She thinks I’m thinking about other girls… but it’s the BTC bullrun. 📈 I’ve got one shot to retire my entire bloodline - emotionally unavailable until new all-time highs. BTC is king 👑
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#BullRun #CryptoMeme #CryptoSkits #CryptoComedy


JuCoin Media
2025-08-06 11:29
🐂 BTC Bullrun – This Is Bigger Than Me, Babe
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Asseto is committed to building a compliant bridge that brings traditional financial assets into the decentralized world. Through smart contracts and multi-stage approval processes, it achieves high security and liquidity, supporting tokenization of stocks, bonds, and other traditional assets. Here are the platform's core highlights:
💰 Three-Layer Architecture:
-
Off-Chain Compliance Layer: KYC/AML verification, fiat settlement, multi-sig custody for asset security
On-Chain Smart Contract Layer: Token issuance/transfer, oracle real-time pricing
Cross-Chain Bridging Layer: Support for Ethereum, BSC, and other multi-chain asset free flow
Modular Governance: Token holders vote to adjust compliance parameters and fee structures
🎯 Privacy & Security Guarantees: 1️⃣ Trusted Execution Environment (TEE): Encrypted user data storage, dedicated audit nodes 2️⃣ Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP): Verify KYC results without exposing sensitive information on-chain 3️⃣ Multi-Signature Timelock: Cross-chain asset transfers remain fully controlled 4️⃣ Third-Party Security Audits: Regular smart contract audits and penetration testing
🏆 Asset Tokenization Process:
-
Asset Custody: Regulated custodians safeguard traditional assets
Contract Minting: On-chain mint transactions generate 1:1 pegged tokens (aStock, aBond)
Cross-Chain Distribution: Bridge tokens to target networks via cross-chain bridge
Redemption & Settlement: Users burn tokens to request redemption, off-chain releases corresponding assets
💡 $ASO Token Economics (100M Total Supply):
-
Rewards & Bribes 60%: Liquidity mining, governance proposal rewards, and "bribe" mechanisms
Public Sale (LBP) 12%: Public offering, initial liquidity foundation
Core Team 11.6%: 3-month lockup, 2-year linear vesting
Protocol Growth 10%: Ecosystem incubation, partner incentives, R&D grants
Community Incentives 4%: Early user airdrops, community activity rewards
Initial Liquidity 2.4%: Trading pair depth support
🔐 Incentive Mechanisms:
-
Staking Yield: Participate in network security verification, earn base APY
Revenue Distribution: Protocol revenues buy back ASO and distribute to stakers
Liquidity Mining: Provide liquidity in designated trading pairs for additional rewards
Governance Voting: Participate in protocol governance, "bribe" mechanism increases voting power
🌟 Dual Yield Model:
-
DeFi Yield: Participate in protocol interest sharing and liquidity mining
Traditional Yield: Connect to traditional asset dividends and coupon payments
Principal Protection: Compliance fund and multi-sig custody emergency compensation mechanism
Community Governance: ASO holders decide asset types, fee adjustments
📱 Supported Asset Types:
-
Current: Stocks, corporate bonds, government bonds, money-market instruments
Planned: Fund shares, commodities expansion
🔮 Participation Process: Complete KYC/AML verification → Deposit funds to compliant custodian account → Mint asset tokens on-chain → DeFi ecosystem applications
⚡ Redemption Service:
-
Standard Redemption: 3-5 business days
Expedited Redemption: 1-2 business days (additional fees)
🛡️ Risk Prevention:
-
Multi-entity custody for risk distribution
Regular audits for transparent operations
Off-chain redundancy backup
Compliance fund emergency mechanisms
Asseto enables traditional financial assets to seamlessly access DeFi ecosystems through innovative compliance architecture, providing investors with "fiat + crypto" composite yields while maintaining regulatory compliance, potentially accelerating traditional asset digitization.
Read the complete compliance mechanism analysis: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/asseto-defi-compliance/?utm_source=blog
#Asseto #ASO #CrossChain #KYC



JU Blog
2025-08-05 10:34
🏦 Asseto: Compliant Bridge Between Traditional Assets and DeFi Revolution!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Layer-2 Scaling Solutions?
Layer-2 scaling solutions are innovative technologies designed to improve the capacity and efficiency of blockchain networks, especially Ethereum. As blockchain technology has gained widespread adoption, the limitations of its underlying architecture have become more apparent. These solutions operate on top of the main blockchain (Layer 1) to handle transactions off-chain or in a more scalable manner, thereby alleviating congestion and reducing transaction costs.
In essence, Layer-2 solutions aim to process many transactions outside the main chain while still maintaining security and decentralization. This approach allows users to enjoy faster transaction speeds and lower fees without compromising the integrity of the network. They are crucial for enabling mainstream adoption of decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, and other blockchain-based services that require high throughput.
Why Are Layer-2 Solutions Necessary for Blockchain Networks?
Blockchain networks like Ethereum face inherent scalability challenges due to their design. The core issue stems from how transactions are processed on Layer 1—every transaction must be validated by all nodes in the network before being added to a block. As user activity increases, this process causes network congestion, leading to slower processing times and higher gas fees.
High transaction costs can make using blockchain applications prohibitively expensive for everyday users or small-scale developers. For instance, during periods of high demand, gas fees on Ethereum can spike dramatically, making simple transfers or interactions with smart contracts costly.
Layer-2 solutions address these issues by shifting most transactional load off-chain or onto secondary layers that can process multiple transactions simultaneously before settling them back onto Layer 1 periodically. This not only reduces congestion but also enhances user experience by providing faster confirmation times and significantly lower costs—key factors for broader adoption.
Types of Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
There are several distinct approaches within layer-2 scaling strategies:
Off-Chain Transactions
State Channels
State channels enable participants to conduct numerous transactions privately without broadcasting each one individually on the main chain. Only opening and closing balances need on-chain validation; all intermediate steps occur off-chain within a secure channel established between parties.
Payment Channels
A subset focused specifically on transferring funds efficiently between two parties through an off-chain channel—examples include Lightning Network for Bitcoin or Raiden Network for Ethereum.
Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains linked securely with their parent chain via bridges or two-way pegs. They operate separately but periodically synchronize with the main chain through cryptographic proofs or validators’ consensus mechanisms. Sidechains allow developers flexibility in customizing features such as consensus algorithms while processing transactions independently from Ethereum’s mainnet.
Rollups
Rollups represent a promising class of layer-2 solutions that bundle multiple transactions into a single batch before submitting it back onto Layer 1:
- Optimistic Rollups: Assume transactions are valid unless challenged within a challenge period; they rely heavily on fraud proofs.
- ZK-Rollups (Zero-Knowledge Rollups): Use cryptographic proofs called zero-knowledge proofs to verify batches instantly without revealing individual transaction details—offering both scalability benefits and privacy enhancements.
Each type offers trade-offs regarding security guarantees, complexity, cost-efficiency, and privacy considerations—all vital factors influencing their suitability across different use cases.
Recent Developments in Layer-2 Technologies
The evolution of layer-2 solutions is closely tied with ongoing upgrades within Ethereum itself:
Transitioning to Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Ethereum's move from proof-of-work (PoW) towards proof-of-stake aims at reducing energy consumption while improving scalability through shard chains combined with rollup integrations—a significant step toward sustainable growth alongside layer-two innovations.
Adoption Trends
Major projects like Optimism and Arbitrum have successfully implemented optimistic rollup frameworks that enable fast finality at low costs while maintaining strong security models aligned with Ethereum’s standards. Polygon has also emerged as an alternative sidechain solution offering fast settlement times suitable for gaming dApps or microtransactions due to its high throughput capabilities.
Regulatory Environment Impact
As governments worldwide develop clearer regulations around cryptocurrencies—and potential compliance requirements—the development landscape may shift accordingly: fostering innovation where regulatory clarity exists but potentially hindering progress where restrictions tighten around certain types of decentralized activities involving cross-border payments or privacy-preserving features offered by some layer-two protocols.
Challenges Facing Layer-Two Scaling Solutions
Despite their advantages, deploying effective layer-two systems involves overcoming several hurdles:
- Security Risks: While designed carefully, some implementations might introduce vulnerabilities if not properly audited—for example: compromised bridges connecting sidechains could threaten overall ecosystem safety.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring seamless communication among various layer-two protocols remains complex; fragmented ecosystems could hinder user experience if interoperability isn’t prioritized.
- User Adoption Barriers: For widespread acceptance beyond crypto enthusiasts—and into mainstream markets—layer-two tools must demonstrate clear benefits such as ease-of-use alongside tangible cost savings; otherwise skeptics may hesitate transitioning from traditional methods.
The Future Outlook for Blockchain Scalability
Layer-2 scaling solutions will continue evolving rapidly as part of broader efforts toward achieving mass adoption in decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), gaming platforms—and beyond. Their success hinges not only on technological robustness but also regulatory support that fosters innovation while protecting consumers’ interests.
Emerging trends suggest increased integration between different types of second-layer protocols—for example: combining rollups with state channels—to optimize performance further across diverse application scenarios. Additionally, advancements in cryptography—including zero knowledge proofs—are likely to enhance privacy features alongside scalability improvements.
By addressing current limitations related to security risks and interoperability challenges through ongoing research & development efforts—and fostering clearer regulatory frameworks—the ecosystem can unlock new levels of efficiency necessary for mainstream acceptance.
This comprehensive overview underscores why layered scaling strategies are pivotal—not just technical upgrades but foundational enablers—to realize blockchain’s full potential at scale responsibly and securely.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 09:39
What are layer-2 scaling solutions, and why are they necessary?
What Are Layer-2 Scaling Solutions?
Layer-2 scaling solutions are innovative technologies designed to improve the capacity and efficiency of blockchain networks, especially Ethereum. As blockchain technology has gained widespread adoption, the limitations of its underlying architecture have become more apparent. These solutions operate on top of the main blockchain (Layer 1) to handle transactions off-chain or in a more scalable manner, thereby alleviating congestion and reducing transaction costs.
In essence, Layer-2 solutions aim to process many transactions outside the main chain while still maintaining security and decentralization. This approach allows users to enjoy faster transaction speeds and lower fees without compromising the integrity of the network. They are crucial for enabling mainstream adoption of decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, and other blockchain-based services that require high throughput.
Why Are Layer-2 Solutions Necessary for Blockchain Networks?
Blockchain networks like Ethereum face inherent scalability challenges due to their design. The core issue stems from how transactions are processed on Layer 1—every transaction must be validated by all nodes in the network before being added to a block. As user activity increases, this process causes network congestion, leading to slower processing times and higher gas fees.
High transaction costs can make using blockchain applications prohibitively expensive for everyday users or small-scale developers. For instance, during periods of high demand, gas fees on Ethereum can spike dramatically, making simple transfers or interactions with smart contracts costly.
Layer-2 solutions address these issues by shifting most transactional load off-chain or onto secondary layers that can process multiple transactions simultaneously before settling them back onto Layer 1 periodically. This not only reduces congestion but also enhances user experience by providing faster confirmation times and significantly lower costs—key factors for broader adoption.
Types of Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
There are several distinct approaches within layer-2 scaling strategies:
Off-Chain Transactions
State Channels
State channels enable participants to conduct numerous transactions privately without broadcasting each one individually on the main chain. Only opening and closing balances need on-chain validation; all intermediate steps occur off-chain within a secure channel established between parties.
Payment Channels
A subset focused specifically on transferring funds efficiently between two parties through an off-chain channel—examples include Lightning Network for Bitcoin or Raiden Network for Ethereum.
Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains linked securely with their parent chain via bridges or two-way pegs. They operate separately but periodically synchronize with the main chain through cryptographic proofs or validators’ consensus mechanisms. Sidechains allow developers flexibility in customizing features such as consensus algorithms while processing transactions independently from Ethereum’s mainnet.
Rollups
Rollups represent a promising class of layer-2 solutions that bundle multiple transactions into a single batch before submitting it back onto Layer 1:
- Optimistic Rollups: Assume transactions are valid unless challenged within a challenge period; they rely heavily on fraud proofs.
- ZK-Rollups (Zero-Knowledge Rollups): Use cryptographic proofs called zero-knowledge proofs to verify batches instantly without revealing individual transaction details—offering both scalability benefits and privacy enhancements.
Each type offers trade-offs regarding security guarantees, complexity, cost-efficiency, and privacy considerations—all vital factors influencing their suitability across different use cases.
Recent Developments in Layer-2 Technologies
The evolution of layer-2 solutions is closely tied with ongoing upgrades within Ethereum itself:
Transitioning to Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Ethereum's move from proof-of-work (PoW) towards proof-of-stake aims at reducing energy consumption while improving scalability through shard chains combined with rollup integrations—a significant step toward sustainable growth alongside layer-two innovations.
Adoption Trends
Major projects like Optimism and Arbitrum have successfully implemented optimistic rollup frameworks that enable fast finality at low costs while maintaining strong security models aligned with Ethereum’s standards. Polygon has also emerged as an alternative sidechain solution offering fast settlement times suitable for gaming dApps or microtransactions due to its high throughput capabilities.
Regulatory Environment Impact
As governments worldwide develop clearer regulations around cryptocurrencies—and potential compliance requirements—the development landscape may shift accordingly: fostering innovation where regulatory clarity exists but potentially hindering progress where restrictions tighten around certain types of decentralized activities involving cross-border payments or privacy-preserving features offered by some layer-two protocols.
Challenges Facing Layer-Two Scaling Solutions
Despite their advantages, deploying effective layer-two systems involves overcoming several hurdles:
- Security Risks: While designed carefully, some implementations might introduce vulnerabilities if not properly audited—for example: compromised bridges connecting sidechains could threaten overall ecosystem safety.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring seamless communication among various layer-two protocols remains complex; fragmented ecosystems could hinder user experience if interoperability isn’t prioritized.
- User Adoption Barriers: For widespread acceptance beyond crypto enthusiasts—and into mainstream markets—layer-two tools must demonstrate clear benefits such as ease-of-use alongside tangible cost savings; otherwise skeptics may hesitate transitioning from traditional methods.
The Future Outlook for Blockchain Scalability
Layer-2 scaling solutions will continue evolving rapidly as part of broader efforts toward achieving mass adoption in decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), gaming platforms—and beyond. Their success hinges not only on technological robustness but also regulatory support that fosters innovation while protecting consumers’ interests.
Emerging trends suggest increased integration between different types of second-layer protocols—for example: combining rollups with state channels—to optimize performance further across diverse application scenarios. Additionally, advancements in cryptography—including zero knowledge proofs—are likely to enhance privacy features alongside scalability improvements.
By addressing current limitations related to security risks and interoperability challenges through ongoing research & development efforts—and fostering clearer regulatory frameworks—the ecosystem can unlock new levels of efficiency necessary for mainstream acceptance.
This comprehensive overview underscores why layered scaling strategies are pivotal—not just technical upgrades but foundational enablers—to realize blockchain’s full potential at scale responsibly and securely.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is DBSCAN and How Does It Detect Unusual Market Conditions?
Understanding DBSCAN: A Key Clustering Algorithm in Financial Analysis
DBSCAN, which stands for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise, is a powerful clustering technique widely used in data analysis across various fields, including finance. Unlike traditional clustering algorithms that rely on distance metrics alone, DBSCAN emphasizes the density of data points to identify meaningful groups and outliers. This makes it particularly effective for detecting anomalies or unusual patterns within complex financial datasets.
In the context of market conditions, DBSCAN helps analysts uncover hidden structures by grouping similar assets or price movements based on their density. When applied correctly, it can reveal sudden shifts—such as abrupt price spikes or drops—that may signal underlying risks or emerging trends. Its ability to distinguish between typical market behavior and anomalies makes it an invaluable tool for traders, risk managers, and financial researchers aiming to stay ahead of market volatility.
How Does DBSCAN Work? Core Concepts Explained
The core strength of DBSCAN lies in its approach to clustering through density estimation. The algorithm requires two main parameters: epsilon (Eps) and MinPts.
- Epsilon (Eps): Defines the maximum radius within which points are considered neighbors. Essentially, if two points are within this distance from each other, they are potential members of the same cluster.
- MinPts: Specifies the minimum number of neighboring points needed to form a dense region that qualifies as a cluster.
The process begins by selecting an unvisited point in the dataset. If this point has at least MinPts neighbors within Eps distance—meaning it's part of a dense region—it becomes a core point around which a cluster forms. The algorithm then recursively searches for all neighboring points connected through these dense regions until no new members can be added.
Points that do not meet these criteria—either because they lack enough neighbors or are isolated—are classified as noise or outliers. These noise points often represent unusual events such as sudden market shocks or irregular trading activity when analyzing financial data.
Applying DBSCAN to Market Data: Practical Use Cases
In financial markets, applying DBSCAN offers several practical advantages:
Detecting Market Anomalies: Sudden price swings often manifest as noise points outside established clusters. Identifying these outliers promptly allows traders and risk managers to respond quickly before minor fluctuations escalate into significant losses.
Pattern Recognition: By grouping similar stocks based on performance metrics like volatility or returns over time, investors can identify sectors exhibiting correlated behaviors—helpful for diversification strategies.
Risk Management: Outlier detection helps assess potential vulnerabilities within portfolios by highlighting assets behaving abnormally compared to their peers—a crucial aspect during volatile periods like economic downturns or geopolitical crises.
Real-Time Monitoring: Advances in computational power enable real-time implementation of DBSCAN algorithms on streaming data feeds from stock exchanges and cryptocurrency markets; this facilitates immediate identification of abnormal trading patterns requiring swift action.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Market Analysis with DBSCAN
Over recent years, integration with machine learning techniques has significantly expanded what’s possible with DBSCAN:
- Combining neural networks with density-based clustering improves pattern recognition accuracy amid noisy datasets typical in high-frequency trading environments.
- Implementing online versions allows continuous updating without reprocessing entire datasets—a necessity given rapid market changes.
- In cryptocurrency markets especially—the high volatility combined with complex trading behaviors makes anomaly detection critical; here too, adaptations of DBSCAN help identify manipulative activities like pump-and-dump schemes before they cause widespread impact.
Challenges & Limitations When Using DBSCAN
Despite its strengths, deploying DBSCAN effectively requires careful consideration:
False Positives: Sometimes normal variations get misclassified as anomalies due to inappropriate parameter settings (Eps/MinPts), leading traders astray.
Data Quality Dependency: Poorly cleaned data—with missing values or errors—can distort clustering results significantly; hence preprocessing is vital before application.
Parameter Sensitivity: Choosing optimal Eps and MinPts values isn’t straightforward; improper tuning may result in either over-clustering (merging distinct patterns) or under-clustering (missing relevant groupings).
Furthermore, regulatory considerations demand transparency when deploying such algorithms in finance; explainability remains essential for compliance purposes while maintaining trust among stakeholders.
Key Facts About DBSCAN's Role in Financial Markets
Some quick facts highlight its importance:
- Developed by Martin Ester et al., 1996 — marking its inception over two decades ago but still highly relevant today
- Focuses on density rather than mere proximity
- Parameters Eps and MinPts critically influence outcomes
- Effective at isolating noise/outliers indicative of abnormal market activity
Historical Timeline & Future Outlook
Since its introduction in 1996 by Ester et al., research has progressively adapted DBSAN for more sophisticated applications:
- Early 2010s:* Gained popularity among quantitative analysts seeking robust anomaly detection tools
- Recent years:* Integration into machine learning frameworks enhanced predictive capabilities
- Present:* Real-time analytics powered by cloud computing enables instant response mechanisms during volatile periods
Looking ahead , ongoing developments aim at improving parameter selection automation through meta-learning techniques while expanding applicability across diverse asset classes—from equities to cryptocurrencies—and integrating explainability features aligned with regulatory standards.
Leveraging Knowledge Effectively
For investors seeking deeper insights into how unusual market conditions develop—and how best to respond—understanding tools like DBSAN is crucial . By recognizing patterns hidden beneath raw numerical data , professionals can better anticipate risks , optimize portfolio resilience , and adapt swiftly amidst unpredictable economic landscapes . As technology continues evolving rapidly , staying informed about advances such as real-time anomaly detection will remain central to successful financial analysis.
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping users—from novice analysts exploring advanced methods—to seasoned professionals refining their risk management strategies—with clear explanations rooted firmly in current research trends surrounding DBSAN’s role within modern finance systems


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-14 17:40
What is DBSCAN and how does it identify unusual market conditions?
What Is DBSCAN and How Does It Detect Unusual Market Conditions?
Understanding DBSCAN: A Key Clustering Algorithm in Financial Analysis
DBSCAN, which stands for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise, is a powerful clustering technique widely used in data analysis across various fields, including finance. Unlike traditional clustering algorithms that rely on distance metrics alone, DBSCAN emphasizes the density of data points to identify meaningful groups and outliers. This makes it particularly effective for detecting anomalies or unusual patterns within complex financial datasets.
In the context of market conditions, DBSCAN helps analysts uncover hidden structures by grouping similar assets or price movements based on their density. When applied correctly, it can reveal sudden shifts—such as abrupt price spikes or drops—that may signal underlying risks or emerging trends. Its ability to distinguish between typical market behavior and anomalies makes it an invaluable tool for traders, risk managers, and financial researchers aiming to stay ahead of market volatility.
How Does DBSCAN Work? Core Concepts Explained
The core strength of DBSCAN lies in its approach to clustering through density estimation. The algorithm requires two main parameters: epsilon (Eps) and MinPts.
- Epsilon (Eps): Defines the maximum radius within which points are considered neighbors. Essentially, if two points are within this distance from each other, they are potential members of the same cluster.
- MinPts: Specifies the minimum number of neighboring points needed to form a dense region that qualifies as a cluster.
The process begins by selecting an unvisited point in the dataset. If this point has at least MinPts neighbors within Eps distance—meaning it's part of a dense region—it becomes a core point around which a cluster forms. The algorithm then recursively searches for all neighboring points connected through these dense regions until no new members can be added.
Points that do not meet these criteria—either because they lack enough neighbors or are isolated—are classified as noise or outliers. These noise points often represent unusual events such as sudden market shocks or irregular trading activity when analyzing financial data.
Applying DBSCAN to Market Data: Practical Use Cases
In financial markets, applying DBSCAN offers several practical advantages:
Detecting Market Anomalies: Sudden price swings often manifest as noise points outside established clusters. Identifying these outliers promptly allows traders and risk managers to respond quickly before minor fluctuations escalate into significant losses.
Pattern Recognition: By grouping similar stocks based on performance metrics like volatility or returns over time, investors can identify sectors exhibiting correlated behaviors—helpful for diversification strategies.
Risk Management: Outlier detection helps assess potential vulnerabilities within portfolios by highlighting assets behaving abnormally compared to their peers—a crucial aspect during volatile periods like economic downturns or geopolitical crises.
Real-Time Monitoring: Advances in computational power enable real-time implementation of DBSCAN algorithms on streaming data feeds from stock exchanges and cryptocurrency markets; this facilitates immediate identification of abnormal trading patterns requiring swift action.
Recent Innovations Enhancing Market Analysis with DBSCAN
Over recent years, integration with machine learning techniques has significantly expanded what’s possible with DBSCAN:
- Combining neural networks with density-based clustering improves pattern recognition accuracy amid noisy datasets typical in high-frequency trading environments.
- Implementing online versions allows continuous updating without reprocessing entire datasets—a necessity given rapid market changes.
- In cryptocurrency markets especially—the high volatility combined with complex trading behaviors makes anomaly detection critical; here too, adaptations of DBSCAN help identify manipulative activities like pump-and-dump schemes before they cause widespread impact.
Challenges & Limitations When Using DBSCAN
Despite its strengths, deploying DBSCAN effectively requires careful consideration:
False Positives: Sometimes normal variations get misclassified as anomalies due to inappropriate parameter settings (Eps/MinPts), leading traders astray.
Data Quality Dependency: Poorly cleaned data—with missing values or errors—can distort clustering results significantly; hence preprocessing is vital before application.
Parameter Sensitivity: Choosing optimal Eps and MinPts values isn’t straightforward; improper tuning may result in either over-clustering (merging distinct patterns) or under-clustering (missing relevant groupings).
Furthermore, regulatory considerations demand transparency when deploying such algorithms in finance; explainability remains essential for compliance purposes while maintaining trust among stakeholders.
Key Facts About DBSCAN's Role in Financial Markets
Some quick facts highlight its importance:
- Developed by Martin Ester et al., 1996 — marking its inception over two decades ago but still highly relevant today
- Focuses on density rather than mere proximity
- Parameters Eps and MinPts critically influence outcomes
- Effective at isolating noise/outliers indicative of abnormal market activity
Historical Timeline & Future Outlook
Since its introduction in 1996 by Ester et al., research has progressively adapted DBSAN for more sophisticated applications:
- Early 2010s:* Gained popularity among quantitative analysts seeking robust anomaly detection tools
- Recent years:* Integration into machine learning frameworks enhanced predictive capabilities
- Present:* Real-time analytics powered by cloud computing enables instant response mechanisms during volatile periods
Looking ahead , ongoing developments aim at improving parameter selection automation through meta-learning techniques while expanding applicability across diverse asset classes—from equities to cryptocurrencies—and integrating explainability features aligned with regulatory standards.
Leveraging Knowledge Effectively
For investors seeking deeper insights into how unusual market conditions develop—and how best to respond—understanding tools like DBSAN is crucial . By recognizing patterns hidden beneath raw numerical data , professionals can better anticipate risks , optimize portfolio resilience , and adapt swiftly amidst unpredictable economic landscapes . As technology continues evolving rapidly , staying informed about advances such as real-time anomaly detection will remain central to successful financial analysis.
This comprehensive overview aims at equipping users—from novice analysts exploring advanced methods—to seasoned professionals refining their risk management strategies—with clear explanations rooted firmly in current research trends surrounding DBSAN’s role within modern finance systems
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
✨ JuChain supports multiple independent Launchpad dApps for Meme token creation, fair launch, and trading.
Here are 3 representative examples: CookPump.ai, Juicy.Meme, and Schili.Meme — what they do and how they work.
👉 Learn more: https://x.com/juchain101/status/1958026182563361106
#JuChain #JuChainVietnam #CookPump #JuicyMeme #Schili #JuToken #Launchpad #MemeToken #Crypto #Blockchain #Web3 #BuildOnJuChain


Lee Jucoin
2025-08-20 12:01
✨ Overview of Launchpad dApps on #JuChain
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
+140x ROI depuis le lancement — du jamais vu dans le marché actuel. Merci à tous les builders, holders & believers Le sommet ? Ce n’est que le départ. Jusqu’au 12 août, 19h00 (UTC+8)
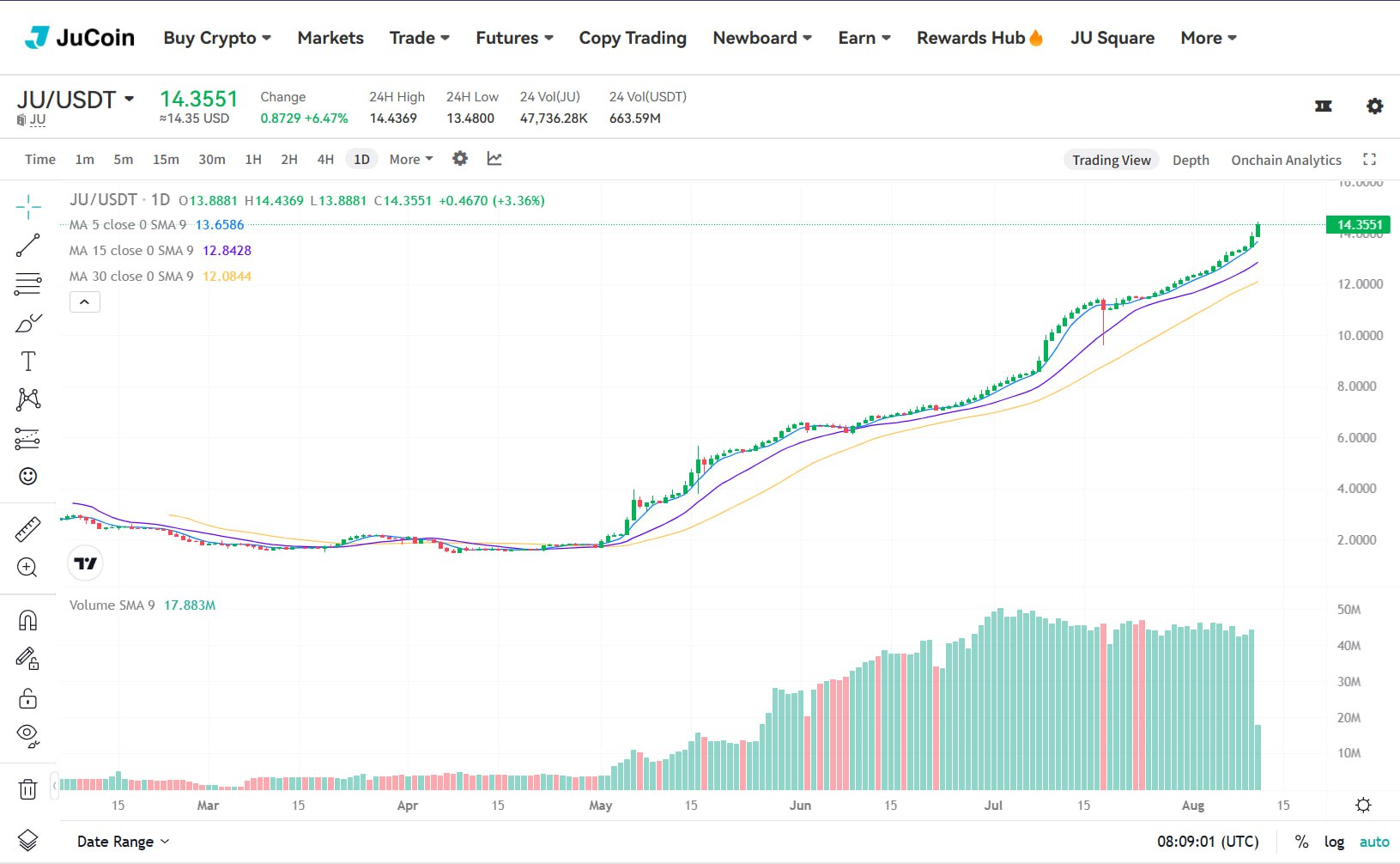


Carmelita
2025-08-11 21:33
$JU explose un nouveau record : 14 $ franchis !
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Digital platform fanC partners with fintech company Initech to launch Korea's groundbreaking 1:1 won-pegged stablecoin. Currently in test phase for internal members and partners, KRWIN aims to revolutionize Korean digital payments and cross-border transactions.
💰 Core Architecture:
-
Multi-signature custody with equivalent won reserves off-chain
Smart contracts on Ethereum and BNB Chain
1:1 peg maintained through multi-party signature confirmation
Third-party audited security with on-chain audit report hashes
🔒 Security & Compliance Features:
-
Strict KYC/AML verification process
Real-time monitoring with suspicious activity alerts
Account freeze capabilities for anomalous transactions
Trademark filed with Korean Intellectual Property Office
🎯 Current Use Cases in Testing:
-
Payment Settlement: Real-time e-commerce and offline merchant payments
Cross-Border Remittance: Low-cost international transfers for Korean businesses
Tourism Spending: Direct payments at Korean merchants and travel platforms
Content & Entertainment: Virtual gifts and premium content purchases on fanC
⚡ Test Phase Highlights:
-
Internal employees and designated partners only
Multi-chain compatibility testing (Ethereum + BNB Chain)
Scenario-linked testing across payment contexts
48-hour response commitment for user feedback
📈 2025 Roadmap:
-
Q4 2025: Public beta launch and exchange listings (KLAYswap, Bithumb, Upbit)
Ecosystem partnerships with financial institutions and e-commerce platforms
Layer-2 integration for reduced costs and higher TPS
Regulatory sandbox participation for compliance validation
🚀 Future Vision:
-
SME payments and supply-chain finance integration
Community governance module for token holder voting
Expansion to other East Asian markets
Dynamic interest rates and automatic clearing functions
💡 Market Position: As Korea's first won-pegged stablecoin, KRWIN combines traditional finance with Web3 technology, offering first-mover advantage in localized payments and regulatory compliance. This positions it to capture significant market share in the regional stablecoin ecosystem.
The bridge between Korean won and crypto is here - KRWIN is paving the way for mainstream adoption of digital currency in South Korea!
Read the full technical breakdown: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/krwin-korean-stablecoin/
#KRWIN #KoreanStablecoin #Stablecoin #KRW



JU Blog
2025-08-06 10:51
KRWIN: Korea's First Won-Pegged Stablecoin Goes Live!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📣 $JU is more than just a token — it’s your voice on JuChain. 😍 Holding $JU means:
🔹 Contributing to network consensus
🔹 Voting on governance upgrades
🔹 Shaping the future of the JuChain ecosystem
💥 It’s a builder’s token, a user’s token, and the key to governance. The more you hold and participate, the more you co-create the future of #JuChain.
👉 Trade $JU now: https://jucoin.com/en/trade/ju_usdt
#JuChain #JuChainVietnam #JUtoken #Governance #BlockchainCommunity #CryptoVietnam #Web3 #TokenUtility #BuildOnJuChain


Lee Jucoin
2025-08-20 12:00
📣 $JU is more than just a token — it’s your voice on JuChain!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Can I Trade from the TradingView Mobile App?
Understanding Trading Capabilities on the Mobile Platform
TradingView is renowned for its advanced charting tools, real-time market data, and vibrant community features. While it excels as a platform for analysis and discussion, many users wonder whether they can execute trades directly through the mobile app. The short answer is that TradingView itself does not function as a brokerage or trading platform; instead, it acts as an analytical hub that integrates with various brokerages to facilitate trading.
TradingView's primary role is providing comprehensive technical analysis tools, alerts, and social features. Its mobile app allows users to monitor markets on-the-go with real-time data and perform detailed charting. However, executing trades requires connecting your TradingView account to a supported broker or trading service.
Does TradingView Support Direct Trading?
As of now, TradingView does not offer in-app trade execution within its mobile application independently. Instead, it relies on integrations with third-party brokers that support API connections or direct integration through their platforms. This means that while you can analyze charts and set alerts via the app seamlessly, placing actual buy or sell orders typically involves redirecting to your broker’s platform—either their website or dedicated trading app.
Many popular brokers such as Interactive Brokers, Tradestation, OANDA (for forex), and others have integrated with TradingView’s ecosystem. When linked correctly:
- Users can initiate trades directly from the chart interface.
- Orders are sent securely through the connected brokerage account.
- Trade execution happens within the broker’s environment rather than solely within TradingView.
This setup provides a streamlined experience where traders can analyze markets visually in TradingView while executing trades via their preferred brokerage platform.
How to Set Up Trade Execution Using Your Broker
To enable trading from your mobile device using TradingView:
- Choose a Supported Broker: Verify if your preferred broker supports integration with TradingView.
- Connect Your Account: Within the desktop or web version of TradingView (most integrations are set up here), link your brokerage account by following specific instructions provided by both platforms.
- Use Compatible Apps: On mobile devices—iOS or Android—you’ll typically access trade execution through either:
- The browser-based version of your broker’s platform
- Their dedicated mobile app
- Trade via Chart Interface: Once connected:
- Tap on charts in the mobile app
- Use order buttons embedded within supported charts
- Place buy/sell orders directly from these interfaces
It’s important to note that some functionalities may be limited compared to full desktop versions due to screen size constraints but generally remain sufficient for active traders.
Limitations of Mobile-Based Trade Execution
While integrating with brokers enables trading from smartphones using the Trading View ecosystem:
- Not all brokers support full API-based order placement via mobile apps.
- Some advanced order types (e.g., complex options strategies) might be restricted.
- The process often involves switching between apps—Trading View for analysis and another app for order placement—which could introduce delays during volatile market conditions.
Additionally, security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA) are essential when executing trades remotely; ensure both your broker's security protocols are robust before relying heavily on this setup.
Benefits of Using Mobile Apps for Analysis & Limited Trades
Even if you cannot execute every type of trade directly within the native mobile application without third-party links:
- You gain quick access to real-time data across multiple asset classes including stocks, cryptocurrencies, forex pairs,
- You can set custom alerts based on price movements,
- Engage actively in community discussions,
- And prepare orders which you then execute swiftly through linked brokerage accounts outside of Traderview's environment,
This hybrid approach offers flexibility suited for both casual investors monitoring markets casually and professional traders requiring rapid decision-making capabilities.
Security Considerations When Trading Via Mobile Devices
Executing financial transactions over smartphones introduces specific risks related to data privacy and security breaches. To mitigate these concerns:
- Use strong passwords combined with biometric authentication where available.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) provided by most reputable brokers.
- Keep your device updated with latest OS patches.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi networks when performing sensitive operations unless utilizing VPNs.5.. Regularly review activity logs provided by your brokerage accounts for unauthorized access attempts.
By adhering to best practices in cybersecurity hygiene — especially when linking multiple platforms — traders can safely conduct transactions remotely without exposing themselves unnecessarily.
The Future Outlook: Will In-App Direct Trades Become Standard?
Given recent developments emphasizing seamless user experiences across financial apps—including enhanced API integrations—the possibility exists that future versions of Traderview might incorporate more direct trade execution capabilities into its native apps across all devices including mobiles.. However,
Currently,
the emphasis remains on combining powerful analysis tools within Traderview while leveraging trusted third-party brokers’ infrastructure for actual trade placement..
This layered approach ensures high-quality analytical features alongside secure transaction processing—a model likely to persist until fully integrated solutions become universally available across all regions and asset classes..
Summary
While you cannot currently place trades directly inside Traderview's official iOS or Android applications without external links,
the platform facilitates efficient analysis combined with seamless integration into supported brokerage services enabling quick trade execution from smartphones.. As technology advances—and regulatory environments evolve—the scope of what is possible will expand further making remote trading even more accessible via intuitive mobile interfaces designed specifically around trader needs..


Lo
2025-05-26 23:10
Can I trade from the TradingView mobile app?
Can I Trade from the TradingView Mobile App?
Understanding Trading Capabilities on the Mobile Platform
TradingView is renowned for its advanced charting tools, real-time market data, and vibrant community features. While it excels as a platform for analysis and discussion, many users wonder whether they can execute trades directly through the mobile app. The short answer is that TradingView itself does not function as a brokerage or trading platform; instead, it acts as an analytical hub that integrates with various brokerages to facilitate trading.
TradingView's primary role is providing comprehensive technical analysis tools, alerts, and social features. Its mobile app allows users to monitor markets on-the-go with real-time data and perform detailed charting. However, executing trades requires connecting your TradingView account to a supported broker or trading service.
Does TradingView Support Direct Trading?
As of now, TradingView does not offer in-app trade execution within its mobile application independently. Instead, it relies on integrations with third-party brokers that support API connections or direct integration through their platforms. This means that while you can analyze charts and set alerts via the app seamlessly, placing actual buy or sell orders typically involves redirecting to your broker’s platform—either their website or dedicated trading app.
Many popular brokers such as Interactive Brokers, Tradestation, OANDA (for forex), and others have integrated with TradingView’s ecosystem. When linked correctly:
- Users can initiate trades directly from the chart interface.
- Orders are sent securely through the connected brokerage account.
- Trade execution happens within the broker’s environment rather than solely within TradingView.
This setup provides a streamlined experience where traders can analyze markets visually in TradingView while executing trades via their preferred brokerage platform.
How to Set Up Trade Execution Using Your Broker
To enable trading from your mobile device using TradingView:
- Choose a Supported Broker: Verify if your preferred broker supports integration with TradingView.
- Connect Your Account: Within the desktop or web version of TradingView (most integrations are set up here), link your brokerage account by following specific instructions provided by both platforms.
- Use Compatible Apps: On mobile devices—iOS or Android—you’ll typically access trade execution through either:
- The browser-based version of your broker’s platform
- Their dedicated mobile app
- Trade via Chart Interface: Once connected:
- Tap on charts in the mobile app
- Use order buttons embedded within supported charts
- Place buy/sell orders directly from these interfaces
It’s important to note that some functionalities may be limited compared to full desktop versions due to screen size constraints but generally remain sufficient for active traders.
Limitations of Mobile-Based Trade Execution
While integrating with brokers enables trading from smartphones using the Trading View ecosystem:
- Not all brokers support full API-based order placement via mobile apps.
- Some advanced order types (e.g., complex options strategies) might be restricted.
- The process often involves switching between apps—Trading View for analysis and another app for order placement—which could introduce delays during volatile market conditions.
Additionally, security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA) are essential when executing trades remotely; ensure both your broker's security protocols are robust before relying heavily on this setup.
Benefits of Using Mobile Apps for Analysis & Limited Trades
Even if you cannot execute every type of trade directly within the native mobile application without third-party links:
- You gain quick access to real-time data across multiple asset classes including stocks, cryptocurrencies, forex pairs,
- You can set custom alerts based on price movements,
- Engage actively in community discussions,
- And prepare orders which you then execute swiftly through linked brokerage accounts outside of Traderview's environment,
This hybrid approach offers flexibility suited for both casual investors monitoring markets casually and professional traders requiring rapid decision-making capabilities.
Security Considerations When Trading Via Mobile Devices
Executing financial transactions over smartphones introduces specific risks related to data privacy and security breaches. To mitigate these concerns:
- Use strong passwords combined with biometric authentication where available.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) provided by most reputable brokers.
- Keep your device updated with latest OS patches.
- Avoid public Wi-Fi networks when performing sensitive operations unless utilizing VPNs.5.. Regularly review activity logs provided by your brokerage accounts for unauthorized access attempts.
By adhering to best practices in cybersecurity hygiene — especially when linking multiple platforms — traders can safely conduct transactions remotely without exposing themselves unnecessarily.
The Future Outlook: Will In-App Direct Trades Become Standard?
Given recent developments emphasizing seamless user experiences across financial apps—including enhanced API integrations—the possibility exists that future versions of Traderview might incorporate more direct trade execution capabilities into its native apps across all devices including mobiles.. However,
Currently,
the emphasis remains on combining powerful analysis tools within Traderview while leveraging trusted third-party brokers’ infrastructure for actual trade placement..
This layered approach ensures high-quality analytical features alongside secure transaction processing—a model likely to persist until fully integrated solutions become universally available across all regions and asset classes..
Summary
While you cannot currently place trades directly inside Traderview's official iOS or Android applications without external links,
the platform facilitates efficient analysis combined with seamless integration into supported brokerage services enabling quick trade execution from smartphones.. As technology advances—and regulatory environments evolve—the scope of what is possible will expand further making remote trading even more accessible via intuitive mobile interfaces designed specifically around trader needs..
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Backed by YZi Labs, HashKey Capital, and Mirana Ventures, Sidekick revolutionizes crypto trading by integrating livestreams with real-time on-chain transactions. No more switching between platforms - watch, learn, and trade all in one seamless experience!
🎯 Core Innovation - "Watch-and-Trade":
-
Live market insights via streaming "Kickers" (hosts)
One-click trading directly within video streams
Real-time charts and order panels embedded in videos
Multi-chain support: Ethereum, Solana, BSC, and more
⚡ How It Works:
-
MetaTx Technology: Bundles all interactions into single on-chain transaction
Real-Time Execution: Live prices, wallet balances, and trade signals in stream
Instant Receipts: Contract confirmations shown directly in livestream
Zero Latency: No protocol switches, reduced gas fees
💰 $K Token Economics (1B Total Supply):
-
Ecosystem Growth: 20% (200M $K)
Community Incentives: 20% (200M $K)
Foundation: 16% (160M $K)
Core Contributors: 15% (150M $K)
Investors: 20% (200M $K)
Initial Circulation: 111.3M $K (11.13%)
🔒 Security & Compliance:
-
Third-party audited smart contracts with on-chain proof
MetaTx simulation prevents re-entrancy and slippage attacks
Multi-sig and time-lock for critical upgrades
Optional zero-knowledge KYC/AML for privacy compliance
🚀 Future Ecosystem:
-
Global Expansion: 500+ Kickers across education, gaming, DeFi
Platform Integration: Zapper, Zerion, OKX Wallet compatibility
DAO Governance: $K holders control rewards and feature roadmaps
AI Agent Support: Smart signals for Kickers, personalized advice for viewers
💡 Revenue Model:
-
Kickers earn through real-time revenue shares and $K rewards
Viewers earn token incentives for trading activity
Platform fees distributed to $K stakers
Tipping and premium feature unlocks
🎮 Use Cases:
-
Educational trading streams with instant execution
Gaming tournaments with live betting and rewards
DeFi project launches with real-time community trading
Expert analysis with follow-along trading capabilities
The future of crypto trading isn't just about charts and orders - it's about community, education, and seamless interaction. Sidekick transforms passive viewing into active earning through the world's first truly integrated LiveFi experience!
Read the complete platform analysis: 👇 https://blog.jucoin.com/sidekick-livefi-analysis/
#Sidekick #LiveFi #DeFi



JU Blog
2025-08-06 10:56
📺 Sidekick: World's First LiveFi Platform - Trade While You Watch!
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Extend Common-Size Analysis to Cash Flows
Understanding a company's financial health is crucial for investors, analysts, and managers alike. Traditionally, common-size analysis has been a staple in evaluating income statements and balance sheets by expressing each line item as a percentage of total revenue or assets. However, extending this analytical approach to cash flow statements offers deeper insights into how companies generate and use cash—an essential factor in assessing long-term sustainability. This article explores how to effectively perform common-size analysis on cash flows, its significance, recent trends influencing its application, and potential pitfalls.
What Is Common-Size Analysis in Financial Statements?
Common-size analysis simplifies the comparison of financial statements across different companies or periods by converting absolute figures into percentages relative to a base figure—such as total revenue for income statements or total assets for balance sheets. This normalization allows stakeholders to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might be obscured when looking solely at raw numbers. For example, two firms with similar revenues might have vastly different expense structures; common-size analysis makes these differences more transparent.
Extending Common-Size Analysis to Cash Flow Statements
Applying the same principle to cash flow statements involves expressing each line item—like cash from operations or capital expenditures—as a percentage of the relevant total cash flow category (operating activities, investing activities, or financing activities). For instance:
- Cash from Operating Activities / Total Cash Flows from Operations
- Capital Expenditures / Total Cash Flows from Investing Activities
- Dividends Paid / Total Cash Flows from Financing Activities
This approach reveals the composition of a company's cash flows over time or compared across peers. It helps identify whether growth is driven primarily by operational efficiency or external financing sources and whether investments are sustainable relative to incoming cash.
Why Is Extending Common-Size Analysis Important?
Performing common-size analysis on cash flows provides several strategic advantages:
Assessing Financial Sustainability: By examining what proportion of total operating cash flow is generated internally versus reliance on external funding (debt issuance), stakeholders can gauge if a company’s core operations are self-sustaining.
Identifying Investment Patterns: Analyzing capital expenditure as part of investing activities highlights whether growth investments are aligned with available internal funds.
Detecting Risks: A high proportion of financing outflows like debt repayment may signal increased leverage risks; conversely, declining operational inflow percentages could indicate deteriorating business performance.
Benchmarking Industry Norms: Different sectors have unique typical ratios—for example, tech firms often reinvest heavily through capital expenditures while retail businesses may prioritize inventory management reflected in their operating cash flows.
Recent Trends Enhancing Cash Flow Common-Size Analysis
Advancements in technology have significantly improved how we perform this type of analysis:
Modern financial software automates calculations across large datasets quickly and accurately.
Enhanced disclosure requirements under regulations such as ASC 606 (Revenue Recognition) and ASC 842 (Leases) provide more detailed data about inflows and outflows—making it easier for analysts to conduct precise common-size evaluations.
Furthermore, there's an increasing emphasis on ESG factors influencing corporate reporting practices related not only to environmental impact but also social governance aspects tied directly into their liquidity profiles.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries exhibit distinct characteristics when it comes to theircash flow profiles:
Technology Sector: High research & development costs lead companies here often show significant capital expenditures relativeto their overall operating inflow during expansion phases.Retail Sector: Inventory management plays an essential role; thus,cash used in working capital changes can dominate the statement.Manufacturing & Capital Goods: These industries typically require substantial investmentsin property plant equipment (PP&E), reflected prominently within investing activities'cash flows.
Understanding these nuances ensures that comparisons remain meaningful rather than misleading due tothe inherent industry differences.
Potential Challenges When Using Common-Size Cash Flow Analysis
While extending this method offers valuable insights,it also presents challenges that users must recognize:
Misleading Indicators: Companies with high capital expenditures might appear inefficient if industry norms aren’t considered properly.Investors should adjust expectations accordingly.
Overreliance on Ratios: Focusing solelyon ratios without considering profitability metrics like net income can give an incomplete pictureof financial health.
Short-Term Variability: Seasonal fluctuationsor one-time events can distort ratios temporarily; analyzing multiple periods helps smooth out such anomalies.
4.. Debt Structures & Off-Balance Sheet Items: Complex financing arrangements may not be fully captured through simple ratio analyses but still influence liquidity positions significantly.
Applying Best Practices for Effective Use
To maximize the benefitsof extending common-size analysisto your evaluation process consider these best practices:
– Always compare ratios against industry benchmarksand historical datafor context– Use multi-period analysesto identify trends rather than snapshot views– Combine ratio insightswith qualitative assessments regarding management strategiesand market conditions– Be cautious interpreting results during extraordinary eventsor economic downturns
Final Thoughts: Enhancing Financial Insights Through Extended Analysis
Extending common-size analysis beyond traditional income statement and balance sheet evaluations into the realmofcash flows enriches your understandingof corporate liquidity dynamicsand investment sustainability.It enables investorsand managers alike todetect underlying strengthsor vulnerabilitiesthat might otherwise go unnoticed when relying solelyon absolute figures.This comprehensive approach aligns well with modern analytical standards emphasizing transparency,and it supports better-informed decision-making amid increasingly complex financial landscapes.
By staying awareof recent technological developmentsand regulatory changes—and understanding industry-specific nuances—you can leverage extendedcommon-sizecash flow analyses effectively while avoiding potential pitfalls.This strategic insight ultimately contributes toward building robust investment portfolios,and fostering sound corporate governance rootedin thoroughfinancial scrutiny


kai
2025-05-19 13:01
How to extend common-size analysis to cash flows?
How to Extend Common-Size Analysis to Cash Flows
Understanding a company's financial health is crucial for investors, analysts, and managers alike. Traditionally, common-size analysis has been a staple in evaluating income statements and balance sheets by expressing each line item as a percentage of total revenue or assets. However, extending this analytical approach to cash flow statements offers deeper insights into how companies generate and use cash—an essential factor in assessing long-term sustainability. This article explores how to effectively perform common-size analysis on cash flows, its significance, recent trends influencing its application, and potential pitfalls.
What Is Common-Size Analysis in Financial Statements?
Common-size analysis simplifies the comparison of financial statements across different companies or periods by converting absolute figures into percentages relative to a base figure—such as total revenue for income statements or total assets for balance sheets. This normalization allows stakeholders to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might be obscured when looking solely at raw numbers. For example, two firms with similar revenues might have vastly different expense structures; common-size analysis makes these differences more transparent.
Extending Common-Size Analysis to Cash Flow Statements
Applying the same principle to cash flow statements involves expressing each line item—like cash from operations or capital expenditures—as a percentage of the relevant total cash flow category (operating activities, investing activities, or financing activities). For instance:
- Cash from Operating Activities / Total Cash Flows from Operations
- Capital Expenditures / Total Cash Flows from Investing Activities
- Dividends Paid / Total Cash Flows from Financing Activities
This approach reveals the composition of a company's cash flows over time or compared across peers. It helps identify whether growth is driven primarily by operational efficiency or external financing sources and whether investments are sustainable relative to incoming cash.
Why Is Extending Common-Size Analysis Important?
Performing common-size analysis on cash flows provides several strategic advantages:
Assessing Financial Sustainability: By examining what proportion of total operating cash flow is generated internally versus reliance on external funding (debt issuance), stakeholders can gauge if a company’s core operations are self-sustaining.
Identifying Investment Patterns: Analyzing capital expenditure as part of investing activities highlights whether growth investments are aligned with available internal funds.
Detecting Risks: A high proportion of financing outflows like debt repayment may signal increased leverage risks; conversely, declining operational inflow percentages could indicate deteriorating business performance.
Benchmarking Industry Norms: Different sectors have unique typical ratios—for example, tech firms often reinvest heavily through capital expenditures while retail businesses may prioritize inventory management reflected in their operating cash flows.
Recent Trends Enhancing Cash Flow Common-Size Analysis
Advancements in technology have significantly improved how we perform this type of analysis:
Modern financial software automates calculations across large datasets quickly and accurately.
Enhanced disclosure requirements under regulations such as ASC 606 (Revenue Recognition) and ASC 842 (Leases) provide more detailed data about inflows and outflows—making it easier for analysts to conduct precise common-size evaluations.
Furthermore, there's an increasing emphasis on ESG factors influencing corporate reporting practices related not only to environmental impact but also social governance aspects tied directly into their liquidity profiles.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries exhibit distinct characteristics when it comes to theircash flow profiles:
Technology Sector: High research & development costs lead companies here often show significant capital expenditures relativeto their overall operating inflow during expansion phases.Retail Sector: Inventory management plays an essential role; thus,cash used in working capital changes can dominate the statement.Manufacturing & Capital Goods: These industries typically require substantial investmentsin property plant equipment (PP&E), reflected prominently within investing activities'cash flows.
Understanding these nuances ensures that comparisons remain meaningful rather than misleading due tothe inherent industry differences.
Potential Challenges When Using Common-Size Cash Flow Analysis
While extending this method offers valuable insights,it also presents challenges that users must recognize:
Misleading Indicators: Companies with high capital expenditures might appear inefficient if industry norms aren’t considered properly.Investors should adjust expectations accordingly.
Overreliance on Ratios: Focusing solelyon ratios without considering profitability metrics like net income can give an incomplete pictureof financial health.
Short-Term Variability: Seasonal fluctuationsor one-time events can distort ratios temporarily; analyzing multiple periods helps smooth out such anomalies.
4.. Debt Structures & Off-Balance Sheet Items: Complex financing arrangements may not be fully captured through simple ratio analyses but still influence liquidity positions significantly.
Applying Best Practices for Effective Use
To maximize the benefitsof extending common-size analysisto your evaluation process consider these best practices:
– Always compare ratios against industry benchmarksand historical datafor context– Use multi-period analysesto identify trends rather than snapshot views– Combine ratio insightswith qualitative assessments regarding management strategiesand market conditions– Be cautious interpreting results during extraordinary eventsor economic downturns
Final Thoughts: Enhancing Financial Insights Through Extended Analysis
Extending common-size analysis beyond traditional income statement and balance sheet evaluations into the realmofcash flows enriches your understandingof corporate liquidity dynamicsand investment sustainability.It enables investorsand managers alike todetect underlying strengthsor vulnerabilitiesthat might otherwise go unnoticed when relying solelyon absolute figures.This comprehensive approach aligns well with modern analytical standards emphasizing transparency,and it supports better-informed decision-making amid increasingly complex financial landscapes.
By staying awareof recent technological developmentsand regulatory changes—and understanding industry-specific nuances—you can leverage extendedcommon-sizecash flow analyses effectively while avoiding potential pitfalls.This strategic insight ultimately contributes toward building robust investment portfolios,and fostering sound corporate governance rootedin thoroughfinancial scrutiny
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is the Engle-Granger Two-Step Method for Cointegration Analysis?
The Engle-Granger two-step method is a fundamental econometric technique used to identify long-term relationships between non-stationary time series data. Developed by Clive Granger and Robert Engle in the late 1980s, this approach has become a cornerstone in analyzing economic and financial data where understanding equilibrium relationships over time is crucial. Its simplicity and effectiveness have made it widely adopted among researchers, policymakers, and financial analysts.
Understanding Cointegration in Time Series Data
Before diving into the specifics of the Engle-Granger method, it's essential to grasp what cointegration entails. In time series analysis, many economic variables—such as GDP, inflation rates, or stock prices—exhibit non-stationary behavior. This means their statistical properties change over time; they may trend upward or downward or fluctuate unpredictably around a changing mean.
However, some non-stationary variables move together in such a way that their linear combination remains stationary—that is, their relationship persists over the long run despite short-term fluctuations. This phenomenon is known as cointegration. Recognizing cointegrated variables allows economists to model these relationships accurately and make meaningful forecasts about their future behavior.
The Two Main Steps of the Engle-Granger Method
The process involves two sequential steps designed to test whether such long-run equilibrium relationships exist:
Step 1: Testing for Unit Roots
Initially, each individual time series must be tested for stationarity using unit root tests like Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) or Phillips-Perron tests. These tests determine whether each variable contains a unit root—a hallmark of non-stationarity. If both series are found to be non-stationary (i.e., they have unit roots), then proceeding with cointegration testing makes sense because stationary linear combinations might exist.
Step 2: Conducting the Cointegration Test
Once confirmed that individual series are non-stationary but integrated of order one (I(1)), researchers regress one variable on others using ordinary least squares (OLS). The residuals from this regression represent deviations from the estimated long-run relationship. If these residuals are stationary—meaning they do not exhibit trends—they indicate that the original variables are cointegrated.
This step effectively checks if there's an underlying equilibrium relationship binding these variables together over time—a critical insight when modeling economic systems like exchange rates versus interest rates or income versus consumption.
Significance and Applications of the Method
Since its introduction by Granger and Engle in 1987 through their influential paper "Cointegration and Error Correction," this methodology has profoundly impacted econometrics research across various fields including macroeconomics, finance, and international economics.
For example:
- Analyzing how GDP relates to inflation rates
- Examining stock prices relative to dividends
- Investigating exchange rate movements against interest differentials
By identifying stable long-term relationships amid volatile short-term movements, policymakers can design more effective interventions while investors can develop strategies based on persistent market linkages.
Limitations of the Engle-Granger Approach
Despite its widespread use and intuitive appeal, several limitations should be acknowledged:
Linearity Assumption: The method assumes that relationships between variables are linear; real-world data often involve nonlinear dynamics.
Sensitivity to Outliers: Outliers can distort regression results leading to incorrect conclusions about stationarity of residuals.
Single Cointegrating Vector: It only detects one cointegrating vector at a time; if multiple vectors exist among several variables simultaneously influencing each other’s dynamics more complex models like Johansen's procedure may be necessary.
These limitations highlight why researchers often complement it with alternative methods when dealing with complex datasets involving multiple interrelated factors.
Recent Developments & Alternatives in Cointegration Analysis
Advancements since its inception include techniques capable of handling multiple cointegrating vectors simultaneously—most notably Johansen's procedure—which offers greater flexibility for multivariate systems. Additionally:
- Researchers now leverage machine learning algorithms alongside traditional econometric tools
- Robust methods address issues related to outliers or structural breaks within data
Such innovations improve accuracy but also require more sophisticated software tools and expertise compared to basic applications of Engel-Granger’s approach.
Practical Implications for Economists & Financial Analysts
Correctly identifying whether two or more economic indicators share a stable long-run relationship influences decision-making significantly:
Economic Policy: Misidentifying relationships could lead policymakers astray—for example, assuming causality where none exists might result in ineffective policies.
Financial Markets: Investors relying on flawed assumptions about asset co-movements risk losses if they misinterpret transient correlations as permanent links.
Therefore, understanding both how-to apply these methods correctly—and recognizing when alternative approaches are needed—is vital for producing reliable insights from econometric analyses.
In summary: The Engle-Granger two-step method remains an essential tool within econometrics due to its straightforward implementation for detecting cointegration between pairs of variables. While newer techniques offer broader capabilities suited for complex datasets with multiple relations or nonlinearities—and technological advancements facilitate easier computation—the core principles behind this approach continue underpin much empirical research today. For anyone involved in analyzing economic phenomena where understanding persistent relationships matters most—from policy formulation through investment strategy—it provides foundational knowledge critical for accurate modeling and forecasting efforts alike.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-14 17:20
What is the Engle-Granger two-step method for cointegration analysis?
What is the Engle-Granger Two-Step Method for Cointegration Analysis?
The Engle-Granger two-step method is a fundamental econometric technique used to identify long-term relationships between non-stationary time series data. Developed by Clive Granger and Robert Engle in the late 1980s, this approach has become a cornerstone in analyzing economic and financial data where understanding equilibrium relationships over time is crucial. Its simplicity and effectiveness have made it widely adopted among researchers, policymakers, and financial analysts.
Understanding Cointegration in Time Series Data
Before diving into the specifics of the Engle-Granger method, it's essential to grasp what cointegration entails. In time series analysis, many economic variables—such as GDP, inflation rates, or stock prices—exhibit non-stationary behavior. This means their statistical properties change over time; they may trend upward or downward or fluctuate unpredictably around a changing mean.
However, some non-stationary variables move together in such a way that their linear combination remains stationary—that is, their relationship persists over the long run despite short-term fluctuations. This phenomenon is known as cointegration. Recognizing cointegrated variables allows economists to model these relationships accurately and make meaningful forecasts about their future behavior.
The Two Main Steps of the Engle-Granger Method
The process involves two sequential steps designed to test whether such long-run equilibrium relationships exist:
Step 1: Testing for Unit Roots
Initially, each individual time series must be tested for stationarity using unit root tests like Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) or Phillips-Perron tests. These tests determine whether each variable contains a unit root—a hallmark of non-stationarity. If both series are found to be non-stationary (i.e., they have unit roots), then proceeding with cointegration testing makes sense because stationary linear combinations might exist.
Step 2: Conducting the Cointegration Test
Once confirmed that individual series are non-stationary but integrated of order one (I(1)), researchers regress one variable on others using ordinary least squares (OLS). The residuals from this regression represent deviations from the estimated long-run relationship. If these residuals are stationary—meaning they do not exhibit trends—they indicate that the original variables are cointegrated.
This step effectively checks if there's an underlying equilibrium relationship binding these variables together over time—a critical insight when modeling economic systems like exchange rates versus interest rates or income versus consumption.
Significance and Applications of the Method
Since its introduction by Granger and Engle in 1987 through their influential paper "Cointegration and Error Correction," this methodology has profoundly impacted econometrics research across various fields including macroeconomics, finance, and international economics.
For example:
- Analyzing how GDP relates to inflation rates
- Examining stock prices relative to dividends
- Investigating exchange rate movements against interest differentials
By identifying stable long-term relationships amid volatile short-term movements, policymakers can design more effective interventions while investors can develop strategies based on persistent market linkages.
Limitations of the Engle-Granger Approach
Despite its widespread use and intuitive appeal, several limitations should be acknowledged:
Linearity Assumption: The method assumes that relationships between variables are linear; real-world data often involve nonlinear dynamics.
Sensitivity to Outliers: Outliers can distort regression results leading to incorrect conclusions about stationarity of residuals.
Single Cointegrating Vector: It only detects one cointegrating vector at a time; if multiple vectors exist among several variables simultaneously influencing each other’s dynamics more complex models like Johansen's procedure may be necessary.
These limitations highlight why researchers often complement it with alternative methods when dealing with complex datasets involving multiple interrelated factors.
Recent Developments & Alternatives in Cointegration Analysis
Advancements since its inception include techniques capable of handling multiple cointegrating vectors simultaneously—most notably Johansen's procedure—which offers greater flexibility for multivariate systems. Additionally:
- Researchers now leverage machine learning algorithms alongside traditional econometric tools
- Robust methods address issues related to outliers or structural breaks within data
Such innovations improve accuracy but also require more sophisticated software tools and expertise compared to basic applications of Engel-Granger’s approach.
Practical Implications for Economists & Financial Analysts
Correctly identifying whether two or more economic indicators share a stable long-run relationship influences decision-making significantly:
Economic Policy: Misidentifying relationships could lead policymakers astray—for example, assuming causality where none exists might result in ineffective policies.
Financial Markets: Investors relying on flawed assumptions about asset co-movements risk losses if they misinterpret transient correlations as permanent links.
Therefore, understanding both how-to apply these methods correctly—and recognizing when alternative approaches are needed—is vital for producing reliable insights from econometric analyses.
In summary: The Engle-Granger two-step method remains an essential tool within econometrics due to its straightforward implementation for detecting cointegration between pairs of variables. While newer techniques offer broader capabilities suited for complex datasets with multiple relations or nonlinearities—and technological advancements facilitate easier computation—the core principles behind this approach continue underpin much empirical research today. For anyone involved in analyzing economic phenomena where understanding persistent relationships matters most—from policy formulation through investment strategy—it provides foundational knowledge critical for accurate modeling and forecasting efforts alike.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Advantages of Using Cumulative Delta Volume in Cryptocurrency Trading
Understanding market sentiment and predicting future price movements are central goals for traders in the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency. Among various technical analysis tools, cumulative delta volume has gained prominence due to its ability to provide nuanced insights into market dynamics. This article explores the key advantages of using cumulative delta volume, highlighting how it enhances trading strategies and risk management.
What Is Cumulative Delta Volume?
Cumulative delta volume is a sophisticated indicator that combines price change data with trading volume to assess market pressure. It involves calculating the delta—representing the difference between buying and selling activity—and then summing these values over time. When this cumulative measure is paired with volume data, traders gain a clearer picture of whether buyers or sellers dominate at any given moment.
This approach offers a more detailed view than traditional volume indicators alone because it captures not just how much is being traded but also who is driving those trades—buyers or sellers. As such, cumulative delta volume serves as an effective tool for analyzing real-time market sentiment and potential trend reversals.
How Cumulative Delta Volume Enhances Market Sentiment Analysis
One of the primary benefits of utilizing cumulative delta volume lies in its ability to reveal underlying market sentiment more accurately than simple price charts or raw volume data. By tracking whether buying or selling pressure accumulates over time, traders can identify shifts in momentum before they become apparent through conventional indicators.
For example, if the cumulative delta shows increasing buying pressure even as prices stagnate or decline slightly, it may signal an upcoming bullish reversal. Conversely, persistent selling pressure reflected by declining cumulative delta suggests bearish trends are likely to continue. This depth of insight helps traders anticipate moves rather than react after they occur.
Improved Risk Management Through Real-Time Data
Risk management remains a critical aspect of successful trading strategies—especially within volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Cumulative delta volume provides real-time feedback on market strength and weakness by illustrating ongoing shifts in trader behavior.
By monitoring changes in the accumulated delta values alongside price action and other technical signals, traders can better gauge when to enter or exit positions. For instance:
- A sudden spike in positive cumulative delta might indicate strong buying interest that warrants taking profits.
- Conversely, a rapid decline could warn about increasing sell pressure requiring caution or position adjustments.
This proactive approach allows traders to manage their exposure more effectively rather than relying solely on lagging indicators such as moving averages.
Confirming Trade Signals for Greater Accuracy
Using multiple confirmation points enhances trade reliability—a principle well-supported by technical analysis best practices. Cumulative delta volume acts as an excellent confirmation tool when combined with other indicators like support/resistance levels or trend lines.
For example:
- If a breakout occurs alongside rising positive cumulative delta readings, confidence increases that the move reflects genuine buyer interest.
- Similarly, divergence between price action and declining negative deltas can signal weakening selling momentum before prices reverse direction.
Such confirmations reduce false signals and improve overall trade accuracy by aligning multiple facets of market data into cohesive insights rooted in trader behavior patterns.
Adaptability Across Different Market Conditions
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility driven by technological developments, regulatory news, macroeconomic factors, and investor sentiment swings. In these environments—where rapid changes happen frequently—the flexibility offered by cumulative delta volume becomes particularly valuable.
Because it captures real-time shifts in buyer-seller dominance regardless of broader trends or external influences—it adapts well across different phases:
- During trending markets (bullish/bearish), it helps confirm trend strength.
- In sideways consolidation periods (range-bound), it identifies subtle shifts indicating potential breakouts.
This adaptability makes cumulatedelta-based analysis suitable for both short-term scalping strategies and longer-term swing trades within dynamic crypto landscapes.
Integration With Advanced Analytical Techniques
Recent advancements have seen integration efforts where machine learning algorithms incorporate features derived from cumulative delta volumes into predictive models. These innovations aim at improving forecast accuracy further while automating complex analyses that would be difficult manually.
Such integrations enhance decision-making processes by providing quantitative backing grounded on behavioral finance principles embedded within cumulatedelta metrics—making them increasingly indispensable tools for professional traders seeking competitive edges.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While there are numerous advantages associated with using cumulative delta volumes — including deeper insight into trader behavior — it's essential also to recognize some challenges:
- Complexity: Calculating accurate deltas requires advanced technical skills; errors can lead to misleading interpretations.
- Data Quality: Reliable results depend heavily on high-quality trade data feeds; inaccuracies here impair effectiveness.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As regulators scrutinize sophisticated trading tools' use within crypto markets—which often lack comprehensive oversight—traders should stay informed about evolving legal frameworks affecting their analytical methods.
Final Thoughts: Why Traders Should Consider Using Cumulative Delta Volume
In summary, incorporating cumulative delta volume into your cryptocurrency trading toolkit offers several compelling benefits—from enhanced sentiment analysis and improved risk management capabilities to better confirmation signals during volatile periods. Its ability to reflect real-time shifts driven by actual trader activity makes it especially valuable amid today's rapidly changing digital asset landscape where understanding underlying pressures can make all the difference between profit and loss.
Keywords: cryptocurrency trading advantages | what is cumulatedelta | risk management tools | technical analysis crypto | real-time market insights


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 03:30
What are the advantages of using cumulative delta volume?
Advantages of Using Cumulative Delta Volume in Cryptocurrency Trading
Understanding market sentiment and predicting future price movements are central goals for traders in the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency. Among various technical analysis tools, cumulative delta volume has gained prominence due to its ability to provide nuanced insights into market dynamics. This article explores the key advantages of using cumulative delta volume, highlighting how it enhances trading strategies and risk management.
What Is Cumulative Delta Volume?
Cumulative delta volume is a sophisticated indicator that combines price change data with trading volume to assess market pressure. It involves calculating the delta—representing the difference between buying and selling activity—and then summing these values over time. When this cumulative measure is paired with volume data, traders gain a clearer picture of whether buyers or sellers dominate at any given moment.
This approach offers a more detailed view than traditional volume indicators alone because it captures not just how much is being traded but also who is driving those trades—buyers or sellers. As such, cumulative delta volume serves as an effective tool for analyzing real-time market sentiment and potential trend reversals.
How Cumulative Delta Volume Enhances Market Sentiment Analysis
One of the primary benefits of utilizing cumulative delta volume lies in its ability to reveal underlying market sentiment more accurately than simple price charts or raw volume data. By tracking whether buying or selling pressure accumulates over time, traders can identify shifts in momentum before they become apparent through conventional indicators.
For example, if the cumulative delta shows increasing buying pressure even as prices stagnate or decline slightly, it may signal an upcoming bullish reversal. Conversely, persistent selling pressure reflected by declining cumulative delta suggests bearish trends are likely to continue. This depth of insight helps traders anticipate moves rather than react after they occur.
Improved Risk Management Through Real-Time Data
Risk management remains a critical aspect of successful trading strategies—especially within volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. Cumulative delta volume provides real-time feedback on market strength and weakness by illustrating ongoing shifts in trader behavior.
By monitoring changes in the accumulated delta values alongside price action and other technical signals, traders can better gauge when to enter or exit positions. For instance:
- A sudden spike in positive cumulative delta might indicate strong buying interest that warrants taking profits.
- Conversely, a rapid decline could warn about increasing sell pressure requiring caution or position adjustments.
This proactive approach allows traders to manage their exposure more effectively rather than relying solely on lagging indicators such as moving averages.
Confirming Trade Signals for Greater Accuracy
Using multiple confirmation points enhances trade reliability—a principle well-supported by technical analysis best practices. Cumulative delta volume acts as an excellent confirmation tool when combined with other indicators like support/resistance levels or trend lines.
For example:
- If a breakout occurs alongside rising positive cumulative delta readings, confidence increases that the move reflects genuine buyer interest.
- Similarly, divergence between price action and declining negative deltas can signal weakening selling momentum before prices reverse direction.
Such confirmations reduce false signals and improve overall trade accuracy by aligning multiple facets of market data into cohesive insights rooted in trader behavior patterns.
Adaptability Across Different Market Conditions
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility driven by technological developments, regulatory news, macroeconomic factors, and investor sentiment swings. In these environments—where rapid changes happen frequently—the flexibility offered by cumulative delta volume becomes particularly valuable.
Because it captures real-time shifts in buyer-seller dominance regardless of broader trends or external influences—it adapts well across different phases:
- During trending markets (bullish/bearish), it helps confirm trend strength.
- In sideways consolidation periods (range-bound), it identifies subtle shifts indicating potential breakouts.
This adaptability makes cumulatedelta-based analysis suitable for both short-term scalping strategies and longer-term swing trades within dynamic crypto landscapes.
Integration With Advanced Analytical Techniques
Recent advancements have seen integration efforts where machine learning algorithms incorporate features derived from cumulative delta volumes into predictive models. These innovations aim at improving forecast accuracy further while automating complex analyses that would be difficult manually.
Such integrations enhance decision-making processes by providing quantitative backing grounded on behavioral finance principles embedded within cumulatedelta metrics—making them increasingly indispensable tools for professional traders seeking competitive edges.
Limitations To Keep In Mind
While there are numerous advantages associated with using cumulative delta volumes — including deeper insight into trader behavior — it's essential also to recognize some challenges:
- Complexity: Calculating accurate deltas requires advanced technical skills; errors can lead to misleading interpretations.
- Data Quality: Reliable results depend heavily on high-quality trade data feeds; inaccuracies here impair effectiveness.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As regulators scrutinize sophisticated trading tools' use within crypto markets—which often lack comprehensive oversight—traders should stay informed about evolving legal frameworks affecting their analytical methods.
Final Thoughts: Why Traders Should Consider Using Cumulative Delta Volume
In summary, incorporating cumulative delta volume into your cryptocurrency trading toolkit offers several compelling benefits—from enhanced sentiment analysis and improved risk management capabilities to better confirmation signals during volatile periods. Its ability to reflect real-time shifts driven by actual trader activity makes it especially valuable amid today's rapidly changing digital asset landscape where understanding underlying pressures can make all the difference between profit and loss.
Keywords: cryptocurrency trading advantages | what is cumulatedelta | risk management tools | technical analysis crypto | real-time market insights
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Clustering Algorithms (e.g., K-means) Categorize Technical Indicator Patterns?
Clustering algorithms have become essential tools in analyzing financial data, especially within the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency markets. They help traders and analysts identify hidden patterns in technical indicators, which are crucial for making informed trading decisions. Among these algorithms, K-means stands out due to its simplicity and effectiveness. This article explores how clustering algorithms like K-means categorize technical indicator patterns, their applications in crypto trading, recent technological advancements, and potential challenges.
Understanding Clustering Algorithms in Financial Data Analysis
Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning technique that groups data points based on their similarities without pre-labeled outcomes. Unlike classification models that require labeled training data, clustering identifies natural groupings within the dataset itself. In finance and cryptocurrency markets—where market behavior can be complex and unpredictable—clustering helps uncover underlying structures or recurring patterns that might not be immediately obvious.
In the context of technical analysis, clustering algorithms analyze historical price movements, volume data, or derived indicators to classify different market states or pattern types. This categorization enables traders to recognize similar scenarios quickly and adapt their strategies accordingly.
How Does K-means Work for Categorizing Technical Indicators?
K-means is one of the most widely used clustering methods because of its straightforward approach:
- Initialization: The algorithm begins by randomly selecting a predefined number of centroids (K). These centroids represent initial cluster centers.
- Assignment: Each data point—such as a specific value from a moving average or candlestick pattern—is assigned to the nearest centroid based on distance metrics like Euclidean distance.
- Update: Once all points are assigned, new centroids are calculated as the mean position of all points within each cluster.
- Iteration: Steps 2 and 3 repeat until convergence criteria are met—usually when cluster assignments stabilize or after reaching a set number of iterations.
This iterative process partitions large datasets into meaningful groups where each cluster shares similar characteristics concerning selected features like price momentum or volatility measures.
Applying Clustering to Technical Indicators in Cryptocurrency Markets
Technical indicators serve as mathematical representations derived from historical price and volume data; they help traders interpret market trends more objectively than raw prices alone. Clustering algorithms can analyze these indicators across different timeframes or assets to identify commonalities:
Candlestick Pattern Grouping: Candlestick charts visually depict price action over specific periods using various formations such as doji, hammer, shooting star etc., which often signal potential reversals or continuations. By applying K-means clustering on features extracted from candlestick shapes (like body size relative to wick length), traders can group similar patterns together—making it easier to spot recurring signals across different assets.
Moving Averages Classification: Moving averages smooth out short-term fluctuations but vary depending on period lengths (e.g., 50-day vs 200-day). Clustering these averages based on their performance during trending versus consolidating phases helps identify which types tend to predict future movements more reliably under certain conditions.
Volume-Based Indicators: Volume spikes often precede significant price moves; grouping such events through clustering allows for better anticipation of breakout scenarios.
By categorizing these patterns effectively through machine learning techniques like K-means, traders gain insights into market behavior clusters rather than relying solely on individual indicator readings.
Recent Developments Enhancing Clustering Applications
The integration of advanced technologies has significantly expanded what’s possible with clustering methods:
Artificial Intelligence & Deep Learning: Combining traditional clustering with deep neural networks enhances pattern recognition capabilities — especially when dealing with high-frequency trading data where complexity increases exponentially.
Real-Time Data Processing: Modern systems now enable live analysis using streaming market feeds; this means clusters can be updated dynamically as new information arrives—a critical advantage in volatile crypto markets where timing is everything.
Blockchain Technology Integration: Blockchain's transparent ledger ensures tamper-proof datasets for analysis purposes; this fosters trustworthiness when deploying automated pattern recognition systems based on clustered technical indicators.
These innovations allow traders not only to classify existing patterns but also adapt swiftly amidst changing market conditions while maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Challenges and Risks When Using Clustering Algorithms
Despite their advantages, applying clustering techniques involves certain pitfalls:
Overfitting Risks: If parameters such as the number of clusters (K) aren’t chosen carefully—or if models overly tailor themselves to historical data—they may perform poorly when faced with new unseen scenarios.
Data Quality Concerns: Noisy datasets caused by erroneous trades or incomplete records can lead clusters astray—misleading analysts about actual market states.
Regulatory Considerations: As AI-driven analytics become more prevalent in financial markets—including cryptocurrencies—regulators scrutinize transparency standards and fairness aspects related to automated decision-making processes involving sensitive financial information.
Addressing these issues requires rigorous validation procedures alongside continuous monitoring during deployment phases.
By leveraging sophisticated clustering algorithms like K-means within technical analysis frameworks—and staying aware of emerging technological trends—traders can enhance their ability to recognize meaningful chart patterns efficiently. However, understanding inherent limitations ensures responsible use aligned with best practices for risk management and compliance standards across evolving financial landscapes.
Key Takeaways:
- Unsupervised learning via clustering uncovers hidden structures in complex crypto-market datasets
- Techniques like K-means categorize candlestick formations & moving averages effectively
- Recent tech advances improve real-time adaptability & security via blockchain integration
- Caution needed regarding overfitting & data quality issues for reliable results


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 23:06
How do clustering algorithms (e.g., K-means) categorize technical indicator patterns?
How Do Clustering Algorithms (e.g., K-means) Categorize Technical Indicator Patterns?
Clustering algorithms have become essential tools in analyzing financial data, especially within the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency markets. They help traders and analysts identify hidden patterns in technical indicators, which are crucial for making informed trading decisions. Among these algorithms, K-means stands out due to its simplicity and effectiveness. This article explores how clustering algorithms like K-means categorize technical indicator patterns, their applications in crypto trading, recent technological advancements, and potential challenges.
Understanding Clustering Algorithms in Financial Data Analysis
Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning technique that groups data points based on their similarities without pre-labeled outcomes. Unlike classification models that require labeled training data, clustering identifies natural groupings within the dataset itself. In finance and cryptocurrency markets—where market behavior can be complex and unpredictable—clustering helps uncover underlying structures or recurring patterns that might not be immediately obvious.
In the context of technical analysis, clustering algorithms analyze historical price movements, volume data, or derived indicators to classify different market states or pattern types. This categorization enables traders to recognize similar scenarios quickly and adapt their strategies accordingly.
How Does K-means Work for Categorizing Technical Indicators?
K-means is one of the most widely used clustering methods because of its straightforward approach:
- Initialization: The algorithm begins by randomly selecting a predefined number of centroids (K). These centroids represent initial cluster centers.
- Assignment: Each data point—such as a specific value from a moving average or candlestick pattern—is assigned to the nearest centroid based on distance metrics like Euclidean distance.
- Update: Once all points are assigned, new centroids are calculated as the mean position of all points within each cluster.
- Iteration: Steps 2 and 3 repeat until convergence criteria are met—usually when cluster assignments stabilize or after reaching a set number of iterations.
This iterative process partitions large datasets into meaningful groups where each cluster shares similar characteristics concerning selected features like price momentum or volatility measures.
Applying Clustering to Technical Indicators in Cryptocurrency Markets
Technical indicators serve as mathematical representations derived from historical price and volume data; they help traders interpret market trends more objectively than raw prices alone. Clustering algorithms can analyze these indicators across different timeframes or assets to identify commonalities:
Candlestick Pattern Grouping: Candlestick charts visually depict price action over specific periods using various formations such as doji, hammer, shooting star etc., which often signal potential reversals or continuations. By applying K-means clustering on features extracted from candlestick shapes (like body size relative to wick length), traders can group similar patterns together—making it easier to spot recurring signals across different assets.
Moving Averages Classification: Moving averages smooth out short-term fluctuations but vary depending on period lengths (e.g., 50-day vs 200-day). Clustering these averages based on their performance during trending versus consolidating phases helps identify which types tend to predict future movements more reliably under certain conditions.
Volume-Based Indicators: Volume spikes often precede significant price moves; grouping such events through clustering allows for better anticipation of breakout scenarios.
By categorizing these patterns effectively through machine learning techniques like K-means, traders gain insights into market behavior clusters rather than relying solely on individual indicator readings.
Recent Developments Enhancing Clustering Applications
The integration of advanced technologies has significantly expanded what’s possible with clustering methods:
Artificial Intelligence & Deep Learning: Combining traditional clustering with deep neural networks enhances pattern recognition capabilities — especially when dealing with high-frequency trading data where complexity increases exponentially.
Real-Time Data Processing: Modern systems now enable live analysis using streaming market feeds; this means clusters can be updated dynamically as new information arrives—a critical advantage in volatile crypto markets where timing is everything.
Blockchain Technology Integration: Blockchain's transparent ledger ensures tamper-proof datasets for analysis purposes; this fosters trustworthiness when deploying automated pattern recognition systems based on clustered technical indicators.
These innovations allow traders not only to classify existing patterns but also adapt swiftly amidst changing market conditions while maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Challenges and Risks When Using Clustering Algorithms
Despite their advantages, applying clustering techniques involves certain pitfalls:
Overfitting Risks: If parameters such as the number of clusters (K) aren’t chosen carefully—or if models overly tailor themselves to historical data—they may perform poorly when faced with new unseen scenarios.
Data Quality Concerns: Noisy datasets caused by erroneous trades or incomplete records can lead clusters astray—misleading analysts about actual market states.
Regulatory Considerations: As AI-driven analytics become more prevalent in financial markets—including cryptocurrencies—regulators scrutinize transparency standards and fairness aspects related to automated decision-making processes involving sensitive financial information.
Addressing these issues requires rigorous validation procedures alongside continuous monitoring during deployment phases.
By leveraging sophisticated clustering algorithms like K-means within technical analysis frameworks—and staying aware of emerging technological trends—traders can enhance their ability to recognize meaningful chart patterns efficiently. However, understanding inherent limitations ensures responsible use aligned with best practices for risk management and compliance standards across evolving financial landscapes.
Key Takeaways:
- Unsupervised learning via clustering uncovers hidden structures in complex crypto-market datasets
- Techniques like K-means categorize candlestick formations & moving averages effectively
- Recent tech advances improve real-time adaptability & security via blockchain integration
- Caution needed regarding overfitting & data quality issues for reliable results
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How to Protect Your Crypto Assets from Scams
Cryptocurrency investments have surged in popularity, but with this growth comes an increased risk of scams and security breaches. Whether you're a seasoned trader or just starting out, understanding how to safeguard your digital assets is essential. This guide covers the most effective strategies to protect your crypto holdings from common threats like phishing, fraud, and hacking.
Understanding Common Cryptocurrency Scams
Crypto scams come in various forms, often targeting individuals who are less familiar with digital security practices. Phishing remains one of the most prevalent tactics—fraudulent emails or messages impersonate legitimate exchanges or service providers to steal private keys or login credentials. Ponzi schemes promise high returns but collapse once new investors stop joining. Fake exchanges lure users into depositing funds that are never recovered, while social engineering attacks manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information.
Recent incidents highlight these risks: for example, a widespread toll road scam via text messages has been circulating across the U.S., emphasizing how scammers exploit public trust and fear. Additionally, ransomware attacks on organizations like PowerSchool demonstrate ongoing extortion threats that can impact both institutions and individual users.
Use Secure Wallets for Storing Crypto Assets
A critical step in safeguarding your cryptocurrencies is choosing secure wallets designed specifically for crypto storage. Hardware wallets such as Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor offer cold storage solutions—meaning they are offline and immune to online hacking attempts—which significantly reduces vulnerability compared to hot wallets connected directly to the internet.
Multi-signature wallets add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple approvals before any transaction can be executed. This setup prevents unauthorized transfers even if one device or key is compromised. Always opt for reputable wallet providers with strong security track records rather than unverified options promising quick gains.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts related to cryptocurrency activities dramatically enhances account security. 2FA requires a second verification step—such as a code sent via SMS or generated through an authenticator app like Google Authenticator—to access your exchange accounts or wallets.
This measure ensures that even if someone obtains your password through phishing or data breaches, they cannot access your assets without the second factor—a crucial safeguard given recent data breaches at platforms like Coinbase exposed user information but did not necessarily compromise assets directly when 2FA was enabled.
Be Vigilant Against Phishing Attempts
Phishing remains one of the leading causes of asset theft in crypto markets today. Always verify URLs before entering login details; scammers often create fake websites resembling legitimate exchanges such as Binance or Coinbase to trick users into revealing private keys or passwords.
Avoid clicking links from unsolicited emails or messages claiming urgent issues with your account unless you confirm their authenticity through official channels. Remember: reputable services will never ask you for sensitive information via email nor request private keys under any circumstances.
Keep Software Up-to-Date
Cybercriminals frequently exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software systems—be it operating systems, browsers, or wallet applications—to gain unauthorized access to devices containing crypto assets. Regularly updating all software ensures you benefit from patches fixing known security flaws.
Set automatic updates where possible and avoid downloading files from untrusted sources. Using up-to-date antivirus programs adds another layer of defense against malware designed explicitly for stealing cryptocurrencies stored on infected devices.
Monitor Accounts Regularly
Active monitoring helps detect suspicious activity early before significant damage occurs. Many exchanges provide alert features—for example, notifications about large transactions—that enable prompt responses if something unusual happens within your account history.
Periodically review transaction histories across all platforms linked with your holdings; unfamiliar transfers should trigger immediate investigation and potential reporting to authorities if necessary.
Educate Yourself About Security Best Practices
Staying informed about emerging scams and evolving cybersecurity techniques empowers you against potential threats effectively reducing vulnerability exposure over time.Follow trusted industry sources such as official exchange blogs, cybersecurity news outlets specializing in blockchain technology updates—and participate in community forums where experienced traders share insights.Understanding concepts like seed phrases recovery methods further enhances resilience against hardware failures while maintaining control over private keys securely stored offline.
Choose Reputable Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Not all trading platforms are created equal; some may lack robust security measures making them attractive targets for hackers.Prioritize well-established exchanges known for strong regulatory compliance standards—including multi-layered security protocols—and transparent operational histories.Avoid new entrants without verifiable credentials who might be more susceptible targets due to weaker defenses.
Diversify Your Investments
Spreading investments across multiple cryptocurrencies reduces overall risk exposure associated with individual token volatility—or targeted scams aimed at specific coins.Implementing diversification strategies also minimizes potential losses should one asset become compromised due to unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Use Advanced Security Tools
Beyond basic protections like 2FA and secure wallets — consider deploying additional tools:
- Anti-virus software capable of detecting malware targeting cryptocurrency files
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) ensuring encrypted online activity
- Hardware-based biometric authentication methods where available
These measures collectively strengthen defenses against cyberattacks aiming at stealing digital assets
Report Suspicious Activity Promptly
If you encounter suspicious emails, links claiming false promotions, unexpected transfer requests—or notice irregularities within accounts—report immediately:
- Contact customer support through verified channels
- Notify relevant authorities such as local cybercrime unitsSharing experiences within trusted communities helps others recognize similar threats early
Staying Ahead: The Future of Crypto Asset Security
Recent developments indicate increasing sophistication among scammers alongside advancements in protective technologies:
- Enhanced AI-driven fraud detection models by companies like Stripe now identify hundreds more subtle transaction signals—raising detection rates significantly
- Major players including Google are expanding their online scam protection features beyond tech support fraud toward broader threat categories
Simultaneously evolving regulations aim at creating safer environments but require active participation from users committed to best practices
By adopting comprehensive safety measures—from using secure hardware wallets and enabling two-factor authentication—to staying informed about latest scams—you can significantly reduce risks associated with cryptocurrency investments.
Remember: Protecting digital assets isn’t a one-time effort but an ongoing process requiring vigilance amid constantly changing threat landscapes.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 06:04
What are the most effective ways to protect my crypto assets from scams?
How to Protect Your Crypto Assets from Scams
Cryptocurrency investments have surged in popularity, but with this growth comes an increased risk of scams and security breaches. Whether you're a seasoned trader or just starting out, understanding how to safeguard your digital assets is essential. This guide covers the most effective strategies to protect your crypto holdings from common threats like phishing, fraud, and hacking.
Understanding Common Cryptocurrency Scams
Crypto scams come in various forms, often targeting individuals who are less familiar with digital security practices. Phishing remains one of the most prevalent tactics—fraudulent emails or messages impersonate legitimate exchanges or service providers to steal private keys or login credentials. Ponzi schemes promise high returns but collapse once new investors stop joining. Fake exchanges lure users into depositing funds that are never recovered, while social engineering attacks manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information.
Recent incidents highlight these risks: for example, a widespread toll road scam via text messages has been circulating across the U.S., emphasizing how scammers exploit public trust and fear. Additionally, ransomware attacks on organizations like PowerSchool demonstrate ongoing extortion threats that can impact both institutions and individual users.
Use Secure Wallets for Storing Crypto Assets
A critical step in safeguarding your cryptocurrencies is choosing secure wallets designed specifically for crypto storage. Hardware wallets such as Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor offer cold storage solutions—meaning they are offline and immune to online hacking attempts—which significantly reduces vulnerability compared to hot wallets connected directly to the internet.
Multi-signature wallets add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple approvals before any transaction can be executed. This setup prevents unauthorized transfers even if one device or key is compromised. Always opt for reputable wallet providers with strong security track records rather than unverified options promising quick gains.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts related to cryptocurrency activities dramatically enhances account security. 2FA requires a second verification step—such as a code sent via SMS or generated through an authenticator app like Google Authenticator—to access your exchange accounts or wallets.
This measure ensures that even if someone obtains your password through phishing or data breaches, they cannot access your assets without the second factor—a crucial safeguard given recent data breaches at platforms like Coinbase exposed user information but did not necessarily compromise assets directly when 2FA was enabled.
Be Vigilant Against Phishing Attempts
Phishing remains one of the leading causes of asset theft in crypto markets today. Always verify URLs before entering login details; scammers often create fake websites resembling legitimate exchanges such as Binance or Coinbase to trick users into revealing private keys or passwords.
Avoid clicking links from unsolicited emails or messages claiming urgent issues with your account unless you confirm their authenticity through official channels. Remember: reputable services will never ask you for sensitive information via email nor request private keys under any circumstances.
Keep Software Up-to-Date
Cybercriminals frequently exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software systems—be it operating systems, browsers, or wallet applications—to gain unauthorized access to devices containing crypto assets. Regularly updating all software ensures you benefit from patches fixing known security flaws.
Set automatic updates where possible and avoid downloading files from untrusted sources. Using up-to-date antivirus programs adds another layer of defense against malware designed explicitly for stealing cryptocurrencies stored on infected devices.
Monitor Accounts Regularly
Active monitoring helps detect suspicious activity early before significant damage occurs. Many exchanges provide alert features—for example, notifications about large transactions—that enable prompt responses if something unusual happens within your account history.
Periodically review transaction histories across all platforms linked with your holdings; unfamiliar transfers should trigger immediate investigation and potential reporting to authorities if necessary.
Educate Yourself About Security Best Practices
Staying informed about emerging scams and evolving cybersecurity techniques empowers you against potential threats effectively reducing vulnerability exposure over time.Follow trusted industry sources such as official exchange blogs, cybersecurity news outlets specializing in blockchain technology updates—and participate in community forums where experienced traders share insights.Understanding concepts like seed phrases recovery methods further enhances resilience against hardware failures while maintaining control over private keys securely stored offline.
Choose Reputable Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Not all trading platforms are created equal; some may lack robust security measures making them attractive targets for hackers.Prioritize well-established exchanges known for strong regulatory compliance standards—including multi-layered security protocols—and transparent operational histories.Avoid new entrants without verifiable credentials who might be more susceptible targets due to weaker defenses.
Diversify Your Investments
Spreading investments across multiple cryptocurrencies reduces overall risk exposure associated with individual token volatility—or targeted scams aimed at specific coins.Implementing diversification strategies also minimizes potential losses should one asset become compromised due to unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Use Advanced Security Tools
Beyond basic protections like 2FA and secure wallets — consider deploying additional tools:
- Anti-virus software capable of detecting malware targeting cryptocurrency files
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) ensuring encrypted online activity
- Hardware-based biometric authentication methods where available
These measures collectively strengthen defenses against cyberattacks aiming at stealing digital assets
Report Suspicious Activity Promptly
If you encounter suspicious emails, links claiming false promotions, unexpected transfer requests—or notice irregularities within accounts—report immediately:
- Contact customer support through verified channels
- Notify relevant authorities such as local cybercrime unitsSharing experiences within trusted communities helps others recognize similar threats early
Staying Ahead: The Future of Crypto Asset Security
Recent developments indicate increasing sophistication among scammers alongside advancements in protective technologies:
- Enhanced AI-driven fraud detection models by companies like Stripe now identify hundreds more subtle transaction signals—raising detection rates significantly
- Major players including Google are expanding their online scam protection features beyond tech support fraud toward broader threat categories
Simultaneously evolving regulations aim at creating safer environments but require active participation from users committed to best practices
By adopting comprehensive safety measures—from using secure hardware wallets and enabling two-factor authentication—to staying informed about latest scams—you can significantly reduce risks associated with cryptocurrency investments.
Remember: Protecting digital assets isn’t a one-time effort but an ongoing process requiring vigilance amid constantly changing threat landscapes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Are Cryptocurrency Gains Taxed?
Understanding how cryptocurrency gains are taxed is essential for investors, traders, and financial professionals navigating the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. As governments worldwide adapt their tax policies to address cryptocurrencies, staying informed about current regulations helps ensure compliance and optimize tax strategies.
Cryptocurrency Taxation in the United States
In the U.S., the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin as property rather than currency. This classification means that any gains or losses from buying, selling, or exchanging digital assets are subject to capital gains tax. When you sell or trade cryptocurrency at a profit, it triggers a taxable event. The IRS requires taxpayers to report these transactions using Form 8949 and Schedule D on their annual tax returns.
Recent legislative changes have increased reporting obligations for crypto transactions. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021 introduced new rules effective from 2023 that mandate reporting transactions exceeding $10,000 in cash to the IRS. These measures aim to improve transparency but also add layers of complexity for taxpayers who must track detailed transaction histories across multiple platforms.
It's important for U.S.-based investors to maintain meticulous records of all crypto activities—purchases, sales, exchanges—to accurately calculate gains or losses and avoid penalties during audits.
How Europe Approaches Cryptocurrency Taxation
Across Europe, taxation policies regarding cryptocurrencies vary significantly by country due to the absence of a unified EU-wide framework. For example:
- Germany considers cryptocurrencies as private assets held for more than one year exempt from capital gains tax if sold after this period; otherwise, they are taxable.
- The UK treats cryptocurrencies as intangible assets subject to capital gains tax (CGT). HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC) requires individuals and businesses engaging in crypto transactions to report profits or losses similarly to other investments.
While some countries provide favorable treatment for long-term holdings or specific types of transactions, others impose taxes on every sale regardless of holding period. This patchwork approach underscores the importance of understanding local laws when investing across borders.
Missouri's Legislation Impacting Crypto Gains
In May 2025, Missouri enacted legislation exempting gold and silver from state capital gains taxes—a move designed to promote investment in precious metals as alternative stores of value. Although this law directly pertains only to physical commodities like gold and silver within Missouri’s jurisdiction,
it signals a broader trend toward recognizing tangible assets' role alongside digital ones like cryptocurrencies. Such legislative shifts could influence investor behavior by offering more diverse options with potentially favorable tax treatment compared with traditional crypto holdings.
However, it's crucial for investors outside Missouri not to assume similar exemptions apply elsewhere; each jurisdiction maintains its own rules governing digital asset taxation.
Recent Developments Shaping Crypto Tax Policies
The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrency taxation continues rapidly evolving:
The U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been actively scrutinizing crypto markets with potential rule changes anticipated in Q2-Q3 2025 that could impact financial products such as Bitcoin ETFs offered through firms like ARK 21Shares.
Increased focus on compliance has led many companies involved in blockchain investments—such as Blockchain Coinvestors Acquisition Corp.—to adapt their operations accordingly amid heightened regulatory oversight.
These developments aim at enhancing investor protections but may also introduce additional compliance burdens that can influence market dynamics significantly over time.
Potential Challenges Due To Changing Regulations
As authorities refine their approach toward taxing cryptocurrency gains:
Investors face growing complexity when calculating taxable events due mainly because different jurisdictions have varying definitions around what constitutes taxable income.
Misunderstanding reporting requirements can lead not only to unintentional non-compliance but also penalties or audits—especially given recent tightening enforcement measures.
Regulatory uncertainty remains high globally; inconsistent laws across countries make cross-border investments riskier without thorough legal guidance tailored specifically per region’s rules.
Key Takeaways:
- Keep detailed records: Track all your crypto transactions meticulously.
- Stay updated: Follow legislative changes affecting your jurisdiction regularly.
- Consult professionals: Work with qualified accountants familiar with digital assets’ taxation nuances.
Navigating Future Changes in Cryptocurrency Tax Laws
As governments continue refining their approaches toward taxing digital currencies—including potential new regulations announced by agencies like SEC—the landscape will remain dynamic well into future years. Investors should proactively monitor policy shifts while seeking expert advice where necessary so they can adapt strategies accordingly—and avoid costly mistakes stemming from misunderstandings about applicable laws.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency gain taxation is complex but manageable when approached with proper knowledge and planning. With ongoing legislative updates—from U.S.-specific reforms under recent acts like infrastructure bills—to regional variations across Europe—and emerging trends such as exemptions on tangible assets—the key lies in staying informed about current regulations relevant both locally and internationally. By doing so responsibly ensures compliance while maximizing investment outcomes amidst an ever-changing regulatory environment.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 01:44
How are cryptocurrency gains taxed?
How Are Cryptocurrency Gains Taxed?
Understanding how cryptocurrency gains are taxed is essential for investors, traders, and financial professionals navigating the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. As governments worldwide adapt their tax policies to address cryptocurrencies, staying informed about current regulations helps ensure compliance and optimize tax strategies.
Cryptocurrency Taxation in the United States
In the U.S., the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin as property rather than currency. This classification means that any gains or losses from buying, selling, or exchanging digital assets are subject to capital gains tax. When you sell or trade cryptocurrency at a profit, it triggers a taxable event. The IRS requires taxpayers to report these transactions using Form 8949 and Schedule D on their annual tax returns.
Recent legislative changes have increased reporting obligations for crypto transactions. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021 introduced new rules effective from 2023 that mandate reporting transactions exceeding $10,000 in cash to the IRS. These measures aim to improve transparency but also add layers of complexity for taxpayers who must track detailed transaction histories across multiple platforms.
It's important for U.S.-based investors to maintain meticulous records of all crypto activities—purchases, sales, exchanges—to accurately calculate gains or losses and avoid penalties during audits.
How Europe Approaches Cryptocurrency Taxation
Across Europe, taxation policies regarding cryptocurrencies vary significantly by country due to the absence of a unified EU-wide framework. For example:
- Germany considers cryptocurrencies as private assets held for more than one year exempt from capital gains tax if sold after this period; otherwise, they are taxable.
- The UK treats cryptocurrencies as intangible assets subject to capital gains tax (CGT). HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC) requires individuals and businesses engaging in crypto transactions to report profits or losses similarly to other investments.
While some countries provide favorable treatment for long-term holdings or specific types of transactions, others impose taxes on every sale regardless of holding period. This patchwork approach underscores the importance of understanding local laws when investing across borders.
Missouri's Legislation Impacting Crypto Gains
In May 2025, Missouri enacted legislation exempting gold and silver from state capital gains taxes—a move designed to promote investment in precious metals as alternative stores of value. Although this law directly pertains only to physical commodities like gold and silver within Missouri’s jurisdiction,
it signals a broader trend toward recognizing tangible assets' role alongside digital ones like cryptocurrencies. Such legislative shifts could influence investor behavior by offering more diverse options with potentially favorable tax treatment compared with traditional crypto holdings.
However, it's crucial for investors outside Missouri not to assume similar exemptions apply elsewhere; each jurisdiction maintains its own rules governing digital asset taxation.
Recent Developments Shaping Crypto Tax Policies
The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrency taxation continues rapidly evolving:
The U.S Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been actively scrutinizing crypto markets with potential rule changes anticipated in Q2-Q3 2025 that could impact financial products such as Bitcoin ETFs offered through firms like ARK 21Shares.
Increased focus on compliance has led many companies involved in blockchain investments—such as Blockchain Coinvestors Acquisition Corp.—to adapt their operations accordingly amid heightened regulatory oversight.
These developments aim at enhancing investor protections but may also introduce additional compliance burdens that can influence market dynamics significantly over time.
Potential Challenges Due To Changing Regulations
As authorities refine their approach toward taxing cryptocurrency gains:
Investors face growing complexity when calculating taxable events due mainly because different jurisdictions have varying definitions around what constitutes taxable income.
Misunderstanding reporting requirements can lead not only to unintentional non-compliance but also penalties or audits—especially given recent tightening enforcement measures.
Regulatory uncertainty remains high globally; inconsistent laws across countries make cross-border investments riskier without thorough legal guidance tailored specifically per region’s rules.
Key Takeaways:
- Keep detailed records: Track all your crypto transactions meticulously.
- Stay updated: Follow legislative changes affecting your jurisdiction regularly.
- Consult professionals: Work with qualified accountants familiar with digital assets’ taxation nuances.
Navigating Future Changes in Cryptocurrency Tax Laws
As governments continue refining their approaches toward taxing digital currencies—including potential new regulations announced by agencies like SEC—the landscape will remain dynamic well into future years. Investors should proactively monitor policy shifts while seeking expert advice where necessary so they can adapt strategies accordingly—and avoid costly mistakes stemming from misunderstandings about applicable laws.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency gain taxation is complex but manageable when approached with proper knowledge and planning. With ongoing legislative updates—from U.S.-specific reforms under recent acts like infrastructure bills—to regional variations across Europe—and emerging trends such as exemptions on tangible assets—the key lies in staying informed about current regulations relevant both locally and internationally. By doing so responsibly ensures compliance while maximizing investment outcomes amidst an ever-changing regulatory environment.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Difference Between a Hardware Wallet and a Software Wallet?
Understanding Cryptocurrency Storage Options
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream, securing digital assets has become a top priority for investors and users alike. The two primary types of wallets—hardware wallets and software wallets—serve different purposes and offer varying levels of security. Knowing the differences between these options helps users make informed decisions aligned with their security needs, convenience preferences, and investment strategies.
Hardware Wallets: Physical Devices for Secure Storage
A hardware wallet is a physical device designed specifically to store cryptocurrency private keys offline. These devices often resemble USB drives or small electronic gadgets, making them portable yet secure. By keeping private keys offline, hardware wallets significantly reduce exposure to hacking attempts that target online vulnerabilities.
The core advantage of hardware wallets lies in their enhanced security features. Since private keys are stored within the device's secure environment and never leave it during transactions, they are less susceptible to malware or phishing attacks that can compromise software-based solutions. Popular models like Ledger Nano S/X, Trezor Model T, and KeepKey have established reputations for robust security protocols.
In addition to security benefits, hardware wallets typically feature user-friendly interfaces—either built-in screens or companion apps—that facilitate easy management of multiple cryptocurrencies. They also support backup options; users can generate seed phrases (recovery phrases) that allow wallet restoration if the device is lost or damaged.
However, hardware wallets do require an initial setup process which might be slightly complex for beginners but provides peace of mind once configured properly. Their cost varies but generally ranges from $50 to over $200 depending on features.
Software Wallets: Digital Applications for Accessibility
Software wallets are applications installed on computers or mobile devices that enable quick access to cryptocurrencies at any time with an internet connection. They come in various forms such as desktop apps (e.g., Electrum), mobile apps (e.g., Trust Wallet), browser extensions (e.g., MetaMask), or web-based platforms like Coinbase Wallet.
These wallets prioritize convenience and ease of use—ideal for frequent traders or those managing smaller amounts of crypto assets. Since they run on internet-connected devices, transactions can be executed swiftly without needing physical devices; this makes them highly accessible from anywhere globally.
Popular examples include MetaMask—a Web3 wallet primarily used with decentralized applications—and MyEtherWallet which offers straightforward Ethereum asset management directly through browsers without requiring downloads beyond initial setup.
While software wallets provide significant convenience—they often feature intuitive interfaces—they inherently carry higher risks due to their online nature. Private keys stored within these applications could potentially be targeted by hackers if proper cybersecurity measures aren’t followed—for example: using strong passwords or enabling two-factor authentication (2FA).
Balancing Security With Convenience
Choosing between a hardware wallet and a software wallet depends largely on individual priorities:
- Security-focused users who hold large amounts of cryptocurrency should consider investing in a hardware wallet due to its offline storage capabilities.
- Casual investors engaging in frequent trading may prefer software solutions because they offer immediate access without additional steps.
- Hybrid approaches are also common; many users keep most assets secured offline while maintaining smaller balances on hot-wallets for daily transactions.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape surrounding cryptocurrency storage continues evolving rapidly:
Security Incidents Highlight Risks: High-profile hacks like Bitfinex’s 2016 breach underscored vulnerabilities associated with online storage methods—prompting increased adoption of cold storage solutions such as hardware wallets.
Advancements in Hardware Technology: Manufacturers like Ledger have introduced innovations such as Ledger Live—a dedicated app streamlining asset management directly through secure devices—which enhances user experience while maintaining high-security standards.
Regulatory Impact: Governments worldwide are tightening regulations around digital asset custody practices amid concerns about fraud prevention and investor protection—pushing both providers and users toward more compliant storage solutions.
Educational Efforts: As awareness grows about potential risks—including phishing scams targeting software-wallet holders—the industry emphasizes educating consumers about best practices in securing their crypto holdings across all types of digital wallets.
Potential Future Outlook
Given increasing regulatory scrutiny coupled with rising cyber threats targeting online platforms, there’s likely going to be greater emphasis on adopting more secure storage methods such as hardware solutions among both individual investors and institutional players alike.
Moreover, technological innovations may further bridge usability gaps by integrating advanced biometric authentication into hardware devices or developing hybrid models combining elements from both categories—for example: firmware updates enabling seamless transaction signing while maintaining offline key safety measures.
Key Considerations When Choosing Your Crypto Wallet
When selecting between a hardware versus software wallet—or even considering hybrid options—it’s essential to evaluate factors including:
- The amount of cryptocurrency you plan to store
- Frequency of transactions
- Level of technical expertise
- Budget constraints
- Long-term security goals
By aligning your choice with these considerations—and staying informed about recent developments—you can better safeguard your digital assets against evolving threats.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms:cryptocurrency storage options | cold vs hot wallet | private key security | blockchain asset management | crypto investment safety | multi-currency compatibility | seed phrase backup | cyberattack prevention | digital currency protection
User Intent Fulfillment
This overview aims at helping readers understand fundamental differences between two prevalent types of crypto wallets—from basic definitions through practical considerations—to empower them in making choices tailored specifically towards their needs while highlighting recent trends shaping the industry today.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-11 11:06
What is the difference between a hardware wallet and a software wallet?
What Is the Difference Between a Hardware Wallet and a Software Wallet?
Understanding Cryptocurrency Storage Options
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream, securing digital assets has become a top priority for investors and users alike. The two primary types of wallets—hardware wallets and software wallets—serve different purposes and offer varying levels of security. Knowing the differences between these options helps users make informed decisions aligned with their security needs, convenience preferences, and investment strategies.
Hardware Wallets: Physical Devices for Secure Storage
A hardware wallet is a physical device designed specifically to store cryptocurrency private keys offline. These devices often resemble USB drives or small electronic gadgets, making them portable yet secure. By keeping private keys offline, hardware wallets significantly reduce exposure to hacking attempts that target online vulnerabilities.
The core advantage of hardware wallets lies in their enhanced security features. Since private keys are stored within the device's secure environment and never leave it during transactions, they are less susceptible to malware or phishing attacks that can compromise software-based solutions. Popular models like Ledger Nano S/X, Trezor Model T, and KeepKey have established reputations for robust security protocols.
In addition to security benefits, hardware wallets typically feature user-friendly interfaces—either built-in screens or companion apps—that facilitate easy management of multiple cryptocurrencies. They also support backup options; users can generate seed phrases (recovery phrases) that allow wallet restoration if the device is lost or damaged.
However, hardware wallets do require an initial setup process which might be slightly complex for beginners but provides peace of mind once configured properly. Their cost varies but generally ranges from $50 to over $200 depending on features.
Software Wallets: Digital Applications for Accessibility
Software wallets are applications installed on computers or mobile devices that enable quick access to cryptocurrencies at any time with an internet connection. They come in various forms such as desktop apps (e.g., Electrum), mobile apps (e.g., Trust Wallet), browser extensions (e.g., MetaMask), or web-based platforms like Coinbase Wallet.
These wallets prioritize convenience and ease of use—ideal for frequent traders or those managing smaller amounts of crypto assets. Since they run on internet-connected devices, transactions can be executed swiftly without needing physical devices; this makes them highly accessible from anywhere globally.
Popular examples include MetaMask—a Web3 wallet primarily used with decentralized applications—and MyEtherWallet which offers straightforward Ethereum asset management directly through browsers without requiring downloads beyond initial setup.
While software wallets provide significant convenience—they often feature intuitive interfaces—they inherently carry higher risks due to their online nature. Private keys stored within these applications could potentially be targeted by hackers if proper cybersecurity measures aren’t followed—for example: using strong passwords or enabling two-factor authentication (2FA).
Balancing Security With Convenience
Choosing between a hardware wallet and a software wallet depends largely on individual priorities:
- Security-focused users who hold large amounts of cryptocurrency should consider investing in a hardware wallet due to its offline storage capabilities.
- Casual investors engaging in frequent trading may prefer software solutions because they offer immediate access without additional steps.
- Hybrid approaches are also common; many users keep most assets secured offline while maintaining smaller balances on hot-wallets for daily transactions.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape surrounding cryptocurrency storage continues evolving rapidly:
Security Incidents Highlight Risks: High-profile hacks like Bitfinex’s 2016 breach underscored vulnerabilities associated with online storage methods—prompting increased adoption of cold storage solutions such as hardware wallets.
Advancements in Hardware Technology: Manufacturers like Ledger have introduced innovations such as Ledger Live—a dedicated app streamlining asset management directly through secure devices—which enhances user experience while maintaining high-security standards.
Regulatory Impact: Governments worldwide are tightening regulations around digital asset custody practices amid concerns about fraud prevention and investor protection—pushing both providers and users toward more compliant storage solutions.
Educational Efforts: As awareness grows about potential risks—including phishing scams targeting software-wallet holders—the industry emphasizes educating consumers about best practices in securing their crypto holdings across all types of digital wallets.
Potential Future Outlook
Given increasing regulatory scrutiny coupled with rising cyber threats targeting online platforms, there’s likely going to be greater emphasis on adopting more secure storage methods such as hardware solutions among both individual investors and institutional players alike.
Moreover, technological innovations may further bridge usability gaps by integrating advanced biometric authentication into hardware devices or developing hybrid models combining elements from both categories—for example: firmware updates enabling seamless transaction signing while maintaining offline key safety measures.
Key Considerations When Choosing Your Crypto Wallet
When selecting between a hardware versus software wallet—or even considering hybrid options—it’s essential to evaluate factors including:
- The amount of cryptocurrency you plan to store
- Frequency of transactions
- Level of technical expertise
- Budget constraints
- Long-term security goals
By aligning your choice with these considerations—and staying informed about recent developments—you can better safeguard your digital assets against evolving threats.
Semantic Keywords & Related Terms:cryptocurrency storage options | cold vs hot wallet | private key security | blockchain asset management | crypto investment safety | multi-currency compatibility | seed phrase backup | cyberattack prevention | digital currency protection
User Intent Fulfillment
This overview aims at helping readers understand fundamental differences between two prevalent types of crypto wallets—from basic definitions through practical considerations—to empower them in making choices tailored specifically towards their needs while highlighting recent trends shaping the industry today.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Does It Mean When ADX Crosses Its Signal Line?
The Average Directional Index (ADX) is a widely used technical indicator that helps traders assess the strength of a prevailing trend in the market. When analyzing price movements, understanding what it signifies when the ADX crosses its signal line can be crucial for making informed trading decisions. This event often signals a shift in trend momentum, either strengthening or weakening, which can influence entry and exit points for traders.
Understanding the ADX and Its Signal Line
The ADX measures trend strength on a scale from 0 to 100. Values below 20 typically indicate weak or no clear trend, while readings above 40 suggest strong trending behavior. The signal line associated with ADX is usually a moving average—commonly a 14-period simple moving average—of the ADX values themselves. This smoothing helps filter out short-term fluctuations and provides clearer signals regarding trend changes.
When traders observe that the ADX crosses above its signal line, it generally indicates that the current trend is gaining strength. Conversely, if it crosses below this line, it suggests that the existing trend may be losing momentum or reversing.
Interpreting Bullish Crossovers
A bullish crossover occurs when the ADX moves from below to above its signal line. This event often signals that an existing uptrend is strengthening or about to begin. Traders interpret this as an indication to consider entering long positions or adding to existing ones because momentum appears favorable for upward price movement.
However, it's important not to rely solely on this crossover; combining it with other technical indicators such as Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), or volume analysis enhances decision-making accuracy. In volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, where sudden shifts are common, confirming signals help mitigate false positives.
Recognizing Bearish Crossovers
On the flip side, when the ADX dips below its signal line after being above it—or if it simply crosses downward—it suggests weakening of current trends. For example:
- An existing bullish market might be losing steam.
- A downtrend could be intensifying if accompanied by other bearish indicators.
This scenario often prompts traders to consider reducing their long exposure or preparing for potential reversals by setting stop-loss orders or taking profits.
Significance in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets are characterized by high volatility and rapid price swings compared to traditional assets like stocks or commodities. As such, technical tools like ADX crossing its signal line become particularly valuable for crypto traders seeking clarity amid chaos.
In recent market observations—for instance:
- ApeCoin (APEUSD) on April 24th showed mixed momentum despite some bullish bias; here an impending cross could hint at consolidation unless new trends develop.
- Ethena (ENAUSD) around May 2nd did not show explicit recent crossings but remains under close watch due to ongoing volatility patterns.
These instances highlight how monitoring such crossings can provide early insights into potential shifts before significant price moves occur.
Practical Implications for Traders
Understanding what an ADX crossing signifies allows traders to:
- Confirm whether current trends are gaining strength.
- Anticipate possible reversals.
- Adjust their trading strategies accordingly—whether entering new trades during confirmed breakouts or exiting positions ahead of reversals.
It’s also essential for risk management: false signals do happen especially in highly volatile environments like crypto markets; hence using additional confirmation tools reduces risk exposure effectively.
How To Use The Crossing of ADX and Its Signal Line Effectively?
To maximize benefits from this indicator event:
- Combine with other technical analysis tools such as RSI for overbought/oversold conditions.
- Watch volume levels—rising volume alongside an upward crossing strengthens confidence.
- Consider overall market sentiment and news events which might influence abrupt movements regardless of technical signals.
- Set appropriate stop-loss orders based on recent support/resistance levels rather than relying solely on indicator signals.
Final Thoughts: Monitoring Trend Strengths With Confidence
The crossing of the ADX over its signal line serves as a vital cue within technical analysis frameworks—especially relevant in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies where timing can significantly impact profitability and risk management strategies.
By understanding these dynamics thoroughly—and integrating them into broader analytical approaches—traders enhance their ability to navigate complex market conditions confidently while maintaining adherence to sound trading principles rooted in data-driven insights.
Keywords:
ADX crossing signal line
Trend strength indicator
Crypto trading strategies
Technical analysis crypto
Market reversal signals
Cryptocurrency volatility tools


Lo
2025-05-14 05:07
What is the interpretation of ADX crossing its signal line?
What Does It Mean When ADX Crosses Its Signal Line?
The Average Directional Index (ADX) is a widely used technical indicator that helps traders assess the strength of a prevailing trend in the market. When analyzing price movements, understanding what it signifies when the ADX crosses its signal line can be crucial for making informed trading decisions. This event often signals a shift in trend momentum, either strengthening or weakening, which can influence entry and exit points for traders.
Understanding the ADX and Its Signal Line
The ADX measures trend strength on a scale from 0 to 100. Values below 20 typically indicate weak or no clear trend, while readings above 40 suggest strong trending behavior. The signal line associated with ADX is usually a moving average—commonly a 14-period simple moving average—of the ADX values themselves. This smoothing helps filter out short-term fluctuations and provides clearer signals regarding trend changes.
When traders observe that the ADX crosses above its signal line, it generally indicates that the current trend is gaining strength. Conversely, if it crosses below this line, it suggests that the existing trend may be losing momentum or reversing.
Interpreting Bullish Crossovers
A bullish crossover occurs when the ADX moves from below to above its signal line. This event often signals that an existing uptrend is strengthening or about to begin. Traders interpret this as an indication to consider entering long positions or adding to existing ones because momentum appears favorable for upward price movement.
However, it's important not to rely solely on this crossover; combining it with other technical indicators such as Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), or volume analysis enhances decision-making accuracy. In volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, where sudden shifts are common, confirming signals help mitigate false positives.
Recognizing Bearish Crossovers
On the flip side, when the ADX dips below its signal line after being above it—or if it simply crosses downward—it suggests weakening of current trends. For example:
- An existing bullish market might be losing steam.
- A downtrend could be intensifying if accompanied by other bearish indicators.
This scenario often prompts traders to consider reducing their long exposure or preparing for potential reversals by setting stop-loss orders or taking profits.
Significance in Cryptocurrency Markets
Cryptocurrency markets are characterized by high volatility and rapid price swings compared to traditional assets like stocks or commodities. As such, technical tools like ADX crossing its signal line become particularly valuable for crypto traders seeking clarity amid chaos.
In recent market observations—for instance:
- ApeCoin (APEUSD) on April 24th showed mixed momentum despite some bullish bias; here an impending cross could hint at consolidation unless new trends develop.
- Ethena (ENAUSD) around May 2nd did not show explicit recent crossings but remains under close watch due to ongoing volatility patterns.
These instances highlight how monitoring such crossings can provide early insights into potential shifts before significant price moves occur.
Practical Implications for Traders
Understanding what an ADX crossing signifies allows traders to:
- Confirm whether current trends are gaining strength.
- Anticipate possible reversals.
- Adjust their trading strategies accordingly—whether entering new trades during confirmed breakouts or exiting positions ahead of reversals.
It’s also essential for risk management: false signals do happen especially in highly volatile environments like crypto markets; hence using additional confirmation tools reduces risk exposure effectively.
How To Use The Crossing of ADX and Its Signal Line Effectively?
To maximize benefits from this indicator event:
- Combine with other technical analysis tools such as RSI for overbought/oversold conditions.
- Watch volume levels—rising volume alongside an upward crossing strengthens confidence.
- Consider overall market sentiment and news events which might influence abrupt movements regardless of technical signals.
- Set appropriate stop-loss orders based on recent support/resistance levels rather than relying solely on indicator signals.
Final Thoughts: Monitoring Trend Strengths With Confidence
The crossing of the ADX over its signal line serves as a vital cue within technical analysis frameworks—especially relevant in fast-moving markets like cryptocurrencies where timing can significantly impact profitability and risk management strategies.
By understanding these dynamics thoroughly—and integrating them into broader analytical approaches—traders enhance their ability to navigate complex market conditions confidently while maintaining adherence to sound trading principles rooted in data-driven insights.
Keywords:
ADX crossing signal line
Trend strength indicator
Crypto trading strategies
Technical analysis crypto
Market reversal signals
Cryptocurrency volatility tools
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Platform Do I Need to Use to Access the TRUMP Tutorial?
Understanding how to access educational resources like the TRUMP tutorial platform is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency and digital asset investments. As a growing trend in financial education, platforms such as TRUMP aim to provide comprehensive guides, tutorials, and insights that cater both to beginners and seasoned investors. But before diving into the content, it’s important to know which platforms or devices are compatible for seamless access.
Compatible Devices and Platforms for Accessing the TRUMP Tutorial
The TRUMP tutorial platform is designed with user accessibility in mind. Typically, such educational platforms are web-based, allowing users to access content through standard internet browsers on various devices. Whether you prefer using a desktop computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone—most modern devices should support accessing the platform without issues.
Web Browsers
Most online educational platforms operate smoothly on popular web browsers including:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari (especially on Apple devices)
To ensure optimal performance and security when accessing the TRUMP tutorial:
- Keep your browser updated.
- Enable JavaScript.
- Disable any ad-blockers that might interfere with website functionality.
Mobile Devices
Given the increasing use of smartphones for learning purposes, mobile compatibility is crucial. The majority of crypto education sites are optimized for mobile browsing via responsive design frameworks. This means you can typically access all features from your smartphone or tablet without needing a dedicated app.
Dedicated Apps (If Available)
As of now, there are no specific reports indicating that the TRUMP tutorial has dedicated mobile apps available on app stores like Google Play or Apple App Store. However:
- Some similar educational platforms offer companion apps; check if this applies once you visit their official site.
In most cases, simply visiting their website through your device's browser will suffice.
How To Access The Platform Safely and Effectively
To get started with the TRUMP tutorial:
- Visit Official Website: Always ensure you're accessing an official source by verifying domain authenticity.
- Create an Account: Some features may require registration; follow secure sign-up procedures.
- Use Secure Connections: Preferably connect via HTTPS-enabled networks to protect personal data.
- Update Your Software: Keep your operating system and browser up-to-date for security reasons.
Additional Tips for Maximizing Your Learning Experience
Since cryptocurrency markets can be volatile and complex topics require reliable information sources:
- Bookmark trusted links related to the platform.
- Subscribe to newsletters if available for updates about new tutorials or features.
- Engage with community forums or support channels if you encounter technical issues.
Summary
Accessing the TRUMP tutorial platform primarily involves using standard internet-connected devices such as desktops, laptops, tablets, or smartphones through modern web browsers like Chrome or Firefox. There’s generally no need for specialized software beyond ensuring your device's browser is current and secure connection protocols are followed.
By choosing compatible devices and following best practices in cybersecurity—such as avoiding unsecured Wi-Fi networks—you can effectively utilize this educational resource without technical hurdles while focusing on expanding your knowledge about cryptocurrency investment strategies.
Remember: Staying informed about regulatory changes affecting digital assets remains critical when engaging with any crypto-related educational content online—regardless of which platform you choose.*


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-06-05 06:11
What platform do I need to use to access the TRUMP tutorial?
What Platform Do I Need to Use to Access the TRUMP Tutorial?
Understanding how to access educational resources like the TRUMP tutorial platform is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrency and digital asset investments. As a growing trend in financial education, platforms such as TRUMP aim to provide comprehensive guides, tutorials, and insights that cater both to beginners and seasoned investors. But before diving into the content, it’s important to know which platforms or devices are compatible for seamless access.
Compatible Devices and Platforms for Accessing the TRUMP Tutorial
The TRUMP tutorial platform is designed with user accessibility in mind. Typically, such educational platforms are web-based, allowing users to access content through standard internet browsers on various devices. Whether you prefer using a desktop computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone—most modern devices should support accessing the platform without issues.
Web Browsers
Most online educational platforms operate smoothly on popular web browsers including:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari (especially on Apple devices)
To ensure optimal performance and security when accessing the TRUMP tutorial:
- Keep your browser updated.
- Enable JavaScript.
- Disable any ad-blockers that might interfere with website functionality.
Mobile Devices
Given the increasing use of smartphones for learning purposes, mobile compatibility is crucial. The majority of crypto education sites are optimized for mobile browsing via responsive design frameworks. This means you can typically access all features from your smartphone or tablet without needing a dedicated app.
Dedicated Apps (If Available)
As of now, there are no specific reports indicating that the TRUMP tutorial has dedicated mobile apps available on app stores like Google Play or Apple App Store. However:
- Some similar educational platforms offer companion apps; check if this applies once you visit their official site.
In most cases, simply visiting their website through your device's browser will suffice.
How To Access The Platform Safely and Effectively
To get started with the TRUMP tutorial:
- Visit Official Website: Always ensure you're accessing an official source by verifying domain authenticity.
- Create an Account: Some features may require registration; follow secure sign-up procedures.
- Use Secure Connections: Preferably connect via HTTPS-enabled networks to protect personal data.
- Update Your Software: Keep your operating system and browser up-to-date for security reasons.
Additional Tips for Maximizing Your Learning Experience
Since cryptocurrency markets can be volatile and complex topics require reliable information sources:
- Bookmark trusted links related to the platform.
- Subscribe to newsletters if available for updates about new tutorials or features.
- Engage with community forums or support channels if you encounter technical issues.
Summary
Accessing the TRUMP tutorial platform primarily involves using standard internet-connected devices such as desktops, laptops, tablets, or smartphones through modern web browsers like Chrome or Firefox. There’s generally no need for specialized software beyond ensuring your device's browser is current and secure connection protocols are followed.
By choosing compatible devices and following best practices in cybersecurity—such as avoiding unsecured Wi-Fi networks—you can effectively utilize this educational resource without technical hurdles while focusing on expanding your knowledge about cryptocurrency investment strategies.
Remember: Staying informed about regulatory changes affecting digital assets remains critical when engaging with any crypto-related educational content online—regardless of which platform you choose.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is a Vesting Schedule for Tokens?
Understanding the concept of a vesting schedule is essential for anyone involved in cryptocurrency projects, whether as an investor, developer, or stakeholder. At its core, a vesting schedule is a structured plan that determines how and when tokens are released to recipients over time. This mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring fair distribution, maintaining market stability, and aligning stakeholders’ interests with the long-term success of the project.
Why Token Vesting Matters in Blockchain Projects
Token vesting is more than just a technical detail; it’s a strategic tool used by blockchain projects to manage token supply and foster trust among investors and team members. When tokens are distributed without restrictions or schedules, it can lead to sudden sell-offs that destabilize the market or create perceptions of unfairness. Implementing vesting schedules helps mitigate these risks by controlling how quickly tokens enter circulation.
For investors and project teams alike, understanding how vesting works provides clarity on token availability and potential influence on market dynamics. It also demonstrates transparency from project developers—an important factor for regulatory compliance and building confidence within the community.
Types of Vesting Schedules
There are several common types of vesting schedules used across blockchain projects:
Linear Vesting: Tokens are gradually released at consistent intervals over the entire vesting period. For example, if 1 million tokens are vested over four years with monthly releases, approximately 20,833 tokens would be unlocked each month.
Cliff Vesting: A specific initial period (the "cliff") must pass before any tokens become available. After this cliff period—say six months—the remaining tokens start to unlock gradually or all at once.
Accelerated Vesting: Under certain conditions such as achieving milestones or during specific events like acquisitions or mergers, token release speeds up significantly compared to standard schedules.
These structures serve different strategic purposes: linear vestings promote steady engagement; cliffs protect early-stage projects from immediate sell-offs; accelerated options reward key achievements.
Key Components of Token Vesting Schedules
A typical vesting schedule incorporates several critical elements:
Vesting Period: The total duration over which tokens will be gradually released (e.g., 1 year, 4 years).
Cliff Period: An initial lock-up phase where no tokens are released until it ends (common durations range from three months to one year).
Release Intervals: The frequency at which vested tokens become accessible—monthly, quarterly, annually.
Vested Amounts: The portion of total allocated tokens that becomes available at each interval.
Some schedules include clawback provisions allowing projects to reclaim unvested tokens under certain circumstances—adding an extra layer of control but also complexity.
Regulatory Considerations for Token Vestings
As regulatory frameworks around cryptocurrencies evolve globally—and particularly within jurisdictions like the United States—the design of token vestings must adhere to legal standards. Agencies such as the SEC have issued guidance emphasizing transparency in token sales and distributions[1]. Properly structured vestings can help demonstrate compliance by showing that token allocations do not constitute unregistered securities offerings.
Projects should ensure theirvesting plans clearly specify timelines and conditions while avoiding practices that could be interpreted as manipulative or deceptive[5]. Transparent communication about these schedules builds trust among investors while reducing legal risks associated with non-compliance.
Recent Trends Enhancing Token Distribution Strategies
The industry has seen significant advancements in how vestings are implemented:
Use of smart contracts automates release processes based on predefined rules[3], increasing transparency and reducing manual errors.
Incorporation of performance metrics aligns token releases with project milestones rather than fixed timelines alone[2].
More sophisticated models now consider multiple factors such as team performance incentives alongside traditional time-based releases[2].
These innovations aim not only to improve fairness but also enhance stakeholder engagement by tying rewards directly to project achievements—a practice increasingly favored by regulators seeking accountability.
Risks Associated With Poorly Managed Vests
While well-designed schemes support healthy markets and stakeholder relations,poor management can have serious repercussions:
- Market Volatility:* If large amounts of vested tokens suddenly become available due to poorly planned schedules,it may flood exchanges causing price swings[4].
Legal Challenges: Non-compliance with jurisdictional regulations could lead to sanctions,legal action,or loss of credibility[5].
Stakeholder Distrust: Lackluster communication about unlocking timelines或 perceived unfairness might erode confidence,damaging long-term relationships within communities[6].
Therefore,careful planning combined with transparent disclosure is essential for safeguarding both project integrity和 investor interests。
How To Design an Effective Token Vestment Schedule
Creating an optimal schedule involves balancing multiple factors:
- Define clear goals:Determine whether your priority is long-term stability、team retention、or incentivizing milestones。
- Choose appropriate structure:Select between linear、cliff、or hybrid models based on your project's needs。
- Set realistic timelines:Align lock-up periods和 release intervals with development phases。
- Ensure regulatory compliance:Consult legal experts确保您的计划符合相关法律法规。
- Automate where possible:Utilize smart contracts来确保自动执行和透明度。
By carefully considering these aspects,你可以建立一个公平、安全且符合法规的vesting体系,为项目的持续成功奠定基础。
The Role Of Smart Contracts In Automating Vests
Smart contracts在现代区块链项目中扮演着关键角色。它们可以自动化token的释放过程,根据预设条件(如时间或达成特定目标)自动解锁tokens。这不仅提高了效率,还增强了透明度,因为所有操作都在区块链上公开记录,无需第三方干预。此外,这种自动化减少了人为错误和潜在的操控风险,使得整个vesting流程更加可信赖。
未来发展趋势显示,将智能合约与性能指标结合使用,将进一步优化token分发策略,实现更动态、更灵活的激励机制。这一技术进步也符合行业对安全性和合规性的不断追求,为投资者提供更有保障的环境。
References
1. SEC Guidance on Token Sales (2020)
2. Industry Trends in Vesting Schedules (2023)
3. Smart Contract-Based Vesting Schedules (2022)
4. Market Volatility Risks (2021)
5. Regulatory Risks in Token Distribution (2020)
6. Stakeholder Trust and Vesting Schedules (2022)
By understanding what a vestingat schedule entails—including its types、components、regulatory considerations以及最新行业趋势—you gain valuable insights into managing digital assets responsibly。 Whether you're developing new blockchain protocols或investors evaluating opportunities,这些知识都是确保安全、公平分配的重要基础。


kai
2025-05-14 08:42
What is a vesting schedule for tokens?
What Is a Vesting Schedule for Tokens?
Understanding the concept of a vesting schedule is essential for anyone involved in cryptocurrency projects, whether as an investor, developer, or stakeholder. At its core, a vesting schedule is a structured plan that determines how and when tokens are released to recipients over time. This mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring fair distribution, maintaining market stability, and aligning stakeholders’ interests with the long-term success of the project.
Why Token Vesting Matters in Blockchain Projects
Token vesting is more than just a technical detail; it’s a strategic tool used by blockchain projects to manage token supply and foster trust among investors and team members. When tokens are distributed without restrictions or schedules, it can lead to sudden sell-offs that destabilize the market or create perceptions of unfairness. Implementing vesting schedules helps mitigate these risks by controlling how quickly tokens enter circulation.
For investors and project teams alike, understanding how vesting works provides clarity on token availability and potential influence on market dynamics. It also demonstrates transparency from project developers—an important factor for regulatory compliance and building confidence within the community.
Types of Vesting Schedules
There are several common types of vesting schedules used across blockchain projects:
Linear Vesting: Tokens are gradually released at consistent intervals over the entire vesting period. For example, if 1 million tokens are vested over four years with monthly releases, approximately 20,833 tokens would be unlocked each month.
Cliff Vesting: A specific initial period (the "cliff") must pass before any tokens become available. After this cliff period—say six months—the remaining tokens start to unlock gradually or all at once.
Accelerated Vesting: Under certain conditions such as achieving milestones or during specific events like acquisitions or mergers, token release speeds up significantly compared to standard schedules.
These structures serve different strategic purposes: linear vestings promote steady engagement; cliffs protect early-stage projects from immediate sell-offs; accelerated options reward key achievements.
Key Components of Token Vesting Schedules
A typical vesting schedule incorporates several critical elements:
Vesting Period: The total duration over which tokens will be gradually released (e.g., 1 year, 4 years).
Cliff Period: An initial lock-up phase where no tokens are released until it ends (common durations range from three months to one year).
Release Intervals: The frequency at which vested tokens become accessible—monthly, quarterly, annually.
Vested Amounts: The portion of total allocated tokens that becomes available at each interval.
Some schedules include clawback provisions allowing projects to reclaim unvested tokens under certain circumstances—adding an extra layer of control but also complexity.
Regulatory Considerations for Token Vestings
As regulatory frameworks around cryptocurrencies evolve globally—and particularly within jurisdictions like the United States—the design of token vestings must adhere to legal standards. Agencies such as the SEC have issued guidance emphasizing transparency in token sales and distributions[1]. Properly structured vestings can help demonstrate compliance by showing that token allocations do not constitute unregistered securities offerings.
Projects should ensure theirvesting plans clearly specify timelines and conditions while avoiding practices that could be interpreted as manipulative or deceptive[5]. Transparent communication about these schedules builds trust among investors while reducing legal risks associated with non-compliance.
Recent Trends Enhancing Token Distribution Strategies
The industry has seen significant advancements in how vestings are implemented:
Use of smart contracts automates release processes based on predefined rules[3], increasing transparency and reducing manual errors.
Incorporation of performance metrics aligns token releases with project milestones rather than fixed timelines alone[2].
More sophisticated models now consider multiple factors such as team performance incentives alongside traditional time-based releases[2].
These innovations aim not only to improve fairness but also enhance stakeholder engagement by tying rewards directly to project achievements—a practice increasingly favored by regulators seeking accountability.
Risks Associated With Poorly Managed Vests
While well-designed schemes support healthy markets and stakeholder relations,poor management can have serious repercussions:
- Market Volatility:* If large amounts of vested tokens suddenly become available due to poorly planned schedules,it may flood exchanges causing price swings[4].
Legal Challenges: Non-compliance with jurisdictional regulations could lead to sanctions,legal action,or loss of credibility[5].
Stakeholder Distrust: Lackluster communication about unlocking timelines或 perceived unfairness might erode confidence,damaging long-term relationships within communities[6].
Therefore,careful planning combined with transparent disclosure is essential for safeguarding both project integrity和 investor interests。
How To Design an Effective Token Vestment Schedule
Creating an optimal schedule involves balancing multiple factors:
- Define clear goals:Determine whether your priority is long-term stability、team retention、or incentivizing milestones。
- Choose appropriate structure:Select between linear、cliff、or hybrid models based on your project's needs。
- Set realistic timelines:Align lock-up periods和 release intervals with development phases。
- Ensure regulatory compliance:Consult legal experts确保您的计划符合相关法律法规。
- Automate where possible:Utilize smart contracts来确保自动执行和透明度。
By carefully considering these aspects,你可以建立一个公平、安全且符合法规的vesting体系,为项目的持续成功奠定基础。
The Role Of Smart Contracts In Automating Vests
Smart contracts在现代区块链项目中扮演着关键角色。它们可以自动化token的释放过程,根据预设条件(如时间或达成特定目标)自动解锁tokens。这不仅提高了效率,还增强了透明度,因为所有操作都在区块链上公开记录,无需第三方干预。此外,这种自动化减少了人为错误和潜在的操控风险,使得整个vesting流程更加可信赖。
未来发展趋势显示,将智能合约与性能指标结合使用,将进一步优化token分发策略,实现更动态、更灵活的激励机制。这一技术进步也符合行业对安全性和合规性的不断追求,为投资者提供更有保障的环境。
References
1. SEC Guidance on Token Sales (2020)
2. Industry Trends in Vesting Schedules (2023)
3. Smart Contract-Based Vesting Schedules (2022)
4. Market Volatility Risks (2021)
5. Regulatory Risks in Token Distribution (2020)
6. Stakeholder Trust and Vesting Schedules (2022)
By understanding what a vestingat schedule entails—including its types、components、regulatory considerations以及最新行业趋势—you gain valuable insights into managing digital assets responsibly。 Whether you're developing new blockchain protocols或investors evaluating opportunities,这些知识都是确保安全、公平分配的重要基础。
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
