
- Caution needed regarding overfitting & data quality issues for reliable results


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 23:06
How do clustering algorithms (e.g., K-means) categorize technical indicator patterns?
How Do Clustering Algorithms (e.g., K-means) Categorize Technical Indicator Patterns?
Clustering algorithms have become essential tools in analyzing financial data, especially within the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency markets. They help traders and analysts identify hidden patterns in technical indicators, which are crucial for making informed trading decisions. Among these algorithms, K-means stands out due to its simplicity and effectiveness. This article explores how clustering algorithms like K-means categorize technical indicator patterns, their applications in crypto trading, recent technological advancements, and potential challenges.
Understanding Clustering Algorithms in Financial Data Analysis
Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning technique that groups data points based on their similarities without pre-labeled outcomes. Unlike classification models that require labeled training data, clustering identifies natural groupings within the dataset itself. In finance and cryptocurrency markets—where market behavior can be complex and unpredictable—clustering helps uncover underlying structures or recurring patterns that might not be immediately obvious.
In the context of technical analysis, clustering algorithms analyze historical price movements, volume data, or derived indicators to classify different market states or pattern types. This categorization enables traders to recognize similar scenarios quickly and adapt their strategies accordingly.
How Does K-means Work for Categorizing Technical Indicators?
K-means is one of the most widely used clustering methods because of its straightforward approach:
- Initialization: The algorithm begins by randomly selecting a predefined number of centroids (K). These centroids represent initial cluster centers.
- Assignment: Each data point—such as a specific value from a moving average or candlestick pattern—is assigned to the nearest centroid based on distance metrics like Euclidean distance.
- Update: Once all points are assigned, new centroids are calculated as the mean position of all points within each cluster.
- Iteration: Steps 2 and 3 repeat until convergence criteria are met—usually when cluster assignments stabilize or after reaching a set number of iterations.
This iterative process partitions large datasets into meaningful groups where each cluster shares similar characteristics concerning selected features like price momentum or volatility measures.
Applying Clustering to Technical Indicators in Cryptocurrency Markets
Technical indicators serve as mathematical representations derived from historical price and volume data; they help traders interpret market trends more objectively than raw prices alone. Clustering algorithms can analyze these indicators across different timeframes or assets to identify commonalities:
Candlestick Pattern Grouping: Candlestick charts visually depict price action over specific periods using various formations such as doji, hammer, shooting star etc., which often signal potential reversals or continuations. By applying K-means clustering on features extracted from candlestick shapes (like body size relative to wick length), traders can group similar patterns together—making it easier to spot recurring signals across different assets.
Moving Averages Classification: Moving averages smooth out short-term fluctuations but vary depending on period lengths (e.g., 50-day vs 200-day). Clustering these averages based on their performance during trending versus consolidating phases helps identify which types tend to predict future movements more reliably under certain conditions.
Volume-Based Indicators: Volume spikes often precede significant price moves; grouping such events through clustering allows for better anticipation of breakout scenarios.
By categorizing these patterns effectively through machine learning techniques like K-means, traders gain insights into market behavior clusters rather than relying solely on individual indicator readings.
Recent Developments Enhancing Clustering Applications
The integration of advanced technologies has significantly expanded what’s possible with clustering methods:
Artificial Intelligence & Deep Learning: Combining traditional clustering with deep neural networks enhances pattern recognition capabilities — especially when dealing with high-frequency trading data where complexity increases exponentially.
Real-Time Data Processing: Modern systems now enable live analysis using streaming market feeds; this means clusters can be updated dynamically as new information arrives—a critical advantage in volatile crypto markets where timing is everything.
Blockchain Technology Integration: Blockchain's transparent ledger ensures tamper-proof datasets for analysis purposes; this fosters trustworthiness when deploying automated pattern recognition systems based on clustered technical indicators.
These innovations allow traders not only to classify existing patterns but also adapt swiftly amidst changing market conditions while maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Challenges and Risks When Using Clustering Algorithms
Despite their advantages, applying clustering techniques involves certain pitfalls:
Overfitting Risks: If parameters such as the number of clusters (K) aren’t chosen carefully—or if models overly tailor themselves to historical data—they may perform poorly when faced with new unseen scenarios.
Data Quality Concerns: Noisy datasets caused by erroneous trades or incomplete records can lead clusters astray—misleading analysts about actual market states.
Regulatory Considerations: As AI-driven analytics become more prevalent in financial markets—including cryptocurrencies—regulators scrutinize transparency standards and fairness aspects related to automated decision-making processes involving sensitive financial information.
Addressing these issues requires rigorous validation procedures alongside continuous monitoring during deployment phases.
By leveraging sophisticated clustering algorithms like K-means within technical analysis frameworks—and staying aware of emerging technological trends—traders can enhance their ability to recognize meaningful chart patterns efficiently. However, understanding inherent limitations ensures responsible use aligned with best practices for risk management and compliance standards across evolving financial landscapes.
Key Takeaways:
- Unsupervised learning via clustering uncovers hidden structures in complex crypto-market datasets
- Techniques like K-means categorize candlestick formations & moving averages effectively
- Recent tech advances improve real-time adaptability & security via blockchain integration
- Caution needed regarding overfitting & data quality issues for reliable results
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Sharding in Blockchain?
Sharding is a transformative scalability solution designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of blockchain networks. As blockchain technology gains widespread adoption, the need to process increasing numbers of transactions quickly and securely becomes critical. Sharding addresses this challenge by dividing the entire network into smaller, manageable segments called shards, each capable of processing transactions independently. This division allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing congestion and improving overall throughput.
In essence, sharding enables a blockchain network to operate more like a distributed database rather than a single monolithic ledger. Each shard functions as its own mini-blockchain with its unique state and transaction history but remains interconnected within the larger network framework. This structure not only boosts transaction speeds but also helps in scaling blockchain solutions for real-world applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and enterprise solutions.
How Does Sharding Work in Blockchain Networks?
The core idea behind sharding involves splitting the workload across various smaller components—shards—that work concurrently. Each shard processes a subset of all transactions based on specific criteria such as user accounts or data types. For example, one shard might handle payment transactions while another manages smart contract interactions.
To maintain consistency across these independent shards, mechanisms like cross-shard communication are implemented. These protocols ensure that when users perform transactions involving multiple shards—say transferring assets from one account managed by one shard to another managed by different shards—the system can verify and record these operations accurately without compromising security or integrity.
Shards typically operate as separate blockchains known as "shard chains." They maintain their own states—such as account balances or smart contract data—and process their designated set of transactions independently before periodically syncing with other shards through consensus protocols designed for cross-shard validation.
Types of Sharding
There are primarily two types of sharding used in blockchain systems:
Horizontal Sharding: This approach divides the network based on transaction types or user groups—for instance, separating payment processing from smart contract execution.
Vertical Sharding: Here, data is partitioned based on storage needs or data categories—for example, storing different kinds of information (user profiles vs transactional logs) separately across various shards.
Both methods aim to optimize resource utilization while maintaining security and decentralization principles inherent in blockchain technology.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Implementing sharding offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By distributing transaction loads across multiple shards, networks can handle many more operations per second compared to traditional single-chain architectures.
Reduced Transaction Fees: Faster processing times mean less congestion; consequently, users often experience lower fees during peak usage periods.
Improved Network Efficiency: Smaller nodes manage fewer tasks within each shard—they require less computational power and storage capacity—making participation easier for more validators.
Parallel Processing: Multiple parts of the network work simultaneously rather than sequentially; this parallelism accelerates overall throughput significantly.
These benefits make sharded blockchains suitable for large-scale applications where high speed and low latency are essential requirements.
Challenges Associated With Blockchain Sharding
Despite its promising potential, implementing sharding introduces complex technical challenges that must be addressed:
Inter-Shard Communication
Ensuring seamless communication between different shards is vital yet difficult. Transactions involving multiple shards require secure protocols that prevent double-spending or inconsistencies—a problem known as cross-shard communication complexity.
Consensus Mechanisms Across Multiple Shards
Traditional consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) are not inherently designed for multi-shard environments. Developing efficient consensus models that work reliably across numerous independent chains remains an ongoing research area within blockchain development communities.
Security Concerns
Dividing a network into smaller segments increases vulnerability risks; if one shard becomes compromised due to an attack or bug exploitation—a scenario called "shard takeover"—it could threaten the entire ecosystem's security integrity unless robust safeguards are implemented effectively throughout all parts of the system.
Standardization & Adoption Barriers
For widespread adoption beyond experimental phases requires industry-wide standards governing how sharded networks communicate and interoperate seamlessly. Without standardization efforts among developers and stakeholders worldwide—including major platforms like Ethereum—the risk exists that fragmentation could hinder progress rather than accelerate it.
Recent Developments in Blockchain Sharding Technology
Major projects have made notable strides toward integrating sharding into their ecosystems:
Ethereum 2.0 has been at the forefront with plans for scalable upgrades through its phased rollout strategy involving beacon chains (launched December 2020). The next steps include deploying dedicated shard chains alongside cross-shard communication protocols aimed at enabling Ethereum’s massive ecosystem to scale efficiently without sacrificing decentralization or security standards.
Polkadot employs relay chains connecting parachains—independent blockchains optimized for specific use cases—that communicate via shared security models facilitating interoperability among diverse networks.
Cosmos, utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithm architecture allows developers to create zones (independent blockchains) capable of interoperation within an overarching hub-and-spoke model similar to Polkadot’s relay chain approach.
Research continues globally exploring innovative techniques such as state sharding, which aims at optimizing how state information is stored across nodes—a crucial factor influencing scalability limits further improvements.
Potential Risks Impacting Future Adoption
While promising solutions exist today—and ongoing research promises even better approaches—the path forward faces hurdles related mainly to:
Security Risks: Smaller individual shards may become targets due to reduced validation power compared with full nodes operating on entire networks.
Interoperability Challenges: Achieving flawless interaction between diverse systems requires standardized protocols; otherwise fragmentation may occur leading toward isolated ecosystems instead of unified platforms.
Adoption Hurdles & Industry Standardization
Without broad agreement on technical standards governing cross-shard communications—as well as regulatory considerations—widespread deployment might slow down considerably despite technological readiness.
Understanding How Blockchain Scaling Evolves Through Sharding
As demand grows exponentially—from DeFi applications demanding rapid trades versus enterprise-level integrations requiring high throughput—the importance lies not just in creating faster blockchains but ensuring they remain secure against evolving threats while interoperable enough for global adoption.
By addressing current limitations through continuous innovation—in protocol design improvements like state sharing techniques—and fostering collaboration among industry leaders worldwide who develop open standards —the future landscape looks promising: scalable yet secure decentralized systems capable enough for mainstream use.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what sharding entails within blockchain technology: how it works technically; why it matters; what benefits it offers; what challenges lie ahead; along with recent advancements shaping its future trajectory—all aligned towards helping users understand both foundational concepts and cutting-edge developments effectively.


Lo
2025-05-15 02:38
What is sharding in blockchain?
What Is Sharding in Blockchain?
Sharding is a transformative scalability solution designed to enhance the performance and efficiency of blockchain networks. As blockchain technology gains widespread adoption, the need to process increasing numbers of transactions quickly and securely becomes critical. Sharding addresses this challenge by dividing the entire network into smaller, manageable segments called shards, each capable of processing transactions independently. This division allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly reducing congestion and improving overall throughput.
In essence, sharding enables a blockchain network to operate more like a distributed database rather than a single monolithic ledger. Each shard functions as its own mini-blockchain with its unique state and transaction history but remains interconnected within the larger network framework. This structure not only boosts transaction speeds but also helps in scaling blockchain solutions for real-world applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and enterprise solutions.
How Does Sharding Work in Blockchain Networks?
The core idea behind sharding involves splitting the workload across various smaller components—shards—that work concurrently. Each shard processes a subset of all transactions based on specific criteria such as user accounts or data types. For example, one shard might handle payment transactions while another manages smart contract interactions.
To maintain consistency across these independent shards, mechanisms like cross-shard communication are implemented. These protocols ensure that when users perform transactions involving multiple shards—say transferring assets from one account managed by one shard to another managed by different shards—the system can verify and record these operations accurately without compromising security or integrity.
Shards typically operate as separate blockchains known as "shard chains." They maintain their own states—such as account balances or smart contract data—and process their designated set of transactions independently before periodically syncing with other shards through consensus protocols designed for cross-shard validation.
Types of Sharding
There are primarily two types of sharding used in blockchain systems:
Horizontal Sharding: This approach divides the network based on transaction types or user groups—for instance, separating payment processing from smart contract execution.
Vertical Sharding: Here, data is partitioned based on storage needs or data categories—for example, storing different kinds of information (user profiles vs transactional logs) separately across various shards.
Both methods aim to optimize resource utilization while maintaining security and decentralization principles inherent in blockchain technology.
Benefits of Implementing Sharding
Implementing sharding offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Scalability: By distributing transaction loads across multiple shards, networks can handle many more operations per second compared to traditional single-chain architectures.
Reduced Transaction Fees: Faster processing times mean less congestion; consequently, users often experience lower fees during peak usage periods.
Improved Network Efficiency: Smaller nodes manage fewer tasks within each shard—they require less computational power and storage capacity—making participation easier for more validators.
Parallel Processing: Multiple parts of the network work simultaneously rather than sequentially; this parallelism accelerates overall throughput significantly.
These benefits make sharded blockchains suitable for large-scale applications where high speed and low latency are essential requirements.
Challenges Associated With Blockchain Sharding
Despite its promising potential, implementing sharding introduces complex technical challenges that must be addressed:
Inter-Shard Communication
Ensuring seamless communication between different shards is vital yet difficult. Transactions involving multiple shards require secure protocols that prevent double-spending or inconsistencies—a problem known as cross-shard communication complexity.
Consensus Mechanisms Across Multiple Shards
Traditional consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) are not inherently designed for multi-shard environments. Developing efficient consensus models that work reliably across numerous independent chains remains an ongoing research area within blockchain development communities.
Security Concerns
Dividing a network into smaller segments increases vulnerability risks; if one shard becomes compromised due to an attack or bug exploitation—a scenario called "shard takeover"—it could threaten the entire ecosystem's security integrity unless robust safeguards are implemented effectively throughout all parts of the system.
Standardization & Adoption Barriers
For widespread adoption beyond experimental phases requires industry-wide standards governing how sharded networks communicate and interoperate seamlessly. Without standardization efforts among developers and stakeholders worldwide—including major platforms like Ethereum—the risk exists that fragmentation could hinder progress rather than accelerate it.
Recent Developments in Blockchain Sharding Technology
Major projects have made notable strides toward integrating sharding into their ecosystems:
Ethereum 2.0 has been at the forefront with plans for scalable upgrades through its phased rollout strategy involving beacon chains (launched December 2020). The next steps include deploying dedicated shard chains alongside cross-shard communication protocols aimed at enabling Ethereum’s massive ecosystem to scale efficiently without sacrificing decentralization or security standards.
Polkadot employs relay chains connecting parachains—independent blockchains optimized for specific use cases—that communicate via shared security models facilitating interoperability among diverse networks.
Cosmos, utilizing Tendermint Core consensus algorithm architecture allows developers to create zones (independent blockchains) capable of interoperation within an overarching hub-and-spoke model similar to Polkadot’s relay chain approach.
Research continues globally exploring innovative techniques such as state sharding, which aims at optimizing how state information is stored across nodes—a crucial factor influencing scalability limits further improvements.
Potential Risks Impacting Future Adoption
While promising solutions exist today—and ongoing research promises even better approaches—the path forward faces hurdles related mainly to:
Security Risks: Smaller individual shards may become targets due to reduced validation power compared with full nodes operating on entire networks.
Interoperability Challenges: Achieving flawless interaction between diverse systems requires standardized protocols; otherwise fragmentation may occur leading toward isolated ecosystems instead of unified platforms.
Adoption Hurdles & Industry Standardization
Without broad agreement on technical standards governing cross-shard communications—as well as regulatory considerations—widespread deployment might slow down considerably despite technological readiness.
Understanding How Blockchain Scaling Evolves Through Sharding
As demand grows exponentially—from DeFi applications demanding rapid trades versus enterprise-level integrations requiring high throughput—the importance lies not just in creating faster blockchains but ensuring they remain secure against evolving threats while interoperable enough for global adoption.
By addressing current limitations through continuous innovation—in protocol design improvements like state sharing techniques—and fostering collaboration among industry leaders worldwide who develop open standards —the future landscape looks promising: scalable yet secure decentralized systems capable enough for mainstream use.
This comprehensive overview provides clarity about what sharding entails within blockchain technology: how it works technically; why it matters; what benefits it offers; what challenges lie ahead; along with recent advancements shaping its future trajectory—all aligned towards helping users understand both foundational concepts and cutting-edge developments effectively.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Hardware Wallets and How Secure Are They?
Understanding Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed specifically for storing cryptocurrencies securely. Unlike software wallets, which are applications or online platforms vulnerable to hacking, hardware wallets keep private keys offline, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks. These devices typically connect to computers or smartphones via USB or Bluetooth, providing a user-friendly interface for managing digital assets without exposing sensitive information to online threats.
The core purpose of a hardware wallet is to safeguard private keys—the cryptographic codes that grant access to your cryptocurrency holdings. By isolating these keys from internet-connected devices, hardware wallets act as a form of cold storage—an offline method that offers enhanced security compared to hot wallets stored on exchanges or software apps.
Key Components and Features
A typical hardware wallet comprises several essential components:
- Secure Private Key Storage: The device's primary function is to store private keys securely within a protected environment.
- Offline Storage: Keys are kept offline at all times unless explicitly used for transactions.
- User Interface: Most models feature small screens and buttons allowing users to verify transaction details directly on the device.
- Backup & Recovery Options: To prevent loss due to damage or theft, many hardware wallets offer seed phrases—mnemonic recovery phrases enabling users to restore access if the device is lost.
These features collectively contribute toward creating an environment where cryptocurrencies can be managed with minimal exposure risk.
Security Advantages of Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets provide multiple layers of security that make them highly resistant against common cyber threats:
- Offline Storage (Cold Storage): Since private keys never leave the device in an unencrypted form during normal operation, they remain insulated from hacking attempts targeting online systems.
- Physical Security Measures: Many devices incorporate tamper-evident seals and secure elements—specialized chips designed for cryptographic operations—to prevent unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Some models integrate biometric verification like fingerprint scanning or facial recognition for added protection during transactions.
- Encryption & Firmware Security: Data stored within these devices is encrypted; regular firmware updates patch vulnerabilities and enhance security features over time.
This combination ensures that even if your computer becomes compromised by malware or phishing attacks, your funds remain protected as long as you do not physically lose the device.
Limitations and Risks
Despite their robust security features, hardware wallets are not entirely foolproof. Several risks should be considered:
Physical Loss or Theft: If someone gains physical possession of your wallet along with your seed phrase backup, they could potentially access your funds unless additional safeguards like PIN codes are in place.
Software Vulnerabilities & Firmware Flaws: Occasionally, vulnerabilities may exist within the firmware code of certain models; however, reputable manufacturers regularly release updates addressing such issues promptly.
Human Error & User Practices: Users must exercise caution when handling seed phrases—storing them securely offline—and avoid sharing sensitive information with others. Mistakes such as entering recovery phrases into malicious websites can compromise security.
While these risks exist, proper usage practices significantly mitigate potential threats associated with hardware wallet ownership.
Recent Innovations in Hardware Wallet Technology
The landscape of cryptocurrency storage continues evolving rapidly through technological advancements:
Market Expansion
Major brands like Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T, and KeepKey have expanded their product lines amid rising demand driven by increased awareness about digital asset safety among investors worldwide.
Cutting-edge Features
Recent developments include:
Quantum-resistant algorithms: As quantum computing advances threaten traditional cryptography methods in future years—a handful of newer models now incorporate algorithms designed specifically against quantum attacks.
Biometric Authentication: Devices integrating fingerprint scanners or facial recognition provide an extra layer beyond PIN codes during transaction approval processes.
Smart Contract Compatibility: Some modern hardware wallets support interactions with decentralized applications (dApps) directly from the device interface—streamlining complex transactions involving smart contracts on blockchain networks like Ethereum.
Regulatory Impact
As governments worldwide tighten regulations around cryptocurrency custody and compliance standards grow stricter—including Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements—the design and operation protocols for hardware wallets adapt accordingly ensuring legal adherence while maintaining user privacy protections.
Timeline: Milestones in Hardware Wallet Development
Understanding key dates helps contextualize how far this technology has come:
- 2008 – The concept emerged alongside Bitcoin’s rise; early ideas focused on secure key management outside online environments
- 2012 – Ledger launched its first product: Ledger Vault
- 2014 – Trezor introduced its first model—the Trezor One
- 2017 – Market boom fueled by surging crypto prices led many new entrants into space
- 2020 – Pandemic accelerated adoption due to increased interest in digital assets
- 2022 – Introduction of advanced features including biometric authentication and quantum-resistant algorithms became mainstream
Future Outlook: Adoption Trends & Challenges Ahead
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream investment vehicles globally,
- Expect continued growth* in demand for reliable cold storage solutions like hardware wallets will drive innovation further—from integrating multi-signature capabilities to enhancing user experience through seamless interfaces compatible across various platforms.
However,
- Regulatory pressures* might impose stricter operational standards affecting availability across regions,and emerging cybersecurity threats could challenge even sophisticated devices requiring ongoing updates,patches,and vigilance from both manufacturers and users alike.
How Secure Are Hardware Wallets?
Hardware wallets stand out as one of the most secure options available today for storing cryptocurrencies thanks primarily to their offline nature combined with advanced encryption measures — making them resilient against most cyberattacks targeting hot-wallet solutions connected directly online.. Nonetheless,
they require responsible handling regarding seed phrase management,physical safeguarding,and timely firmware updates.. When used correctly within best practices frameworks,hardware wallets offer peace-of-mind assurance suitable even for institutional-grade custody needs while supporting individual investors seeking robust protection against thefts and hacks alike.


Lo
2025-05-14 07:15
What are hardware wallets, and how secure are they?
What Are Hardware Wallets and How Secure Are They?
Understanding Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed specifically for storing cryptocurrencies securely. Unlike software wallets, which are applications or online platforms vulnerable to hacking, hardware wallets keep private keys offline, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks. These devices typically connect to computers or smartphones via USB or Bluetooth, providing a user-friendly interface for managing digital assets without exposing sensitive information to online threats.
The core purpose of a hardware wallet is to safeguard private keys—the cryptographic codes that grant access to your cryptocurrency holdings. By isolating these keys from internet-connected devices, hardware wallets act as a form of cold storage—an offline method that offers enhanced security compared to hot wallets stored on exchanges or software apps.
Key Components and Features
A typical hardware wallet comprises several essential components:
- Secure Private Key Storage: The device's primary function is to store private keys securely within a protected environment.
- Offline Storage: Keys are kept offline at all times unless explicitly used for transactions.
- User Interface: Most models feature small screens and buttons allowing users to verify transaction details directly on the device.
- Backup & Recovery Options: To prevent loss due to damage or theft, many hardware wallets offer seed phrases—mnemonic recovery phrases enabling users to restore access if the device is lost.
These features collectively contribute toward creating an environment where cryptocurrencies can be managed with minimal exposure risk.
Security Advantages of Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets provide multiple layers of security that make them highly resistant against common cyber threats:
- Offline Storage (Cold Storage): Since private keys never leave the device in an unencrypted form during normal operation, they remain insulated from hacking attempts targeting online systems.
- Physical Security Measures: Many devices incorporate tamper-evident seals and secure elements—specialized chips designed for cryptographic operations—to prevent unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Some models integrate biometric verification like fingerprint scanning or facial recognition for added protection during transactions.
- Encryption & Firmware Security: Data stored within these devices is encrypted; regular firmware updates patch vulnerabilities and enhance security features over time.
This combination ensures that even if your computer becomes compromised by malware or phishing attacks, your funds remain protected as long as you do not physically lose the device.
Limitations and Risks
Despite their robust security features, hardware wallets are not entirely foolproof. Several risks should be considered:
Physical Loss or Theft: If someone gains physical possession of your wallet along with your seed phrase backup, they could potentially access your funds unless additional safeguards like PIN codes are in place.
Software Vulnerabilities & Firmware Flaws: Occasionally, vulnerabilities may exist within the firmware code of certain models; however, reputable manufacturers regularly release updates addressing such issues promptly.
Human Error & User Practices: Users must exercise caution when handling seed phrases—storing them securely offline—and avoid sharing sensitive information with others. Mistakes such as entering recovery phrases into malicious websites can compromise security.
While these risks exist, proper usage practices significantly mitigate potential threats associated with hardware wallet ownership.
Recent Innovations in Hardware Wallet Technology
The landscape of cryptocurrency storage continues evolving rapidly through technological advancements:
Market Expansion
Major brands like Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T, and KeepKey have expanded their product lines amid rising demand driven by increased awareness about digital asset safety among investors worldwide.
Cutting-edge Features
Recent developments include:
Quantum-resistant algorithms: As quantum computing advances threaten traditional cryptography methods in future years—a handful of newer models now incorporate algorithms designed specifically against quantum attacks.
Biometric Authentication: Devices integrating fingerprint scanners or facial recognition provide an extra layer beyond PIN codes during transaction approval processes.
Smart Contract Compatibility: Some modern hardware wallets support interactions with decentralized applications (dApps) directly from the device interface—streamlining complex transactions involving smart contracts on blockchain networks like Ethereum.
Regulatory Impact
As governments worldwide tighten regulations around cryptocurrency custody and compliance standards grow stricter—including Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements—the design and operation protocols for hardware wallets adapt accordingly ensuring legal adherence while maintaining user privacy protections.
Timeline: Milestones in Hardware Wallet Development
Understanding key dates helps contextualize how far this technology has come:
- 2008 – The concept emerged alongside Bitcoin’s rise; early ideas focused on secure key management outside online environments
- 2012 – Ledger launched its first product: Ledger Vault
- 2014 – Trezor introduced its first model—the Trezor One
- 2017 – Market boom fueled by surging crypto prices led many new entrants into space
- 2020 – Pandemic accelerated adoption due to increased interest in digital assets
- 2022 – Introduction of advanced features including biometric authentication and quantum-resistant algorithms became mainstream
Future Outlook: Adoption Trends & Challenges Ahead
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream investment vehicles globally,
- Expect continued growth* in demand for reliable cold storage solutions like hardware wallets will drive innovation further—from integrating multi-signature capabilities to enhancing user experience through seamless interfaces compatible across various platforms.
However,
- Regulatory pressures* might impose stricter operational standards affecting availability across regions,and emerging cybersecurity threats could challenge even sophisticated devices requiring ongoing updates,patches,and vigilance from both manufacturers and users alike.
How Secure Are Hardware Wallets?
Hardware wallets stand out as one of the most secure options available today for storing cryptocurrencies thanks primarily to their offline nature combined with advanced encryption measures — making them resilient against most cyberattacks targeting hot-wallet solutions connected directly online.. Nonetheless,
they require responsible handling regarding seed phrase management,physical safeguarding,and timely firmware updates.. When used correctly within best practices frameworks,hardware wallets offer peace-of-mind assurance suitable even for institutional-grade custody needs while supporting individual investors seeking robust protection against thefts and hacks alike.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Apply Forensic Analysis to Detect Fraud
Fraudulent activities pose a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and financial institutions worldwide. As fraud schemes become more sophisticated—especially with the rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies—traditional detection methods often fall short. Forensic analysis has emerged as a vital approach in uncovering and preventing these crimes. This article explores how forensic analysis can be effectively applied to detect fraud, emphasizing practical techniques, recent technological advancements, and best practices.
Understanding the Role of Forensic Analysis in Fraud Detection
Forensic analysis involves applying scientific principles and investigative techniques to examine evidence related to fraudulent activities. Its primary goal is to verify the authenticity of transactions, documents, or digital footprints that may indicate deception or illegal activity. In financial contexts, forensic analysts scrutinize complex transaction data and digital artifacts to identify anomalies that suggest fraud.
This process is crucial not only for criminal investigations but also for corporate compliance efforts aimed at preventing internal misconduct or external scams. Given the increasing complexity of financial transactions—particularly with online banking, mobile payments, and cryptocurrencies—advanced forensic methods are essential for effective detection.
Key Techniques Used in Forensic Fraud Investigation
Applying forensic analysis requires a combination of specialized tools and methodologies tailored to different types of evidence:
Digital Forensics
Digital forensics involves analyzing electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, servers, emails, text messages, and online activity logs. By recovering deleted files or tracing IP addresses involved in suspicious transactions, investigators can build a timeline of events that reveal fraudulent schemes.
Data Analysis & Machine Learning
Data analytics leverages statistical models and machine learning algorithms capable of sifting through vast datasets quickly. These tools help identify patterns or outliers—such as unusual transaction volumes or irregular account behaviors—that may signal fraudulent activity.
Document Examination
Analyzing physical or digital documents is critical when verifying paperwork associated with transactions. Experts look for inconsistencies like misspellings, formatting errors (anachronisms), altered signatures—or other signs indicating forgery—that could point toward document fraud.
Applying Forensic Techniques Step-by-Step
To effectively detect fraud using forensic analysis:
- Identify Suspicious Activity: Start by monitoring transactional data for anomalies such as unexpected large transfers or irregular access patterns.
- Collect Evidence: Gather relevant digital artifacts (emails; transaction logs; metadata) while maintaining chain-of-custody protocols.
- Analyze Digital Footprints: Use specialized software like EnCase or FTK to recover deleted files; trace communication channels involved.
- Perform Data Analytics: Deploy machine learning models trained on historical data sets representing normal versus fraudulent behavior.
- Examine Documents Thoroughly: Cross-check documentation against known standards; look for discrepancies indicating tampering.
- Correlate Findings: Integrate insights from various sources—digital traces plus document reviews—to form a comprehensive picture.
- Report & Act: Summarize findings clearly; collaborate with legal teams if necessary before taking corrective actions.
Recent Technological Advancements Enhancing Fraud Detection
The landscape of forensic investigation continues evolving rapidly thanks to innovations like blockchain technology and artificial intelligence (AI). Blockchain’s transparent ledger system allows investigators to trace cryptocurrency transactions more accurately than ever before—a significant advantage given the rise in crypto-related scams such as phishing attacks or Ponzi schemes.
AI-powered tools now assist analysts by automatically flagging suspicious patterns across massive datasets without manual intervention — improving both speed and accuracy in detecting complex fraud networks.
Additionally,, companies like Google have integrated enhanced security features into their platforms (e.g., Android 16) designed specifically to combat scams involving cryptocurrencies by alerting users about potential threats proactively.
Challenges Faced When Applying Forensic Analysis
Despite technological progress,, several hurdles remain:
- The sheer volume of digital data can overwhelm traditional investigative processes unless supported by advanced analytics tools.
- Cybercriminals continually adapt their tactics—for example,, using encrypted messaging apps—which complicates evidence collection.
- Ensuring compliance with privacy laws during investigations requires careful handling so as not infringe on individual rights while gathering sufficient evidence.
- The need for highly trained professionals who stay updated on emerging technologies adds an ongoing resource challenge within organizations seeking effective detection capabilities.
Best Practices for Effective Fraud Detection Using Forensics
To maximize success rates when applying forensic analysis:
- Maintain meticulous documentation throughout investigations—including chain-of-custody records—to ensure admissibility if legal proceedings follow.
- Invest in continuous training programs so analysts stay current with latest software updates,, cyber threats,, regulatory changes—and emerging scam tactics.
- Use layered approaches combining multiple techniques: e.g., initial pattern recognition via AI followed by detailed manual review where needed..
- Foster collaboration between IT teams,, legal advisors,, auditors—and external experts when necessary—to ensure comprehensive coverage..
By integrating these practices into your organization’s risk management framework,,, you enhance your ability not onlyto detect existing fraud but also prevent future incidents through proactive monitoring strategies..
Real-Life Examples Demonstrating Effective Application
One notable case involved authorities uncovering fake art sales linked via forged documents analyzed through forensic document examination techniques.. A Miami dealer was caught selling counterfeit Warhol artworks after investigators identified inconsistencies within paperwork—a classic example illustrating how thorough document scrutiny can expose deception even amidst sophisticated schemes..
Similarly,,, cryptocurrency exchanges increasingly rely on blockchain analytics software such as Chainalysis—which tracks illicit crypto flows—to identify scammers operating across borders.. These real-world applications highlight how combining traditional investigative skills with cutting-edge technology yields tangible results against diverse formsof financial crime..
Applying forensic analysis effectively requires understanding its core principles—from examining electronic footprintsand scrutinizing documents,to leveraging modern tech innovations—all aimed at exposing hidden fraudulent activities swiftlyand accurately.. As financial landscapes evolve—with new assets emerging—the importanceof staying ahead through continuous learningand adopting best practices cannot be overstated.. Whether dealingwith conventional financial scamsor navigating complex crypto schemes,—a strategic approach rootedin scientific investigation remains your strongest assetin safeguarding assetsand maintaining trustworthiness within your organization.or community


kai
2025-05-19 17:16
How to apply forensic analysis to detect fraud?
How to Apply Forensic Analysis to Detect Fraud
Fraudulent activities pose a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and financial institutions worldwide. As fraud schemes become more sophisticated—especially with the rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies—traditional detection methods often fall short. Forensic analysis has emerged as a vital approach in uncovering and preventing these crimes. This article explores how forensic analysis can be effectively applied to detect fraud, emphasizing practical techniques, recent technological advancements, and best practices.
Understanding the Role of Forensic Analysis in Fraud Detection
Forensic analysis involves applying scientific principles and investigative techniques to examine evidence related to fraudulent activities. Its primary goal is to verify the authenticity of transactions, documents, or digital footprints that may indicate deception or illegal activity. In financial contexts, forensic analysts scrutinize complex transaction data and digital artifacts to identify anomalies that suggest fraud.
This process is crucial not only for criminal investigations but also for corporate compliance efforts aimed at preventing internal misconduct or external scams. Given the increasing complexity of financial transactions—particularly with online banking, mobile payments, and cryptocurrencies—advanced forensic methods are essential for effective detection.
Key Techniques Used in Forensic Fraud Investigation
Applying forensic analysis requires a combination of specialized tools and methodologies tailored to different types of evidence:
Digital Forensics
Digital forensics involves analyzing electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, servers, emails, text messages, and online activity logs. By recovering deleted files or tracing IP addresses involved in suspicious transactions, investigators can build a timeline of events that reveal fraudulent schemes.
Data Analysis & Machine Learning
Data analytics leverages statistical models and machine learning algorithms capable of sifting through vast datasets quickly. These tools help identify patterns or outliers—such as unusual transaction volumes or irregular account behaviors—that may signal fraudulent activity.
Document Examination
Analyzing physical or digital documents is critical when verifying paperwork associated with transactions. Experts look for inconsistencies like misspellings, formatting errors (anachronisms), altered signatures—or other signs indicating forgery—that could point toward document fraud.
Applying Forensic Techniques Step-by-Step
To effectively detect fraud using forensic analysis:
- Identify Suspicious Activity: Start by monitoring transactional data for anomalies such as unexpected large transfers or irregular access patterns.
- Collect Evidence: Gather relevant digital artifacts (emails; transaction logs; metadata) while maintaining chain-of-custody protocols.
- Analyze Digital Footprints: Use specialized software like EnCase or FTK to recover deleted files; trace communication channels involved.
- Perform Data Analytics: Deploy machine learning models trained on historical data sets representing normal versus fraudulent behavior.
- Examine Documents Thoroughly: Cross-check documentation against known standards; look for discrepancies indicating tampering.
- Correlate Findings: Integrate insights from various sources—digital traces plus document reviews—to form a comprehensive picture.
- Report & Act: Summarize findings clearly; collaborate with legal teams if necessary before taking corrective actions.
Recent Technological Advancements Enhancing Fraud Detection
The landscape of forensic investigation continues evolving rapidly thanks to innovations like blockchain technology and artificial intelligence (AI). Blockchain’s transparent ledger system allows investigators to trace cryptocurrency transactions more accurately than ever before—a significant advantage given the rise in crypto-related scams such as phishing attacks or Ponzi schemes.
AI-powered tools now assist analysts by automatically flagging suspicious patterns across massive datasets without manual intervention — improving both speed and accuracy in detecting complex fraud networks.
Additionally,, companies like Google have integrated enhanced security features into their platforms (e.g., Android 16) designed specifically to combat scams involving cryptocurrencies by alerting users about potential threats proactively.
Challenges Faced When Applying Forensic Analysis
Despite technological progress,, several hurdles remain:
- The sheer volume of digital data can overwhelm traditional investigative processes unless supported by advanced analytics tools.
- Cybercriminals continually adapt their tactics—for example,, using encrypted messaging apps—which complicates evidence collection.
- Ensuring compliance with privacy laws during investigations requires careful handling so as not infringe on individual rights while gathering sufficient evidence.
- The need for highly trained professionals who stay updated on emerging technologies adds an ongoing resource challenge within organizations seeking effective detection capabilities.
Best Practices for Effective Fraud Detection Using Forensics
To maximize success rates when applying forensic analysis:
- Maintain meticulous documentation throughout investigations—including chain-of-custody records—to ensure admissibility if legal proceedings follow.
- Invest in continuous training programs so analysts stay current with latest software updates,, cyber threats,, regulatory changes—and emerging scam tactics.
- Use layered approaches combining multiple techniques: e.g., initial pattern recognition via AI followed by detailed manual review where needed..
- Foster collaboration between IT teams,, legal advisors,, auditors—and external experts when necessary—to ensure comprehensive coverage..
By integrating these practices into your organization’s risk management framework,,, you enhance your ability not onlyto detect existing fraud but also prevent future incidents through proactive monitoring strategies..
Real-Life Examples Demonstrating Effective Application
One notable case involved authorities uncovering fake art sales linked via forged documents analyzed through forensic document examination techniques.. A Miami dealer was caught selling counterfeit Warhol artworks after investigators identified inconsistencies within paperwork—a classic example illustrating how thorough document scrutiny can expose deception even amidst sophisticated schemes..
Similarly,,, cryptocurrency exchanges increasingly rely on blockchain analytics software such as Chainalysis—which tracks illicit crypto flows—to identify scammers operating across borders.. These real-world applications highlight how combining traditional investigative skills with cutting-edge technology yields tangible results against diverse formsof financial crime..
Applying forensic analysis effectively requires understanding its core principles—from examining electronic footprintsand scrutinizing documents,to leveraging modern tech innovations—all aimed at exposing hidden fraudulent activities swiftlyand accurately.. As financial landscapes evolve—with new assets emerging—the importanceof staying ahead through continuous learningand adopting best practices cannot be overstated.. Whether dealingwith conventional financial scamsor navigating complex crypto schemes,—a strategic approach rootedin scientific investigation remains your strongest assetin safeguarding assetsand maintaining trustworthiness within your organization.or community
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is DBSCAN and How Does It Detect Unusual Market Conditions?
Understanding how financial markets, especially volatile ones like cryptocurrencies, can be monitored for anomalies is crucial for traders, analysts, and regulators alike. One powerful tool gaining traction in this space is DBSCAN—short for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise. This clustering algorithm helps identify unusual patterns or outliers in complex datasets by grouping similar data points together based on their density.
How Does DBSCAN Work?
At its core, DBSCAN analyzes data points—such as price movements or trading volumes—and groups them into clusters where points are densely packed. It operates based on two key parameters: Eps (epsilon), which defines the radius around a point to consider neighboring points, and MinPts (minimum points), the minimum number of neighboring points needed to form a cluster.
The process begins by selecting an unvisited data point. If this point has at least MinPts within its Eps-neighborhood, it becomes a core point and initiates a new cluster. The algorithm then expands this cluster by recursively including all neighboring core points and their neighbors that meet the density criteria. Points that do not belong to any cluster are labeled as noise or outliers—potential indicators of anomalies.
This approach makes DBSCAN particularly effective at handling noisy financial data because it naturally distinguishes between normal market fluctuations and genuine anomalies without requiring prior knowledge about the number of clusters.
Why Is Detecting Anomalies Important in Cryptocurrency Markets?
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility and rapid price swings. Identifying abnormal market conditions early can provide traders with critical insights into potential risks or opportunities. For example:
- Market Manipulation: Sudden spikes or drops might indicate pump-and-dump schemes.
- Systemic Risks: Unusual trading volumes could signal systemic issues or impending crashes.
- Fraud Detection: Outlier transactions may reveal fraudulent activities such as wash trading.
By applying algorithms like DBSCAN to historical price data, traders can detect these irregularities more effectively than traditional methods that might overlook subtle but significant deviations.
Recent Advances in Using DBSCAN for Market Analysis
Recent research highlights several innovative applications of DBSCAN within financial analytics:
Cryptocurrency Anomaly Detection: Studies have demonstrated how applying DBSCAN to Bitcoin's price movements helps identify unusual patterns preceding market downturns [1]. These insights enable better risk management strategies.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems: With advancements in computational power, integrating DBSCAN into live monitoring tools allows instant detection of anomalies as they occur [2]. Traders receive timely alerts that inform decision-making processes.
Combining Machine Learning Techniques: Combining density-based clustering with neural networks enhances anomaly detection accuracy [3]. This hybrid approach leverages both pattern recognition capabilities and statistical robustness.
These developments underscore how machine learning integrations make anomaly detection more precise while enabling real-time analysis—a vital feature given cryptocurrency markets' speed and unpredictability.
Key Factors Influencing Effective Use of DBSCAN
While powerful, deploying DBSCAN effectively requires attention to several factors:
Parameter Tuning: Selecting appropriate values for Eps and MinPts is critical; too small Eps may fragment genuine clusters into noise, while too large could merge distinct patterns incorrectly [4][5].
Handling Noisy Data: Financial datasets often contain significant noise due to random fluctuations; thus, understanding how well the algorithm manages false positives is essential [6].
Computational Efficiency: Although generally efficient with O(n log n) complexity [4], large-scale datasets demand optimized implementations for real-time applications.
Validation & Testing: Regular validation ensures that detected anomalies genuinely reflect abnormal conditions rather than false alarms caused by parameter misconfiguration [7].
Challenges & Considerations When Using Density-Based Clustering
Despite its strengths, practitioners should be aware of potential pitfalls:
False Positives: Incorrectly flagging normal market behavior as anomalous can lead to unnecessary trades or panic selling.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are inherently volatile; distinguishing between regular swings and true anomalies requires careful calibration.
Regulatory Implications: As anomaly detection influences trading decisions significantly—sometimes automatically—it’s vital these systems comply with relevant regulations concerning transparency and fairness [8][9].
Incorporating robust validation procedures alongside advanced algorithms like DBSCAN helps mitigate these issues while enhancing trustworthiness in automated analysis systems.
By leveraging density-based clustering techniques such as DBSCAN within cryptocurrency markets’ dynamic environment—and combining them with machine learning enhancements—traders gain a sophisticated method for detecting early signs of abnormal activity. Proper parameter tuning combined with ongoing validation ensures reliable performance amid high volatility levels typical of digital assets today.
References
- "Anomaly Detection in Bitcoin Price Movements Using DBSCAN" (2023) - Journal of Financial Data Science
- "Real-Time Anomaly Detection in Cryptocurrency Markets Using Dbscan" (2024) - International Journal of Financial Engineering
- "Enhancing Anomaly Detection in Cryptocurrency Markets with Dbscan and Neural Networks" (2024) - IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems
4."Time Complexity Analysis of Dbscan" (2019) - Journal Of Algorithms
5."Optimal Parameter Selection For Dbscan In Financial Data" (2022) - Journal Of Data Science
6."Noise Handling In Dbscan For Financial Data Analysis" (2021) - International Journal Of Data Mining And Bioinformatics
7."False Positive Reduction In Anomaly Detection Using Dbscan" (2023) - Journal Of Artificial Intelligence Research
8."Regulatory Compliance For Anomaly Detection Systems In Financial Markets" (2023) - Journal Of Financial Regulation


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 23:09
What is DBSCAN and how does it identify unusual market conditions?
What Is DBSCAN and How Does It Detect Unusual Market Conditions?
Understanding how financial markets, especially volatile ones like cryptocurrencies, can be monitored for anomalies is crucial for traders, analysts, and regulators alike. One powerful tool gaining traction in this space is DBSCAN—short for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise. This clustering algorithm helps identify unusual patterns or outliers in complex datasets by grouping similar data points together based on their density.
How Does DBSCAN Work?
At its core, DBSCAN analyzes data points—such as price movements or trading volumes—and groups them into clusters where points are densely packed. It operates based on two key parameters: Eps (epsilon), which defines the radius around a point to consider neighboring points, and MinPts (minimum points), the minimum number of neighboring points needed to form a cluster.
The process begins by selecting an unvisited data point. If this point has at least MinPts within its Eps-neighborhood, it becomes a core point and initiates a new cluster. The algorithm then expands this cluster by recursively including all neighboring core points and their neighbors that meet the density criteria. Points that do not belong to any cluster are labeled as noise or outliers—potential indicators of anomalies.
This approach makes DBSCAN particularly effective at handling noisy financial data because it naturally distinguishes between normal market fluctuations and genuine anomalies without requiring prior knowledge about the number of clusters.
Why Is Detecting Anomalies Important in Cryptocurrency Markets?
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility and rapid price swings. Identifying abnormal market conditions early can provide traders with critical insights into potential risks or opportunities. For example:
- Market Manipulation: Sudden spikes or drops might indicate pump-and-dump schemes.
- Systemic Risks: Unusual trading volumes could signal systemic issues or impending crashes.
- Fraud Detection: Outlier transactions may reveal fraudulent activities such as wash trading.
By applying algorithms like DBSCAN to historical price data, traders can detect these irregularities more effectively than traditional methods that might overlook subtle but significant deviations.
Recent Advances in Using DBSCAN for Market Analysis
Recent research highlights several innovative applications of DBSCAN within financial analytics:
Cryptocurrency Anomaly Detection: Studies have demonstrated how applying DBSCAN to Bitcoin's price movements helps identify unusual patterns preceding market downturns [1]. These insights enable better risk management strategies.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems: With advancements in computational power, integrating DBSCAN into live monitoring tools allows instant detection of anomalies as they occur [2]. Traders receive timely alerts that inform decision-making processes.
Combining Machine Learning Techniques: Combining density-based clustering with neural networks enhances anomaly detection accuracy [3]. This hybrid approach leverages both pattern recognition capabilities and statistical robustness.
These developments underscore how machine learning integrations make anomaly detection more precise while enabling real-time analysis—a vital feature given cryptocurrency markets' speed and unpredictability.
Key Factors Influencing Effective Use of DBSCAN
While powerful, deploying DBSCAN effectively requires attention to several factors:
Parameter Tuning: Selecting appropriate values for Eps and MinPts is critical; too small Eps may fragment genuine clusters into noise, while too large could merge distinct patterns incorrectly [4][5].
Handling Noisy Data: Financial datasets often contain significant noise due to random fluctuations; thus, understanding how well the algorithm manages false positives is essential [6].
Computational Efficiency: Although generally efficient with O(n log n) complexity [4], large-scale datasets demand optimized implementations for real-time applications.
Validation & Testing: Regular validation ensures that detected anomalies genuinely reflect abnormal conditions rather than false alarms caused by parameter misconfiguration [7].
Challenges & Considerations When Using Density-Based Clustering
Despite its strengths, practitioners should be aware of potential pitfalls:
False Positives: Incorrectly flagging normal market behavior as anomalous can lead to unnecessary trades or panic selling.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are inherently volatile; distinguishing between regular swings and true anomalies requires careful calibration.
Regulatory Implications: As anomaly detection influences trading decisions significantly—sometimes automatically—it’s vital these systems comply with relevant regulations concerning transparency and fairness [8][9].
Incorporating robust validation procedures alongside advanced algorithms like DBSCAN helps mitigate these issues while enhancing trustworthiness in automated analysis systems.
By leveraging density-based clustering techniques such as DBSCAN within cryptocurrency markets’ dynamic environment—and combining them with machine learning enhancements—traders gain a sophisticated method for detecting early signs of abnormal activity. Proper parameter tuning combined with ongoing validation ensures reliable performance amid high volatility levels typical of digital assets today.
References
- "Anomaly Detection in Bitcoin Price Movements Using DBSCAN" (2023) - Journal of Financial Data Science
- "Real-Time Anomaly Detection in Cryptocurrency Markets Using Dbscan" (2024) - International Journal of Financial Engineering
- "Enhancing Anomaly Detection in Cryptocurrency Markets with Dbscan and Neural Networks" (2024) - IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems
4."Time Complexity Analysis of Dbscan" (2019) - Journal Of Algorithms
5."Optimal Parameter Selection For Dbscan In Financial Data" (2022) - Journal Of Data Science
6."Noise Handling In Dbscan For Financial Data Analysis" (2021) - International Journal Of Data Mining And Bioinformatics
7."False Positive Reduction In Anomaly Detection Using Dbscan" (2023) - Journal Of Artificial Intelligence Research
8."Regulatory Compliance For Anomaly Detection Systems In Financial Markets" (2023) - Journal Of Financial Regulation
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
The Golden Rule for Investing in Cryptocurrency: How Much Money Should You Allocate?
Understanding the appropriate amount of money to invest in cryptocurrency is crucial for managing risk and building a resilient investment portfolio. The "golden rule" offers a practical guideline that helps investors navigate this volatile market while maintaining financial stability.
What Is the Golden Rule for Cryptocurrency Investment?
The golden rule suggests that investors should allocate only a small percentage of their total investment portfolio to cryptocurrencies. Typically, financial advisors recommend no more than 5-10%. This approach aims to balance potential gains from the high-growth opportunities in digital assets with the inherent risks associated with their volatility and regulatory uncertainties.
Why Limit Your Cryptocurrency Exposure?
Cryptocurrencies are known for their rapid price swings, which can lead to significant gains or devastating losses within short periods. By limiting exposure, investors can participate in potential upside without jeopardizing their overall financial health. For example, if Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies experience a sharp decline, having only a small portion of your portfolio invested ensures that your core finances remain protected.
Diversification as a Risk Management Strategy
Diversification remains one of the most effective strategies for reducing investment risk. The golden rule emphasizes spreading investments across various asset classes—stocks, bonds, real estate—and including cryptocurrencies at a modest level. This diversification helps cushion against market downturns specific to any single asset class and enhances long-term stability.
Recent Market Trends Supporting Limited Investment
In recent months, notable developments have fueled interest in cryptocurrencies:
Bitcoin Price Surge: Bitcoin has experienced significant upward momentum recently, with forecasts suggesting it could reach $200,000 or higher by 2025[1]. While promising growth prospects exist, such surges also attract speculative behavior.
ETF Inflows: The introduction of Bitcoin and gold ETFs has attracted substantial investor inflows[2][3], indicating increased institutional interest but also highlighting market volatility driven by speculation.
These trends underscore why cautious allocation—adhering to the golden rule—is essential; it allows investors to benefit from growth opportunities without exposing themselves excessively during volatile periods.
Financial Advice on Cryptocurrency Allocation
Most financial experts agree on setting clear boundaries when investing in digital assets:
Maximum Allocation: Generally recommended not to exceed 10% of your total investment portfolio.
Personal Financial Goals: Investors should assess their individual goals and risk tolerance before committing funds. For instance:
- Young investors with high-risk appetite might consider slightly higher allocations.
- Those nearing retirement should prioritize stability over aggressive growth.
Additionally, ensuring sufficient liquidity and emergency funds is vital before venturing into high-volatility markets like crypto.
Risks Associated With Overexposure
Investing more than recommended can expose you to severe consequences:
Market Volatility: Sudden price drops can wipe out large portions of an over-concentrated crypto holding.
Regulatory Changes: Lack of clear regulations means sudden policy shifts could impact prices dramatically.
Speculative Bubbles: Rapid surges driven by hype may lead to bubbles that burst unexpectedly.
Sticking within advised limits helps mitigate these risks while still allowing participation in potential upside scenarios.
Recent Developments Impacting Crypto Investments
The ongoing inflow into gold and Bitcoin ETFs reflects broader investor confidence but also signals heightened market speculation[2][3]. Investor sentiment remains positive due to factors like lower interest rates and increasing adoption; however, rapid shifts are possible if regulatory environments change or macroeconomic conditions deteriorate. Staying within prudent allocation limits ensures you’re prepared regardless of these fluctuations.
How To Apply the Golden Rule Effectively
To implement this guideline effectively:
- Assess your total investment portfolio value.
- Decide on an appropriate percentage (commonly between 5%–10%) based on your risk tolerance.
- Choose reputable exchanges or platforms for purchasing cryptocurrencies.
- Diversify within your crypto holdings—consider different coins rather than concentrating solely on Bitcoin or Ethereum.
- Regularly review your investments relative to market changes and personal circumstances.
By following these steps alongside sound financial advice—and keeping allocations modest—you position yourself better for long-term success while avoiding unnecessary exposure during turbulent times.
Balancing Growth Potential With Financial Security
While recent developments suggest promising growth prospects—such as Bitcoin’s forecasted surge—the importance lies in balancing opportunity with caution. Allocating too much capital exposes you not only to potential losses but also undermines overall financial security if markets turn unfavorable overnight.
Building Trust Through Knowledge & Caution
Investors aiming at sustainable wealth accumulation must prioritize education about cryptocurrency markets’ dynamics—including understanding volatility patterns and regulatory landscapes—to make informed decisions aligned with best practices like adhering strictly to the golden rule.
Staying Updated With Market Trends & Regulatory Changes
Given how rapidly digital asset markets evolve—with new ETFs launching or regulations shifting—it’s essential always stay informed through reputable sources such as industry reports or expert analyses[1][2][3]. This ongoing awareness supports disciplined investing aligned with sound principles rather than impulsive reactions.
Summary
Investing responsibly in cryptocurrency involves understanding how much exposure aligns with your overall financial plan—a principle encapsulated by what’s commonly called "the golden rule." Limiting investments typically between 5%–10%, diversifying holdings wisely, assessing personal risk tolerance carefully—all contribute toward harnessing crypto's growth potential without compromising long-term stability.
References[1] Perplexity AI. Bitcoin Price Nears $95,000 Amid ETF Inflows and Volatility. 2025-04-27.
[2] Perplexity AI.. Perplexity Finance.. 2025-05-22.
[3] Perplexity AI.. JPMorgan International Research Enhanced Equity ETF.. 2025-05-16.


Lo
2025-05-22 19:02
What is the golden rule about how much money to invest in cryptocurrency?
The Golden Rule for Investing in Cryptocurrency: How Much Money Should You Allocate?
Understanding the appropriate amount of money to invest in cryptocurrency is crucial for managing risk and building a resilient investment portfolio. The "golden rule" offers a practical guideline that helps investors navigate this volatile market while maintaining financial stability.
What Is the Golden Rule for Cryptocurrency Investment?
The golden rule suggests that investors should allocate only a small percentage of their total investment portfolio to cryptocurrencies. Typically, financial advisors recommend no more than 5-10%. This approach aims to balance potential gains from the high-growth opportunities in digital assets with the inherent risks associated with their volatility and regulatory uncertainties.
Why Limit Your Cryptocurrency Exposure?
Cryptocurrencies are known for their rapid price swings, which can lead to significant gains or devastating losses within short periods. By limiting exposure, investors can participate in potential upside without jeopardizing their overall financial health. For example, if Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies experience a sharp decline, having only a small portion of your portfolio invested ensures that your core finances remain protected.
Diversification as a Risk Management Strategy
Diversification remains one of the most effective strategies for reducing investment risk. The golden rule emphasizes spreading investments across various asset classes—stocks, bonds, real estate—and including cryptocurrencies at a modest level. This diversification helps cushion against market downturns specific to any single asset class and enhances long-term stability.
Recent Market Trends Supporting Limited Investment
In recent months, notable developments have fueled interest in cryptocurrencies:
Bitcoin Price Surge: Bitcoin has experienced significant upward momentum recently, with forecasts suggesting it could reach $200,000 or higher by 2025[1]. While promising growth prospects exist, such surges also attract speculative behavior.
ETF Inflows: The introduction of Bitcoin and gold ETFs has attracted substantial investor inflows[2][3], indicating increased institutional interest but also highlighting market volatility driven by speculation.
These trends underscore why cautious allocation—adhering to the golden rule—is essential; it allows investors to benefit from growth opportunities without exposing themselves excessively during volatile periods.
Financial Advice on Cryptocurrency Allocation
Most financial experts agree on setting clear boundaries when investing in digital assets:
Maximum Allocation: Generally recommended not to exceed 10% of your total investment portfolio.
Personal Financial Goals: Investors should assess their individual goals and risk tolerance before committing funds. For instance:
- Young investors with high-risk appetite might consider slightly higher allocations.
- Those nearing retirement should prioritize stability over aggressive growth.
Additionally, ensuring sufficient liquidity and emergency funds is vital before venturing into high-volatility markets like crypto.
Risks Associated With Overexposure
Investing more than recommended can expose you to severe consequences:
Market Volatility: Sudden price drops can wipe out large portions of an over-concentrated crypto holding.
Regulatory Changes: Lack of clear regulations means sudden policy shifts could impact prices dramatically.
Speculative Bubbles: Rapid surges driven by hype may lead to bubbles that burst unexpectedly.
Sticking within advised limits helps mitigate these risks while still allowing participation in potential upside scenarios.
Recent Developments Impacting Crypto Investments
The ongoing inflow into gold and Bitcoin ETFs reflects broader investor confidence but also signals heightened market speculation[2][3]. Investor sentiment remains positive due to factors like lower interest rates and increasing adoption; however, rapid shifts are possible if regulatory environments change or macroeconomic conditions deteriorate. Staying within prudent allocation limits ensures you’re prepared regardless of these fluctuations.
How To Apply the Golden Rule Effectively
To implement this guideline effectively:
- Assess your total investment portfolio value.
- Decide on an appropriate percentage (commonly between 5%–10%) based on your risk tolerance.
- Choose reputable exchanges or platforms for purchasing cryptocurrencies.
- Diversify within your crypto holdings—consider different coins rather than concentrating solely on Bitcoin or Ethereum.
- Regularly review your investments relative to market changes and personal circumstances.
By following these steps alongside sound financial advice—and keeping allocations modest—you position yourself better for long-term success while avoiding unnecessary exposure during turbulent times.
Balancing Growth Potential With Financial Security
While recent developments suggest promising growth prospects—such as Bitcoin’s forecasted surge—the importance lies in balancing opportunity with caution. Allocating too much capital exposes you not only to potential losses but also undermines overall financial security if markets turn unfavorable overnight.
Building Trust Through Knowledge & Caution
Investors aiming at sustainable wealth accumulation must prioritize education about cryptocurrency markets’ dynamics—including understanding volatility patterns and regulatory landscapes—to make informed decisions aligned with best practices like adhering strictly to the golden rule.
Staying Updated With Market Trends & Regulatory Changes
Given how rapidly digital asset markets evolve—with new ETFs launching or regulations shifting—it’s essential always stay informed through reputable sources such as industry reports or expert analyses[1][2][3]. This ongoing awareness supports disciplined investing aligned with sound principles rather than impulsive reactions.
Summary
Investing responsibly in cryptocurrency involves understanding how much exposure aligns with your overall financial plan—a principle encapsulated by what’s commonly called "the golden rule." Limiting investments typically between 5%–10%, diversifying holdings wisely, assessing personal risk tolerance carefully—all contribute toward harnessing crypto's growth potential without compromising long-term stability.
References[1] Perplexity AI. Bitcoin Price Nears $95,000 Amid ETF Inflows and Volatility. 2025-04-27.
[2] Perplexity AI.. Perplexity Finance.. 2025-05-22.
[3] Perplexity AI.. JPMorgan International Research Enhanced Equity ETF.. 2025-05-16.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Digital platform fanC partners with fintech company Initech to launch Korea's groundbreaking 1:1 won-pegged stablecoin. Currently in test phase for internal members and partners, KRWIN aims to revolutionize Korean digital payments and cross-border transactions.
💰 Core Architecture:
-
Multi-signature custody with equivalent won reserves off-chain
Smart contracts on Ethereum and BNB Chain
1:1 peg maintained through multi-party signature confirmation
Third-party audited security with on-chain audit report hashes
🔒 Security & Compliance Features:
-
Strict KYC/AML verification process
Real-time monitoring with suspicious activity alerts
Account freeze capabilities for anomalous transactions
Trademark filed with Korean Intellectual Property Office
🎯 Current Use Cases in Testing:
-
Payment Settlement: Real-time e-commerce and offline merchant payments
Cross-Border Remittance: Low-cost international transfers for Korean businesses
Tourism Spending: Direct payments at Korean merchants and travel platforms
Content & Entertainment: Virtual gifts and premium content purchases on fanC
⚡ Test Phase Highlights:
-
Internal employees and designated partners only
Multi-chain compatibility testing (Ethereum + BNB Chain)
Scenario-linked testing across payment contexts
48-hour response commitment for user feedback
📈 2025 Roadmap:
-
Q4 2025: Public beta launch and exchange listings (KLAYswap, Bithumb, Upbit)
Ecosystem partnerships with financial institutions and e-commerce platforms
Layer-2 integration for reduced costs and higher TPS
Regulatory sandbox participation for compliance validation
🚀 Future Vision:
-
SME payments and supply-chain finance integration
Community governance module for token holder voting
Expansion to other East Asian markets
Dynamic interest rates and automatic clearing functions
💡 Market Position: As Korea's first won-pegged stablecoin, KRWIN combines traditional finance with Web3 technology, offering first-mover advantage in localized payments and regulatory compliance. This positions it to capture significant market share in the regional stablecoin ecosystem.
The bridge between Korean won and crypto is here - KRWIN is paving the way for mainstream adoption of digital currency in South Korea!
Read the full technical breakdown: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/krwin-korean-stablecoin/
#KRWIN #KoreanStablecoin #Stablecoin #KRW



JU Blog
2025-08-06 10:51
KRWIN: Korea's First Won-Pegged Stablecoin Goes Live!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Opening Range Defines Intraday Support and Resistance Levels
Understanding how to identify support and resistance levels is fundamental for successful intraday trading. One of the most effective tools traders use for this purpose is the opening range (OR). By analyzing the initial price action during the first few minutes of trading, traders can gain valuable insights into potential market direction and key levels that may influence future price movements. This article explores how opening range helps define intraday support and resistance, backed by recent developments and practical strategies.
What Is Opening Range in Intraday Trading?
The opening range refers to the high and low prices established during a specific initial period after a security's market opens—typically within the first 30 to 60 minutes of trading. During this window, traders observe how prices fluctuate before committing to larger positions. The highest price reached during this period marks one boundary, while the lowest sets another. These two points create a "range" that serves as a benchmark for subsequent trading activity.
This initial phase captures early market sentiment—whether buyers or sellers dominate—and provides clues about potential trends or consolidations throughout the day. Because markets often react strongly at open due to overnight news or economic releases, analyzing this early data offers an edge in predicting intraday support and resistance levels.
How Does Opening Range Help Identify Support & Resistance?
Support and resistance are critical concepts in technical analysis—they represent price levels where buying or selling pressure tends to halt or reverse trends. The opening range plays a pivotal role here because it establishes immediate reference points based on real-time market behavior.
- Support Level: If prices decline toward the lower boundary of the opening range but fail to break below it, that level may act as support—a floor preventing further declines.
- Resistance Level: Conversely, if prices rise toward the upper boundary but struggle to surpass it, that level can serve as resistance—a ceiling limiting upward movement.
When prices break above or below these boundaries with significant volume, it often signals a shift in momentum—either confirming continuation beyond these levels or indicating reversal opportunities.
For example:
- A breakout above the opening high suggests bullish strength; traders might see this as an entry point for long positions.
- A breakdown below the opening low could signal bearish sentiment; traders might consider shorting or exiting longs.
By monitoring whether prices respect these boundaries within their respective ranges—or break through them—traders can make more informed decisions about entry and exit points during active hours.
Practical Strategies Using Opening Range
Traders employ various strategies centered around opening range analysis:
Range Trading:
- Buy near support (opening low)
- Sell near resistance (opening high)
- Use tight stop-loss orders just outside these boundaries
Breakout Trading:
- Enter trades when price breaks above resistance or below support with increased volume
- Confirm breakout validity with other indicators like RSI or moving averages
Fade Strategy:
- Trade against false breakouts by betting on reversals when price quickly re-enters previous ranges
Adjusting Stops & Targets:
- Use openings' high/low as dynamic stop-loss points
- Set profit targets based on measured distance between open-range boundaries
These approaches help manage risk effectively while capitalizing on predictable intraday patterns derived from early market activity.
Recent Advances Enhancing Opening Range Analysis
Technological progress has significantly improved how traders utilize opening ranges:
- Modern trading platforms provide real-time data feeds enabling precise calculation of initial highs/lows.
- Algorithmic tools now automatically identify key breakout moments based on predefined criteria.
- Integration with other technical indicators such as Bollinger Bands, RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), enhances confirmation signals.
- Increased adoption in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies demonstrates its versatility; crypto's rapid moves make early-range analysis particularly valuable for quick decision-making.
Furthermore, machine learning models are being developed to analyze historical patterns related to open-range behavior across different assets—adding predictive power beyond traditional methods.
Risks & Limitations of Relying Solely on Opening Range
While powerful, relying exclusively on opening range analysis carries risks:
- Overdependence may lead traders astray if unexpected news causes sudden volatility outside established ranges.
- Market manipulation tactics such as "spoofing" can artificially influence perceived support/resistance levels at open.
- False breakouts are common; not all breaches result in sustained moves—requiring confirmation from additional indicators.
Therefore, it's crucial always to combine OR-based insights with broader technical frameworks—including trend analysis and volume studies—to improve accuracy while managing risk effectively.
Applying Support & Resistance Levels Derived from Opening Range
In practice:
- Observe initial trade activity closely during first hour after market opens.
- Mark highest (resistance) and lowest (support) points reached within this period.
- Watch for signs of breakout beyond these bounds — confirmed by increased volume — which could signal strong directional moves.
- Use these levels dynamically throughout your trading session—for setting stops/limits—and adapt quickly if new information emerges.
Final Thoughts: Enhancing Intraday Strategies With Opening Range Insights
The ability of closing-in-time data from an asset’s first few minutes offers invaluable guidance for defining intraday support/resistance zones through its establishing of key thresholds reflective of current market sentiment—not just historical averages but real-time reactions at open sessions enable more responsive decision-making processes than static chart patterns alone would permit.
By integrating modern technological tools alongside traditional technical principles—including careful validation via multiple indicators—you elevate your capacity not only to recognize potential turning points but also craft disciplined strategies aligned with evolving conditions—all essential elements underpinning sustainable success in active day-trading environments.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 04:46
How can opening range define intraday support/resistance levels?
How Opening Range Defines Intraday Support and Resistance Levels
Understanding how to identify support and resistance levels is fundamental for successful intraday trading. One of the most effective tools traders use for this purpose is the opening range (OR). By analyzing the initial price action during the first few minutes of trading, traders can gain valuable insights into potential market direction and key levels that may influence future price movements. This article explores how opening range helps define intraday support and resistance, backed by recent developments and practical strategies.
What Is Opening Range in Intraday Trading?
The opening range refers to the high and low prices established during a specific initial period after a security's market opens—typically within the first 30 to 60 minutes of trading. During this window, traders observe how prices fluctuate before committing to larger positions. The highest price reached during this period marks one boundary, while the lowest sets another. These two points create a "range" that serves as a benchmark for subsequent trading activity.
This initial phase captures early market sentiment—whether buyers or sellers dominate—and provides clues about potential trends or consolidations throughout the day. Because markets often react strongly at open due to overnight news or economic releases, analyzing this early data offers an edge in predicting intraday support and resistance levels.
How Does Opening Range Help Identify Support & Resistance?
Support and resistance are critical concepts in technical analysis—they represent price levels where buying or selling pressure tends to halt or reverse trends. The opening range plays a pivotal role here because it establishes immediate reference points based on real-time market behavior.
- Support Level: If prices decline toward the lower boundary of the opening range but fail to break below it, that level may act as support—a floor preventing further declines.
- Resistance Level: Conversely, if prices rise toward the upper boundary but struggle to surpass it, that level can serve as resistance—a ceiling limiting upward movement.
When prices break above or below these boundaries with significant volume, it often signals a shift in momentum—either confirming continuation beyond these levels or indicating reversal opportunities.
For example:
- A breakout above the opening high suggests bullish strength; traders might see this as an entry point for long positions.
- A breakdown below the opening low could signal bearish sentiment; traders might consider shorting or exiting longs.
By monitoring whether prices respect these boundaries within their respective ranges—or break through them—traders can make more informed decisions about entry and exit points during active hours.
Practical Strategies Using Opening Range
Traders employ various strategies centered around opening range analysis:
Range Trading:
- Buy near support (opening low)
- Sell near resistance (opening high)
- Use tight stop-loss orders just outside these boundaries
Breakout Trading:
- Enter trades when price breaks above resistance or below support with increased volume
- Confirm breakout validity with other indicators like RSI or moving averages
Fade Strategy:
- Trade against false breakouts by betting on reversals when price quickly re-enters previous ranges
Adjusting Stops & Targets:
- Use openings' high/low as dynamic stop-loss points
- Set profit targets based on measured distance between open-range boundaries
These approaches help manage risk effectively while capitalizing on predictable intraday patterns derived from early market activity.
Recent Advances Enhancing Opening Range Analysis
Technological progress has significantly improved how traders utilize opening ranges:
- Modern trading platforms provide real-time data feeds enabling precise calculation of initial highs/lows.
- Algorithmic tools now automatically identify key breakout moments based on predefined criteria.
- Integration with other technical indicators such as Bollinger Bands, RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), enhances confirmation signals.
- Increased adoption in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies demonstrates its versatility; crypto's rapid moves make early-range analysis particularly valuable for quick decision-making.
Furthermore, machine learning models are being developed to analyze historical patterns related to open-range behavior across different assets—adding predictive power beyond traditional methods.
Risks & Limitations of Relying Solely on Opening Range
While powerful, relying exclusively on opening range analysis carries risks:
- Overdependence may lead traders astray if unexpected news causes sudden volatility outside established ranges.
- Market manipulation tactics such as "spoofing" can artificially influence perceived support/resistance levels at open.
- False breakouts are common; not all breaches result in sustained moves—requiring confirmation from additional indicators.
Therefore, it's crucial always to combine OR-based insights with broader technical frameworks—including trend analysis and volume studies—to improve accuracy while managing risk effectively.
Applying Support & Resistance Levels Derived from Opening Range
In practice:
- Observe initial trade activity closely during first hour after market opens.
- Mark highest (resistance) and lowest (support) points reached within this period.
- Watch for signs of breakout beyond these bounds — confirmed by increased volume — which could signal strong directional moves.
- Use these levels dynamically throughout your trading session—for setting stops/limits—and adapt quickly if new information emerges.
Final Thoughts: Enhancing Intraday Strategies With Opening Range Insights
The ability of closing-in-time data from an asset’s first few minutes offers invaluable guidance for defining intraday support/resistance zones through its establishing of key thresholds reflective of current market sentiment—not just historical averages but real-time reactions at open sessions enable more responsive decision-making processes than static chart patterns alone would permit.
By integrating modern technological tools alongside traditional technical principles—including careful validation via multiple indicators—you elevate your capacity not only to recognize potential turning points but also craft disciplined strategies aligned with evolving conditions—all essential elements underpinning sustainable success in active day-trading environments.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
