1️⃣Stripe and Paradigm launch new L1 chain
◻️Stripe and Paradigm investment fund cooperate to introduce layer-1 blockchain called Tempo, specifically designed for payment purposes.
2️⃣Mega Matrix files with SEC for stablecoin governance token treasury strategy
◻️Mega Matrix (MPU) has filed a $2 billion shelf registration with the SEC to conduct a treasury strategy focused on stablecoin governance tokens - especially Ethena's ENA token
3️⃣Ukraine officially votes in favor of legalizing and taxing crypto
◻️The Ukrainian parliament has voted with a result of 246/321 votes in favor, moving towards legalizing and taxing the crypto market.
4️⃣World Liberty blacklists Justin Sun's wallet address
◻️World Liberty has frozen Justin Sun's address, locking billions of dollars in WLFI tokens after $9 million was transferred to exchanges, although Sun denies selling.
5️⃣19:30 tonight, the US releases non-farm payroll data for August:
◻️Unemployment rate expected at 4.3% (previously 4.2%).
◻️New jobs (Non-farm) forecast to increase by 75,000 (previously 73,000)
◻️This information will have a strong impact on Fed expectations and the risk asset market, especially crypto
🔔 Connect with JuCoin now to not miss hot news about Crypto, financial policy and global geopolitics!
#JuCoin #CryptoNews #Stripe #Paradigm #MegaMatrix #ENAtoken #Stablecoin #DeFi #NFP #Ukraine


Lee Jucoin
2025-09-05 12:45
📰Crypto News 24h With #JuCoin! (05/09/2025)
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the FATF Travel Rule and How Does It Impact Cryptocurrency and Money Transfers?
The FATF Travel Rule is a significant regulation shaping how cross-border financial transactions, especially those involving cryptocurrencies, are conducted worldwide. As digital assets become more integrated into global finance, understanding this rule’s implications is crucial for both service providers and users.
Understanding the FATF Travel Rule
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) introduced the Travel Rule in 1996 as part of its efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. Originally designed for traditional banking systems, it mandated that financial institutions collect and verify information about both parties involved in a transaction exceeding a specific threshold—typically $1,000 or more. This information includes names, addresses, account numbers, and other identifying details.
In 2019, recognizing the rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies, the FATF expanded its scope to include virtual asset service providers (VASPs). This update aimed to bring transparency to crypto transactions by applying similar standards used in conventional finance. The goal was to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering through untraceable transfers.
Why Was the Travel Rule Introduced?
The primary purpose of the Travel Rule is enhancing transparency across borders. By requiring detailed information exchange between institutions handling transactions—whether banks or crypto exchanges—it becomes harder for criminals to move illicit funds undetected. For governments worldwide, this regulation supports international cooperation against financial crimes.
For cryptocurrency markets specifically, implementing these rules helps legitimize digital assets within regulatory frameworks. It provides clarity on compliance expectations for exchanges and wallet providers operating across jurisdictions.
How Does the Travel Rule Affect Cryptocurrency Transactions?
Applying traditional AML/CFT standards like the Travel Rule presents unique challenges within decentralized digital ecosystems:
- Regulatory Clarity: The rule offers clearer guidelines for crypto exchanges on what data they need to collect from users when facilitating cross-border transfers.
- Compliance Challenges: Unlike banks with centralized customer data systems, many cryptocurrency platforms operate with pseudonymous addresses that do not inherently link back easily to real-world identities.
- Technological Solutions: To bridge this gap, industry players are developing tools such as Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols integrated into their platforms or third-party compliance solutions that facilitate secure data sharing while respecting privacy concerns.
Despite these efforts, some smaller or decentralized services struggle with full compliance due to resource constraints or technical limitations—potentially leading them out of certain markets if they cannot meet regulatory requirements.
Impact on Money Transfer Services
Traditional money transfer services have long relied on KYC procedures; however, integrating these processes globally under the auspices of FATF guidance aims at creating uniformity:
- Enhanced Security: Collecting verified sender/receiver data reduces risks associated with frauds and illegal activities.
- Operational Costs: Implementing comprehensive compliance measures increases operational expenses for financial institutions—and these costs may be passed onto consumers through higher fees.
- Global Cooperation: Standardized AML/CFT practices foster better international collaboration among regulators by establishing common standards for cross-border transfers.
This harmonization aims at making illicit fund movement more difficult while streamlining legitimate international commerce.
Recent Developments in Regulatory Guidance
In June 2023, FATF issued updated guidance focusing specifically on digital assets' travel rules implementation. This new advice emphasizes robust customer due diligence processes alongside leveraging advanced technologies like blockchain analytics tools that can trace transaction flows without compromising user privacy excessively.
Many cryptocurrency exchanges have responded proactively by upgrading their KYC/AML systems or partnering with specialized firms offering compliant solutions tailored toward meeting evolving regulations efficiently. These adaptations aim at balancing regulatory adherence with user experience considerations—a key factor in fostering broader adoption of compliant crypto services.
Challenges Facing Industry Stakeholders
While regulations improve overall security and legitimacy within crypto markets:
- Critics argue there’s potential overreach—regulations might stifle innovation if overly burdensome.
- Privacy advocates express concern over increased personal data collection which could compromise user anonymity—a core appeal of cryptocurrencies.
- Smaller operators face operational hurdles; some may exit certain regions if compliance costs outweigh benefits or if they lack necessary infrastructure support.
Balancing effective regulation without hindering technological progress remains an ongoing debate among policymakers and industry leaders alike.
How Will Future Regulations Shape Cross-Border Crypto Transactions?
As global regulators continue refining policies around cryptocurrencies under frameworks like those set by FATF's updated guidance from June 2023 onwards—the landscape will likely see increased standardization but also heightened scrutiny regarding privacy rights versus security needs.
Emerging technological innovations such as decentralized identity verification methods could help reconcile these competing interests by enabling secure yet private verification processes aligned with travel rule requirements.
Final Thoughts
The FATF Travel Rule marks a pivotal step toward integrating cryptocurrencies into mainstream financial oversight mechanisms globally. While it introduces notable compliance challenges—particularly around privacy concerns—it also offers opportunities for greater legitimacy and cooperation across borders in fighting financial crimes effectively. As technology evolves alongside regulation updates from bodies like FATF—including recent guidance issued mid-2023—the industry must adapt swiftly while safeguarding user rights amid increasing demands for transparency.
By understanding what the FATF Travel Rule entails—and how it influences both traditional money transfer services and emerging crypto markets—you can better navigate this complex regulatory environment.


kai
2025-05-22 12:14
What is the FATF Travel Rule, and how does it impact transfers?
What Is the FATF Travel Rule and How Does It Impact Cryptocurrency and Money Transfers?
The FATF Travel Rule is a significant regulation shaping how cross-border financial transactions, especially those involving cryptocurrencies, are conducted worldwide. As digital assets become more integrated into global finance, understanding this rule’s implications is crucial for both service providers and users.
Understanding the FATF Travel Rule
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) introduced the Travel Rule in 1996 as part of its efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. Originally designed for traditional banking systems, it mandated that financial institutions collect and verify information about both parties involved in a transaction exceeding a specific threshold—typically $1,000 or more. This information includes names, addresses, account numbers, and other identifying details.
In 2019, recognizing the rise of digital assets like cryptocurrencies, the FATF expanded its scope to include virtual asset service providers (VASPs). This update aimed to bring transparency to crypto transactions by applying similar standards used in conventional finance. The goal was to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering through untraceable transfers.
Why Was the Travel Rule Introduced?
The primary purpose of the Travel Rule is enhancing transparency across borders. By requiring detailed information exchange between institutions handling transactions—whether banks or crypto exchanges—it becomes harder for criminals to move illicit funds undetected. For governments worldwide, this regulation supports international cooperation against financial crimes.
For cryptocurrency markets specifically, implementing these rules helps legitimize digital assets within regulatory frameworks. It provides clarity on compliance expectations for exchanges and wallet providers operating across jurisdictions.
How Does the Travel Rule Affect Cryptocurrency Transactions?
Applying traditional AML/CFT standards like the Travel Rule presents unique challenges within decentralized digital ecosystems:
- Regulatory Clarity: The rule offers clearer guidelines for crypto exchanges on what data they need to collect from users when facilitating cross-border transfers.
- Compliance Challenges: Unlike banks with centralized customer data systems, many cryptocurrency platforms operate with pseudonymous addresses that do not inherently link back easily to real-world identities.
- Technological Solutions: To bridge this gap, industry players are developing tools such as Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols integrated into their platforms or third-party compliance solutions that facilitate secure data sharing while respecting privacy concerns.
Despite these efforts, some smaller or decentralized services struggle with full compliance due to resource constraints or technical limitations—potentially leading them out of certain markets if they cannot meet regulatory requirements.
Impact on Money Transfer Services
Traditional money transfer services have long relied on KYC procedures; however, integrating these processes globally under the auspices of FATF guidance aims at creating uniformity:
- Enhanced Security: Collecting verified sender/receiver data reduces risks associated with frauds and illegal activities.
- Operational Costs: Implementing comprehensive compliance measures increases operational expenses for financial institutions—and these costs may be passed onto consumers through higher fees.
- Global Cooperation: Standardized AML/CFT practices foster better international collaboration among regulators by establishing common standards for cross-border transfers.
This harmonization aims at making illicit fund movement more difficult while streamlining legitimate international commerce.
Recent Developments in Regulatory Guidance
In June 2023, FATF issued updated guidance focusing specifically on digital assets' travel rules implementation. This new advice emphasizes robust customer due diligence processes alongside leveraging advanced technologies like blockchain analytics tools that can trace transaction flows without compromising user privacy excessively.
Many cryptocurrency exchanges have responded proactively by upgrading their KYC/AML systems or partnering with specialized firms offering compliant solutions tailored toward meeting evolving regulations efficiently. These adaptations aim at balancing regulatory adherence with user experience considerations—a key factor in fostering broader adoption of compliant crypto services.
Challenges Facing Industry Stakeholders
While regulations improve overall security and legitimacy within crypto markets:
- Critics argue there’s potential overreach—regulations might stifle innovation if overly burdensome.
- Privacy advocates express concern over increased personal data collection which could compromise user anonymity—a core appeal of cryptocurrencies.
- Smaller operators face operational hurdles; some may exit certain regions if compliance costs outweigh benefits or if they lack necessary infrastructure support.
Balancing effective regulation without hindering technological progress remains an ongoing debate among policymakers and industry leaders alike.
How Will Future Regulations Shape Cross-Border Crypto Transactions?
As global regulators continue refining policies around cryptocurrencies under frameworks like those set by FATF's updated guidance from June 2023 onwards—the landscape will likely see increased standardization but also heightened scrutiny regarding privacy rights versus security needs.
Emerging technological innovations such as decentralized identity verification methods could help reconcile these competing interests by enabling secure yet private verification processes aligned with travel rule requirements.
Final Thoughts
The FATF Travel Rule marks a pivotal step toward integrating cryptocurrencies into mainstream financial oversight mechanisms globally. While it introduces notable compliance challenges—particularly around privacy concerns—it also offers opportunities for greater legitimacy and cooperation across borders in fighting financial crimes effectively. As technology evolves alongside regulation updates from bodies like FATF—including recent guidance issued mid-2023—the industry must adapt swiftly while safeguarding user rights amid increasing demands for transparency.
By understanding what the FATF Travel Rule entails—and how it influences both traditional money transfer services and emerging crypto markets—you can better navigate this complex regulatory environment.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Liquidity Mining in the DeFi Ecosystem?
Liquidity mining is a fundamental concept within the decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape that has significantly contributed to its rapid growth. It involves incentivizing users to supply liquidity—essentially, funds—to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and other financial protocols. This process not only enhances the trading experience by reducing slippage but also fosters community participation and decentralization.
Understanding Liquidity Mining: How Does It Work?
At its core, liquidity mining encourages users to deposit their cryptocurrencies into liquidity pools on DeFi platforms. These pools are used to facilitate trading, lending, or other financial activities without relying on centralized intermediaries. In return for providing this liquidity, participants earn rewards—often in the form of governance tokens or interest payments.
For example, when a user deposits ETH and USDT into a DEX like Uniswap or SushiSwap, they become a liquidity provider (LP). As trades occur within these pools, LPs earn transaction fees proportional to their share of the pool. Additionally, many protocols distribute native governance tokens as incentives—these tokens can grant voting rights and influence protocol development.
This mechanism aligns with DeFi's ethos of decentralization by allowing individual users rather than centralized entities to control significant parts of financial operations. It also helps improve market efficiency by increasing available liquidity for various assets.
The Evolution of Liquidity Mining in DeFi
Liquidity mining emerged as an innovative solution to traditional finance’s limitations regarding capital requirements and central control over markets. Unlike conventional market-making—which often requires substantial capital reserves—liquidity mining democratizes access by enabling anyone with crypto assets to participate actively.
In recent years, yield farming—a subset of liquidity mining—has gained popularity among crypto enthusiasts seeking higher returns. Yield farms allow users to deposit assets into specific pools managed across multiple protocols like Compound or Yearn.finance; these platforms then optimize yields through complex strategies involving staking and lending.
The rise of yield farming has led some investors to deploy large sums into DeFi projects rapidly but has also introduced new risks such as impermanent loss—the potential loss incurred when token prices fluctuate relative to each other—and smart contract vulnerabilities.
Key Benefits for Participants
Participating in liquidity mining offers several advantages:
- Earning Rewards: Users receive governance tokens that can be held or traded; these often appreciate over time if the platform succeeds.
- Interest Income: Some protocols provide interest payments similar to traditional savings accounts.
- Influence Over Protocol Development: Governance tokens enable holders voting rights on key decisions affecting platform upgrades or fee structures.
- Supporting Decentralization: By contributing funds directly into protocols, LPs help maintain open-access markets free from central authority control.
However, it’s essential for participants always considering risks such as token volatility and smart contract security issues before engaging extensively in liquidity mining activities.
Challenges Facing Liquidity Mining
While lucrative opportunities exist within DeFi’s ecosystem through liquidity mining practices, several challenges threaten sustainability:
Market Volatility
Governance tokens earned via liquidity provision tend to be highly volatile due to fluctuating cryptocurrency prices and market sentiment shifts. This volatility can diminish long-term profitability if token values decline sharply after initial rewards are earned.
Regulatory Risks
As authorities worldwide scrutinize DeFi activities more closely—including yield farming—they may impose regulations that restrict certain operations or classify some tokens as securities. Such regulatory uncertainty could impact user participation levels significantly.
Security Concerns
Smart contract exploits have been notable setbacks for many platforms; high-profile hacks like those targeting Ronin Network highlight vulnerabilities inherent in complex codebases lacking thorough audits. These incidents erode trust among participants and can lead to substantial financial losses if exploited maliciously.
Scalability Issues
As demand increases during periods of high activity within popular protocols like Aave or Curve Finance—the network congestion causes elevated transaction fees (gas costs) and slower processing times which hinder seamless user experiences especially during peak periods.
The Future Outlook: Opportunities & Risks
The ongoing transition from Ethereum 1.x towards Ethereum 2.0 aims at improving scalability through proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms which could make transactions faster while reducing costs—a positive development for liquid providers seeking efficiency gains amid growing demand.
Furthermore,
- Competition among different protocols continues driving innovation,
- New incentive models emerge regularly,
- Cross-chain integrations expand access across multiple blockchains,
all promising further growth avenues for liquid miners.
However,
regulatory developments remain unpredictable,security remains paramount with ongoing efforts toward better auditing practices,and scalability challenges must be addressed comprehensively before mass adoption becomes truly sustainable.
Final Thoughts on Liquidity Mining's Role in DeFi
Liquidity mining remains one of the most impactful innovations shaping decentralized finance today—it enables broader participation while fueling platform growth through incentivized asset provision. Its success hinges on balancing attractive rewards against inherent risks such as price volatility, security vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainties—and ensuring robust infrastructure capable of handling increased activity efficiently.
As DeFi continues evolving rapidly—with technological advancements like layer-two solutions promising enhanced scalability—the landscape around liquidity provisioning will likely become more sophisticated yet safer for everyday investors seeking exposure beyond traditional banking systems.
By understanding how it works—and recognizing both its opportunities and pitfalls—participants can better navigate this dynamic environment while contributing meaningfully toward building resilient decentralized financial ecosystems rooted firmly in transparency and community-driven governance.
Keywords: Liquidity Mining , Decentralized Finance , Yield Farming , Crypto Rewards , Smart Contract Security , Blockchain Protocols , Governance Tokens , Market Volatility


kai
2025-05-22 08:10
What is "liquidity mining" within the DeFi ecosystem?
What Is Liquidity Mining in the DeFi Ecosystem?
Liquidity mining is a fundamental concept within the decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape that has significantly contributed to its rapid growth. It involves incentivizing users to supply liquidity—essentially, funds—to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and other financial protocols. This process not only enhances the trading experience by reducing slippage but also fosters community participation and decentralization.
Understanding Liquidity Mining: How Does It Work?
At its core, liquidity mining encourages users to deposit their cryptocurrencies into liquidity pools on DeFi platforms. These pools are used to facilitate trading, lending, or other financial activities without relying on centralized intermediaries. In return for providing this liquidity, participants earn rewards—often in the form of governance tokens or interest payments.
For example, when a user deposits ETH and USDT into a DEX like Uniswap or SushiSwap, they become a liquidity provider (LP). As trades occur within these pools, LPs earn transaction fees proportional to their share of the pool. Additionally, many protocols distribute native governance tokens as incentives—these tokens can grant voting rights and influence protocol development.
This mechanism aligns with DeFi's ethos of decentralization by allowing individual users rather than centralized entities to control significant parts of financial operations. It also helps improve market efficiency by increasing available liquidity for various assets.
The Evolution of Liquidity Mining in DeFi
Liquidity mining emerged as an innovative solution to traditional finance’s limitations regarding capital requirements and central control over markets. Unlike conventional market-making—which often requires substantial capital reserves—liquidity mining democratizes access by enabling anyone with crypto assets to participate actively.
In recent years, yield farming—a subset of liquidity mining—has gained popularity among crypto enthusiasts seeking higher returns. Yield farms allow users to deposit assets into specific pools managed across multiple protocols like Compound or Yearn.finance; these platforms then optimize yields through complex strategies involving staking and lending.
The rise of yield farming has led some investors to deploy large sums into DeFi projects rapidly but has also introduced new risks such as impermanent loss—the potential loss incurred when token prices fluctuate relative to each other—and smart contract vulnerabilities.
Key Benefits for Participants
Participating in liquidity mining offers several advantages:
- Earning Rewards: Users receive governance tokens that can be held or traded; these often appreciate over time if the platform succeeds.
- Interest Income: Some protocols provide interest payments similar to traditional savings accounts.
- Influence Over Protocol Development: Governance tokens enable holders voting rights on key decisions affecting platform upgrades or fee structures.
- Supporting Decentralization: By contributing funds directly into protocols, LPs help maintain open-access markets free from central authority control.
However, it’s essential for participants always considering risks such as token volatility and smart contract security issues before engaging extensively in liquidity mining activities.
Challenges Facing Liquidity Mining
While lucrative opportunities exist within DeFi’s ecosystem through liquidity mining practices, several challenges threaten sustainability:
Market Volatility
Governance tokens earned via liquidity provision tend to be highly volatile due to fluctuating cryptocurrency prices and market sentiment shifts. This volatility can diminish long-term profitability if token values decline sharply after initial rewards are earned.
Regulatory Risks
As authorities worldwide scrutinize DeFi activities more closely—including yield farming—they may impose regulations that restrict certain operations or classify some tokens as securities. Such regulatory uncertainty could impact user participation levels significantly.
Security Concerns
Smart contract exploits have been notable setbacks for many platforms; high-profile hacks like those targeting Ronin Network highlight vulnerabilities inherent in complex codebases lacking thorough audits. These incidents erode trust among participants and can lead to substantial financial losses if exploited maliciously.
Scalability Issues
As demand increases during periods of high activity within popular protocols like Aave or Curve Finance—the network congestion causes elevated transaction fees (gas costs) and slower processing times which hinder seamless user experiences especially during peak periods.
The Future Outlook: Opportunities & Risks
The ongoing transition from Ethereum 1.x towards Ethereum 2.0 aims at improving scalability through proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms which could make transactions faster while reducing costs—a positive development for liquid providers seeking efficiency gains amid growing demand.
Furthermore,
- Competition among different protocols continues driving innovation,
- New incentive models emerge regularly,
- Cross-chain integrations expand access across multiple blockchains,
all promising further growth avenues for liquid miners.
However,
regulatory developments remain unpredictable,security remains paramount with ongoing efforts toward better auditing practices,and scalability challenges must be addressed comprehensively before mass adoption becomes truly sustainable.
Final Thoughts on Liquidity Mining's Role in DeFi
Liquidity mining remains one of the most impactful innovations shaping decentralized finance today—it enables broader participation while fueling platform growth through incentivized asset provision. Its success hinges on balancing attractive rewards against inherent risks such as price volatility, security vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainties—and ensuring robust infrastructure capable of handling increased activity efficiently.
As DeFi continues evolving rapidly—with technological advancements like layer-two solutions promising enhanced scalability—the landscape around liquidity provisioning will likely become more sophisticated yet safer for everyday investors seeking exposure beyond traditional banking systems.
By understanding how it works—and recognizing both its opportunities and pitfalls—participants can better navigate this dynamic environment while contributing meaningfully toward building resilient decentralized financial ecosystems rooted firmly in transparency and community-driven governance.
Keywords: Liquidity Mining , Decentralized Finance , Yield Farming , Crypto Rewards , Smart Contract Security , Blockchain Protocols , Governance Tokens , Market Volatility
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Key Management Best Practice?
Understanding the Fundamentals of Key Management
Key management is a cornerstone of cybersecurity, especially in cryptographic systems that safeguard sensitive data. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys—from their creation to their eventual disposal. Proper key management ensures that data remains confidential, authentic, and unaltered during storage and transmission. Without robust practices, even the strongest encryption algorithms can be rendered ineffective if keys are mishandled or compromised.
Secure Key Generation: The First Line of Defense
The foundation of effective key management begins with secure key generation. Using high-quality random number generators (RNGs) is essential to produce unpredictable and uniformly distributed cryptographic keys. This randomness prevents attackers from predicting or reproducing keys through brute-force methods. Industry standards like NIST SP 800-90B recommend deterministic random bit generators (DRBGs) for generating cryptographically secure keys, ensuring they are resilient against attacks.
Key Distribution: Safeguarding Data During Exchange
Once generated, keys must be securely shared between parties without interception by malicious actors. Implementing secure key exchange protocols such as Diffie-Hellman or Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) provides a reliable method for establishing shared secrets over insecure channels. These protocols enable two parties to agree on a common secret without transmitting the actual key material openly—reducing risks associated with eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Secure Storage Solutions: Protecting Keys at Rest
Storing cryptographic keys securely is equally vital as generating and exchanging them safely. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) and Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) offer tamper-resistant environments designed specifically for safeguarding sensitive keys. These hardware solutions provide features like tamper-evidence and tamper-resistance, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult compared to software-based storage options.
Effective Key Revocation Strategies
Keys should not remain valid indefinitely; they need periodic revocation when compromised or expired to prevent unauthorized access over time. Implementing mechanisms such as Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) allows organizations to revoke compromised or outdated certificates promptly. Regularly updating revocation lists ensures that systems do not rely on invalid credentials, maintaining overall security integrity.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Adhering to industry-specific regulations is crucial for organizations handling sensitive information across sectors like finance, healthcare, and government agencies. Standards such as PCI-DSS for payment card security, HIPAA for healthcare data privacy, and GDPR for data protection in Europe set clear guidelines on how encryption keys should be managed throughout their lifecycle—covering aspects from generation to destruction.
Recent Advances Shaping Key Management Practices
Emerging technologies are transforming traditional approaches toward more resilient security frameworks:
Quantum Computing Threats: The rise of quantum computers presents significant challenges by potentially breaking widely used encryption schemes like RSA and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC). To counter this threat, researchers advocate adopting post-quantum cryptography algorithms based on lattice structures or hash functions that resist quantum attacks.
AI-Powered Automation: Artificial intelligence enhances efficiency in managing large volumes of cryptographic operations—automating tasks such as key generation, distribution monitoring, anomaly detection during usage—and reducing human error risks.
Blockchain-Based Solutions: Decentralized blockchain platforms offer promising avenues for transparent and tamper-proof key management systems capable of resisting manipulation attempts while providing auditability across distributed networks.
Risks Associated with Poor Key Management
Neglecting best practices can lead directly to severe consequences:
Security Breaches: Inadequate protection may allow hackers access to encrypted data through stolen or weakly stored keys.
Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with standards like GDPR can result in hefty fines alongside reputational damage.
Technological Vulnerabilities: Failing to adapt strategies amid rapid technological changes increases exposure risk—especially considering advancements in quantum computing which threaten existing encryption methods.
Implementing Best Practices Across Industries
Organizations should adopt comprehensive policies aligned with recognized standards:
- Use strong RNGs compliant with NIST guidelines during key creation.
- Employ secure protocols like ECDH during distribution phases.
- Store all critical keys within HSMs/TPMs rather than unsecured servers.
- Establish clear procedures for timely revocation using CRLs/OCSP.5.. Ensure compliance by regularly auditing processes against relevant regulations such as PCI-DSS or GDPR.
Staying Ahead With Emerging Technologies
To future-proof their security infrastructure:
Invest in research into quantum-resistant algorithms before widespread adoption becomes necessary.
Leverage AI tools cautiously—balancing automation benefits against potential new attack vectors introduced via machine learning models.
Explore blockchain solutions carefully considering scalability issues but recognizing their potential benefits in transparency and decentralization.
Final Thoughts on Effective Key Management
Robust key management practices form the backbone of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy involving encryption technologies today—and tomorrow’s emerging threats make it even more critical to stay vigilant about evolving best practices . By prioritizing secure generation methods , protected storage environments , diligent revocation procedures , regulatory compliance , along with embracing technological innovations responsibly — businesses can significantly reduce risks associated with data breaches while enhancing trustworthiness among clients and partners alike .
Keywords: Cryptographic Keys | Data Security | Secure Storage | Encryption Best Practices | Quantum Resistance | AI Security Tools | Blockchain Security


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-15 01:34
What is key management best practice?
What Is Key Management Best Practice?
Understanding the Fundamentals of Key Management
Key management is a cornerstone of cybersecurity, especially in cryptographic systems that safeguard sensitive data. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys—from their creation to their eventual disposal. Proper key management ensures that data remains confidential, authentic, and unaltered during storage and transmission. Without robust practices, even the strongest encryption algorithms can be rendered ineffective if keys are mishandled or compromised.
Secure Key Generation: The First Line of Defense
The foundation of effective key management begins with secure key generation. Using high-quality random number generators (RNGs) is essential to produce unpredictable and uniformly distributed cryptographic keys. This randomness prevents attackers from predicting or reproducing keys through brute-force methods. Industry standards like NIST SP 800-90B recommend deterministic random bit generators (DRBGs) for generating cryptographically secure keys, ensuring they are resilient against attacks.
Key Distribution: Safeguarding Data During Exchange
Once generated, keys must be securely shared between parties without interception by malicious actors. Implementing secure key exchange protocols such as Diffie-Hellman or Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) provides a reliable method for establishing shared secrets over insecure channels. These protocols enable two parties to agree on a common secret without transmitting the actual key material openly—reducing risks associated with eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Secure Storage Solutions: Protecting Keys at Rest
Storing cryptographic keys securely is equally vital as generating and exchanging them safely. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) and Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) offer tamper-resistant environments designed specifically for safeguarding sensitive keys. These hardware solutions provide features like tamper-evidence and tamper-resistance, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult compared to software-based storage options.
Effective Key Revocation Strategies
Keys should not remain valid indefinitely; they need periodic revocation when compromised or expired to prevent unauthorized access over time. Implementing mechanisms such as Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) allows organizations to revoke compromised or outdated certificates promptly. Regularly updating revocation lists ensures that systems do not rely on invalid credentials, maintaining overall security integrity.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Adhering to industry-specific regulations is crucial for organizations handling sensitive information across sectors like finance, healthcare, and government agencies. Standards such as PCI-DSS for payment card security, HIPAA for healthcare data privacy, and GDPR for data protection in Europe set clear guidelines on how encryption keys should be managed throughout their lifecycle—covering aspects from generation to destruction.
Recent Advances Shaping Key Management Practices
Emerging technologies are transforming traditional approaches toward more resilient security frameworks:
Quantum Computing Threats: The rise of quantum computers presents significant challenges by potentially breaking widely used encryption schemes like RSA and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC). To counter this threat, researchers advocate adopting post-quantum cryptography algorithms based on lattice structures or hash functions that resist quantum attacks.
AI-Powered Automation: Artificial intelligence enhances efficiency in managing large volumes of cryptographic operations—automating tasks such as key generation, distribution monitoring, anomaly detection during usage—and reducing human error risks.
Blockchain-Based Solutions: Decentralized blockchain platforms offer promising avenues for transparent and tamper-proof key management systems capable of resisting manipulation attempts while providing auditability across distributed networks.
Risks Associated with Poor Key Management
Neglecting best practices can lead directly to severe consequences:
Security Breaches: Inadequate protection may allow hackers access to encrypted data through stolen or weakly stored keys.
Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with standards like GDPR can result in hefty fines alongside reputational damage.
Technological Vulnerabilities: Failing to adapt strategies amid rapid technological changes increases exposure risk—especially considering advancements in quantum computing which threaten existing encryption methods.
Implementing Best Practices Across Industries
Organizations should adopt comprehensive policies aligned with recognized standards:
- Use strong RNGs compliant with NIST guidelines during key creation.
- Employ secure protocols like ECDH during distribution phases.
- Store all critical keys within HSMs/TPMs rather than unsecured servers.
- Establish clear procedures for timely revocation using CRLs/OCSP.5.. Ensure compliance by regularly auditing processes against relevant regulations such as PCI-DSS or GDPR.
Staying Ahead With Emerging Technologies
To future-proof their security infrastructure:
Invest in research into quantum-resistant algorithms before widespread adoption becomes necessary.
Leverage AI tools cautiously—balancing automation benefits against potential new attack vectors introduced via machine learning models.
Explore blockchain solutions carefully considering scalability issues but recognizing their potential benefits in transparency and decentralization.
Final Thoughts on Effective Key Management
Robust key management practices form the backbone of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy involving encryption technologies today—and tomorrow’s emerging threats make it even more critical to stay vigilant about evolving best practices . By prioritizing secure generation methods , protected storage environments , diligent revocation procedures , regulatory compliance , along with embracing technological innovations responsibly — businesses can significantly reduce risks associated with data breaches while enhancing trustworthiness among clients and partners alike .
Keywords: Cryptographic Keys | Data Security | Secure Storage | Encryption Best Practices | Quantum Resistance | AI Security Tools | Blockchain Security
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Proposals to Upgrade the Dogecoin (DOGE) Consensus Mechanism
Dogecoin (DOGE) has established itself as a popular cryptocurrency largely due to its vibrant community and meme-inspired branding. As with all blockchain networks, maintaining a secure, scalable, and energy-efficient consensus mechanism is vital for its long-term viability. Over recent months, discussions within the Dogecoin community have centered around potential upgrades to its current Proof of Work (PoW) system. This article explores the main proposals under consideration, their implications, and what they could mean for DOGE’s future.
Understanding Dogecoin’s Current Proof of Work System
Dogecoin operates on a PoW consensus mechanism similar to Bitcoin’s. Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. While this method has proven effective in securing decentralization and network integrity over time, it comes with notable drawbacks—most prominently high energy consumption and scalability challenges.
PoW requires significant computational power, which translates into substantial electricity use—a concern increasingly scrutinized amid global efforts toward sustainability. Additionally, as transaction volumes grow, network speed can become a bottleneck without further protocol adjustments.
Main Proposals for Upgrading Dogecoin’s Consensus Mechanism
Given these limitations, several proposals have emerged within the community aiming to modernize or diversify how DOGE achieves consensus:
Transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake (PoS)
One prominent idea is shifting from PoW towards a PoS model. In PoS systems, validators are chosen based on the amount of coins they stake rather than solving puzzles through computational work. This change could significantly reduce energy consumption while potentially increasing transaction throughput.
However, transitioning from PoW to PoS involves complex technical modifications that would require extensive development work and careful planning—especially considering Dogecoin's existing infrastructure built around mining-based validation. Critics also raise concerns about security; some argue that PoS may be more vulnerable if not properly implemented because it relies heavily on coin ownership rather than computational effort.
Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS)
Leased Proof of Stake is an alternative variant designed primarily for enhanced flexibility and decentralization. In LPoS models like those used in other cryptocurrencies such as Waves or Tron networks—users lease their coins temporarily to validators without transferring ownership directly—allowing smaller holders participation in validation processes.
For DOGE enthusiasts considering this approach: LPoS offers an attractive middle ground by enabling broader validator participation without requiring large upfront stakes or technical expertise associated with traditional staking setups.
While still in discussion phases at present—and lacking formal implementation plans—the concept holds promise for balancing security with inclusivity if adopted carefully.
Hybrid Consensus Models
Another avenue being explored involves hybrid systems combining elements from both PoW and PoS mechanisms—or even other algorithms—to leverage their respective strengths while mitigating weaknesses like high energy use or centralization risks.
A hybrid approach might see DOGE retain some aspects of mining-based validation but incorporate staking components that improve efficiency or security features such as resistance against 51% attacks—a common concern among critics wary of single points-of-failure within purely one-mechanism systems.
Implementing such models would demand rigorous testing phases before deployment but could ultimately provide a balanced solution aligned with evolving industry standards.
Recent Developments & Community Engagement
The ongoing debate about upgrading Dogecoin's consensus protocol reflects active engagement across multiple channels—including online forums like Reddit and Twitter—as well as developer meetings dedicated specifically to this topic. Community members are sharing ideas openly; some propose incremental changes while others advocate comprehensive overhauls aligned with broader industry trends toward sustainable blockchain solutions.
Developers have contributed by analyzing feasibility studies related to these proposals—testing prototypes where possible—and gathering feedback from users worldwide who remain invested in DOGE's future stability.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Upgrades
Any significant change carries inherent risks:
- Community Split: Major protocol modifications might divide supporters into factions favoring current versus proposed systems.
- Security Concerns: Transition periods can introduce vulnerabilities if not managed meticulously.
- Regulatory Considerations: Depending on how upgrades are implemented—for example: changing staking rules—they may attract regulatory scrutiny related especially to securities laws or anti-money laundering measures.
Furthermore, ensuring backward compatibility during upgrades is crucial so existing users experience minimal disruption.
The Path Forward for Dogecoin
Upgrading Dogecoin’s consensus mechanism presents both opportunities and challenges rooted deeply in technical feasibility alongside community sentiment. While proposals like moving toward proof-of-stake variants or hybrid models aim at making DOGE more sustainable amid environmental concerns—and possibly improving scalability—they require careful planning backed by thorough testing phases before any live deployment occurs.
As developments continue unfolding through active discussions among developers and stakeholders worldwide—with transparency being key—the future trajectory will depend heavily on balancing innovation with security assurances that uphold user trust.
Staying informed about these ongoing debates helps investors, developers, and enthusiasts understand how one of crypto's most beloved meme coins aims not just at maintaining relevance but also adapting responsibly amidst rapid technological evolution within blockchain ecosystems.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-11 08:47
What proposals exist to upgrade the Dogecoin (DOGE) consensus mechanism?
Proposals to Upgrade the Dogecoin (DOGE) Consensus Mechanism
Dogecoin (DOGE) has established itself as a popular cryptocurrency largely due to its vibrant community and meme-inspired branding. As with all blockchain networks, maintaining a secure, scalable, and energy-efficient consensus mechanism is vital for its long-term viability. Over recent months, discussions within the Dogecoin community have centered around potential upgrades to its current Proof of Work (PoW) system. This article explores the main proposals under consideration, their implications, and what they could mean for DOGE’s future.
Understanding Dogecoin’s Current Proof of Work System
Dogecoin operates on a PoW consensus mechanism similar to Bitcoin’s. Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. While this method has proven effective in securing decentralization and network integrity over time, it comes with notable drawbacks—most prominently high energy consumption and scalability challenges.
PoW requires significant computational power, which translates into substantial electricity use—a concern increasingly scrutinized amid global efforts toward sustainability. Additionally, as transaction volumes grow, network speed can become a bottleneck without further protocol adjustments.
Main Proposals for Upgrading Dogecoin’s Consensus Mechanism
Given these limitations, several proposals have emerged within the community aiming to modernize or diversify how DOGE achieves consensus:
Transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake (PoS)
One prominent idea is shifting from PoW towards a PoS model. In PoS systems, validators are chosen based on the amount of coins they stake rather than solving puzzles through computational work. This change could significantly reduce energy consumption while potentially increasing transaction throughput.
However, transitioning from PoW to PoS involves complex technical modifications that would require extensive development work and careful planning—especially considering Dogecoin's existing infrastructure built around mining-based validation. Critics also raise concerns about security; some argue that PoS may be more vulnerable if not properly implemented because it relies heavily on coin ownership rather than computational effort.
Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS)
Leased Proof of Stake is an alternative variant designed primarily for enhanced flexibility and decentralization. In LPoS models like those used in other cryptocurrencies such as Waves or Tron networks—users lease their coins temporarily to validators without transferring ownership directly—allowing smaller holders participation in validation processes.
For DOGE enthusiasts considering this approach: LPoS offers an attractive middle ground by enabling broader validator participation without requiring large upfront stakes or technical expertise associated with traditional staking setups.
While still in discussion phases at present—and lacking formal implementation plans—the concept holds promise for balancing security with inclusivity if adopted carefully.
Hybrid Consensus Models
Another avenue being explored involves hybrid systems combining elements from both PoW and PoS mechanisms—or even other algorithms—to leverage their respective strengths while mitigating weaknesses like high energy use or centralization risks.
A hybrid approach might see DOGE retain some aspects of mining-based validation but incorporate staking components that improve efficiency or security features such as resistance against 51% attacks—a common concern among critics wary of single points-of-failure within purely one-mechanism systems.
Implementing such models would demand rigorous testing phases before deployment but could ultimately provide a balanced solution aligned with evolving industry standards.
Recent Developments & Community Engagement
The ongoing debate about upgrading Dogecoin's consensus protocol reflects active engagement across multiple channels—including online forums like Reddit and Twitter—as well as developer meetings dedicated specifically to this topic. Community members are sharing ideas openly; some propose incremental changes while others advocate comprehensive overhauls aligned with broader industry trends toward sustainable blockchain solutions.
Developers have contributed by analyzing feasibility studies related to these proposals—testing prototypes where possible—and gathering feedback from users worldwide who remain invested in DOGE's future stability.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Upgrades
Any significant change carries inherent risks:
- Community Split: Major protocol modifications might divide supporters into factions favoring current versus proposed systems.
- Security Concerns: Transition periods can introduce vulnerabilities if not managed meticulously.
- Regulatory Considerations: Depending on how upgrades are implemented—for example: changing staking rules—they may attract regulatory scrutiny related especially to securities laws or anti-money laundering measures.
Furthermore, ensuring backward compatibility during upgrades is crucial so existing users experience minimal disruption.
The Path Forward for Dogecoin
Upgrading Dogecoin’s consensus mechanism presents both opportunities and challenges rooted deeply in technical feasibility alongside community sentiment. While proposals like moving toward proof-of-stake variants or hybrid models aim at making DOGE more sustainable amid environmental concerns—and possibly improving scalability—they require careful planning backed by thorough testing phases before any live deployment occurs.
As developments continue unfolding through active discussions among developers and stakeholders worldwide—with transparency being key—the future trajectory will depend heavily on balancing innovation with security assurances that uphold user trust.
Staying informed about these ongoing debates helps investors, developers, and enthusiasts understand how one of crypto's most beloved meme coins aims not just at maintaining relevance but also adapting responsibly amidst rapid technological evolution within blockchain ecosystems.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
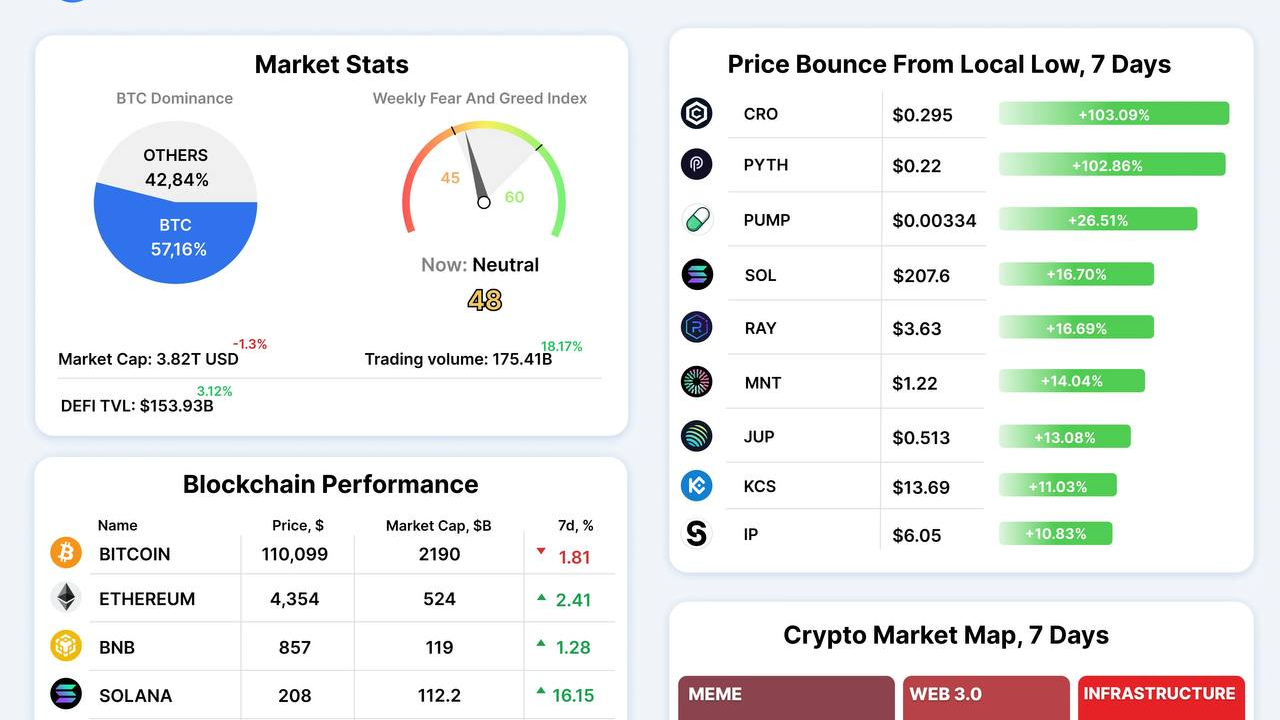


JioCoins
2025-08-29 18:26
Top 100 24h Gainers 🚀 M $0.5222
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Upcoming Events for Degenerate Ape Owners: What to Expect in 2024
Overview of Degenerate Ape and Its Community Engagement
Degenerate Ape is a notable subset within the broader Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) ecosystem, which has become one of the most influential NFT collections since its launch in April 2021. Known for their distinctive, often humorous designs, Degenerate Apes have cultivated a dedicated community of collectors and enthusiasts. These digital assets are more than just images; they represent membership in an active social network that regularly organizes events, collaborations, and investment discussions.
The community's engagement is evident through frequent online meetups on platforms like Discord and Twitter Spaces. These virtual gatherings serve as forums for sharing insights about market trends, upcoming projects, or simply celebrating new drops. Additionally, there have been several in-person meetups where owners can showcase their NFTs and connect face-to-face with fellow collectors—further strengthening community bonds.
Key Upcoming Events for Degenerate Ape Owners
While specific event dates are subject to change based on ongoing developments within the NFT space, several recurring themes highlight what Degenerate Ape owners can anticipate in 2024:
Community Meetups & Social Gatherings:
The community continues to prioritize real-world interactions through organized meetups across major cities worldwide. These events provide opportunities for networking, showcasing rare NFTs, and participating in live discussions about future trends.Collaborative Drops & Exclusive Content:
Yuga Labs frequently partners with brands such as Adidas or Sotheby’s to create exclusive content or limited-edition drops tailored specifically for BAYC members—including those holding Degenerate Apes. Expect upcoming collaborations that could include special merchandise releases or virtual experiences.NFT Art Exhibitions & Blockchain Conferences:
As part of broader industry events focused on blockchain technology and digital art innovation—such as NFT NYC or ETHGlobal—Degenerate Ape owners may find exclusive access or VIP sessions designed around their collection.Investment Seminars & Market Trend Discussions:
Given the volatile nature of NFTs and cryptocurrencies today, many community-led webinars focus on investment strategies amid fluctuating markets. These sessions aim to educate members about maximizing value while navigating regulatory uncertainties.
Strategic Partnerships Impacting Future Events
Yuga Labs’ ongoing collaborations significantly influence upcoming activities relevant to Degenerate Apes owners. Recent partnerships with high-profile brands like Adidas have led to unique digital collectibles and physical merchandise tied directly into the BAYC universe. Such alliances often translate into special events—virtual launches or offline exhibitions—that enhance member engagement while expanding brand visibility.
Furthermore, Yuga Labs’ involvement with major auction houses like Sotheby’s has opened avenues for high-profile sales featuring rare NFTs from the collection—including some from the Degenerate Apes series. These auctions not only boost market interest but also create opportunities for owners seeking liquidity or recognition within elite circles.
Investment Opportunities Through New Projects
The NFT landscape remains dynamic with continuous project launches related to BAYC properties. In recent years—and particularly throughout 2023—the company announced multiple initiatives aimed at expanding its ecosystem:
- Launching new collections that complement existing ones
- Developing metaverse integrations where avatars can interact
- Creating utility-driven tokens linked directly to ownership rights
For Degenerate Ape holders interested in long-term value appreciation—or diversifying their portfolios—these developments present potential investment avenues worth monitoring closely during upcoming industry events.
Risks Facing Community Members: Market Volatility & Regulatory Changes
Despite optimism surrounding future activities, it’s essential for members to remain aware of inherent risks:
Market Fluctuations: The NFT market is known for rapid price swings driven by macroeconomic factors or shifts in investor sentiment.
Regulatory Environment: Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrencies and digital assets; potential policy changes could impact trading capabilities or ownership rights.
Being informed about these risks allows collectors not only to participate actively but also responsibly manage their investments amid evolving legal landscapes.
How To Stay Updated on Future Events
To maximize participation in upcoming activities:
- Follow official channels such as Yuga Labs’ social media accounts (Twitter/X), Discord servers dedicated to BAYC communities.
- Subscribe to newsletters from prominent NFT news outlets covering event announcements.
- Engage actively during online discussions—these often reveal early insights into scheduled meetups or collaborative projects.
- Attend major blockchain conferences where BAYC-related panels might feature updates regarding future initiatives involving Degenerate Apes.
By staying connected through these channels, owners can ensure they don’t miss out on valuable opportunities aligned with their interests within this vibrant ecosystem.
Final Thoughts: What To Expect Moving Forward
As we progress further into 2024, it’s clear that the world of degenerates—and specifically those owning unique NFTs like DeGenerate Apes—is set up for continued growth through diverse events ranging from social gatherings and art exhibitions to strategic partnerships with global brands. While market volatility remains a concern requiring cautious participation by investors—and regulatory landscapes continue evolving—the overall outlook remains optimistic thanks largely due to active community engagement fostered by Yuga Labs' innovative approach toward expanding its ecosystem globally.
For current holders eager not only just enjoy their assets but also leverage them strategically via participating actively at forthcoming events will be crucial — ensuring they stay ahead amidst an ever-changing landscape driven by technological advancements and cultural shifts shaping tomorrow's digital economy.
Keywords: degenerated ape upcoming events | Bored Ape Yacht Club activities | NFT community meetups | Yuga Labs partnerships | crypto art exhibitions | blockchain conferences


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-29 03:16
Are there any upcoming events for Degenerate Ape owners?
Upcoming Events for Degenerate Ape Owners: What to Expect in 2024
Overview of Degenerate Ape and Its Community Engagement
Degenerate Ape is a notable subset within the broader Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) ecosystem, which has become one of the most influential NFT collections since its launch in April 2021. Known for their distinctive, often humorous designs, Degenerate Apes have cultivated a dedicated community of collectors and enthusiasts. These digital assets are more than just images; they represent membership in an active social network that regularly organizes events, collaborations, and investment discussions.
The community's engagement is evident through frequent online meetups on platforms like Discord and Twitter Spaces. These virtual gatherings serve as forums for sharing insights about market trends, upcoming projects, or simply celebrating new drops. Additionally, there have been several in-person meetups where owners can showcase their NFTs and connect face-to-face with fellow collectors—further strengthening community bonds.
Key Upcoming Events for Degenerate Ape Owners
While specific event dates are subject to change based on ongoing developments within the NFT space, several recurring themes highlight what Degenerate Ape owners can anticipate in 2024:
Community Meetups & Social Gatherings:
The community continues to prioritize real-world interactions through organized meetups across major cities worldwide. These events provide opportunities for networking, showcasing rare NFTs, and participating in live discussions about future trends.Collaborative Drops & Exclusive Content:
Yuga Labs frequently partners with brands such as Adidas or Sotheby’s to create exclusive content or limited-edition drops tailored specifically for BAYC members—including those holding Degenerate Apes. Expect upcoming collaborations that could include special merchandise releases or virtual experiences.NFT Art Exhibitions & Blockchain Conferences:
As part of broader industry events focused on blockchain technology and digital art innovation—such as NFT NYC or ETHGlobal—Degenerate Ape owners may find exclusive access or VIP sessions designed around their collection.Investment Seminars & Market Trend Discussions:
Given the volatile nature of NFTs and cryptocurrencies today, many community-led webinars focus on investment strategies amid fluctuating markets. These sessions aim to educate members about maximizing value while navigating regulatory uncertainties.
Strategic Partnerships Impacting Future Events
Yuga Labs’ ongoing collaborations significantly influence upcoming activities relevant to Degenerate Apes owners. Recent partnerships with high-profile brands like Adidas have led to unique digital collectibles and physical merchandise tied directly into the BAYC universe. Such alliances often translate into special events—virtual launches or offline exhibitions—that enhance member engagement while expanding brand visibility.
Furthermore, Yuga Labs’ involvement with major auction houses like Sotheby’s has opened avenues for high-profile sales featuring rare NFTs from the collection—including some from the Degenerate Apes series. These auctions not only boost market interest but also create opportunities for owners seeking liquidity or recognition within elite circles.
Investment Opportunities Through New Projects
The NFT landscape remains dynamic with continuous project launches related to BAYC properties. In recent years—and particularly throughout 2023—the company announced multiple initiatives aimed at expanding its ecosystem:
- Launching new collections that complement existing ones
- Developing metaverse integrations where avatars can interact
- Creating utility-driven tokens linked directly to ownership rights
For Degenerate Ape holders interested in long-term value appreciation—or diversifying their portfolios—these developments present potential investment avenues worth monitoring closely during upcoming industry events.
Risks Facing Community Members: Market Volatility & Regulatory Changes
Despite optimism surrounding future activities, it’s essential for members to remain aware of inherent risks:
Market Fluctuations: The NFT market is known for rapid price swings driven by macroeconomic factors or shifts in investor sentiment.
Regulatory Environment: Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrencies and digital assets; potential policy changes could impact trading capabilities or ownership rights.
Being informed about these risks allows collectors not only to participate actively but also responsibly manage their investments amid evolving legal landscapes.
How To Stay Updated on Future Events
To maximize participation in upcoming activities:
- Follow official channels such as Yuga Labs’ social media accounts (Twitter/X), Discord servers dedicated to BAYC communities.
- Subscribe to newsletters from prominent NFT news outlets covering event announcements.
- Engage actively during online discussions—these often reveal early insights into scheduled meetups or collaborative projects.
- Attend major blockchain conferences where BAYC-related panels might feature updates regarding future initiatives involving Degenerate Apes.
By staying connected through these channels, owners can ensure they don’t miss out on valuable opportunities aligned with their interests within this vibrant ecosystem.
Final Thoughts: What To Expect Moving Forward
As we progress further into 2024, it’s clear that the world of degenerates—and specifically those owning unique NFTs like DeGenerate Apes—is set up for continued growth through diverse events ranging from social gatherings and art exhibitions to strategic partnerships with global brands. While market volatility remains a concern requiring cautious participation by investors—and regulatory landscapes continue evolving—the overall outlook remains optimistic thanks largely due to active community engagement fostered by Yuga Labs' innovative approach toward expanding its ecosystem globally.
For current holders eager not only just enjoy their assets but also leverage them strategically via participating actively at forthcoming events will be crucial — ensuring they stay ahead amidst an ever-changing landscape driven by technological advancements and cultural shifts shaping tomorrow's digital economy.
Keywords: degenerated ape upcoming events | Bored Ape Yacht Club activities | NFT community meetups | Yuga Labs partnerships | crypto art exhibitions | blockchain conferences
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Each Platform’s Approach to Mobile-Web Parity?
Understanding how different digital platforms support and promote mobile-web parity is essential for businesses aiming to deliver consistent user experiences across devices. Each platform—Google, Apple, Microsoft, Mozilla—has its own set of tools, guidelines, and initiatives designed to facilitate this goal. Recognizing these differences helps developers and organizations optimize their websites effectively for all users.
Google’s Role in Promoting Mobile-Web Parity
Google has been a pioneer in advocating for mobile-web parity through various initiatives that influence search rankings and web development standards. Its push toward mobile-first indexing means that Google primarily uses the mobile version of a website for indexing and ranking purposes. This shift emphasizes the importance of having a fully functional, responsive site on mobile devices.
One of Google’s significant contributions is the development of Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), which aim to deliver fast-loading content optimized specifically for mobile users. Additionally, Google supports Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), enabling websites to function like native apps with offline capabilities, push notifications, and smooth performance on smartphones. These tools help ensure that websites are not only accessible but also engaging across platforms.
Apple’s Focus on Native Design Guidelines
Apple emphasizes seamless integration between hardware and software through its iOS ecosystem. Its Safari browser supports PWAs but with certain limitations compared to other browsers; nonetheless, Apple encourages developers to adhere to its Human Interface Guidelines (HIG). These guidelines focus heavily on creating intuitive interfaces tailored for iPhone and iPad screens while ensuring accessibility features are integrated.
Recent updates from Apple have reinforced the importance of optimizing web experiences within their ecosystem by providing detailed design recommendations that prioritize touch interactions, fast load times, and visual consistency across devices. While Apple does not directly control web standards as extensively as Google does with search algorithms, it influences best practices through its developer resources aimed at achieving better web performance on iOS devices.
Microsoft’s Support Through Developer Tools
Microsoft's approach centers around supporting universal Windows platform (UWP) applications alongside traditional websites optimized for Edge browser compatibility. With Microsoft Edge adopting Chromium-based architecture similar to Chrome—another major player supporting robust PWA features—the company promotes cross-platform consistency.
Microsoft offers comprehensive developer tools within Visual Studio Code and Azure cloud services that assist in testing responsiveness across multiple device types. Their emphasis lies in ensuring enterprise-level applications can be accessed seamlessly whether via desktop or mobile without sacrificing functionality or security protocols.
Mozilla's Contributions Toward Consistent Web Experiences
Mozilla Firefox champions open standards compliance by encouraging adherence to HTML5/CSS3 specifications vital for responsive design implementation. The organization actively participates in developing web APIs that enhance cross-browser compatibility—a key factor in maintaining uniform experiences regardless of platform choice.
Firefox also supports PWAs robustly by allowing installation directly from the browser interface while emphasizing privacy controls alongside performance enhancements tailored specifically for diverse device environments—including smartphones running Android or iOS via compatible browsers.
Industry Trends Shaping Platform Strategies
Over recent years—especially during 2020–2022—the industry has seen an accelerated push toward achieving true mobile-web parity driven largely by external factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic's impact on digital engagement levels[5]. E-commerce giants like Amazon have invested heavily into optimizing their sites' responsiveness because they recognize poor mobile experiences lead directly to lost sales[6].
Furthermore, major players continuously update their guidelines: Google's enhanced support for PWAs reinforces this trend[3], while Apple's updated design principles emphasize faster load times and better touch interactions[4]. These collective efforts underscore a shared industry understanding: delivering consistent user experience is critical not just from a usability perspective but also from a business growth standpoint.
Implications For Businesses And Developers
For organizations aiming at competitive advantage online—and especially those operating multi-platform digital assets—it is crucial first-to understand each platform's unique approach toward achieving mobility parity:
- Leverage Platform-Specific Features: Use Google's AMP technology where appropriate; adopt Apple's HIG recommendations; utilize Microsoft's developer tools.
- Prioritize Responsive Design: Ensure your website adapts seamlessly across screen sizes using flexible layouts.
- Implement Progressive Web Apps: Take advantage of PWA capabilities supported broadly today—for offline access or push notifications.
- Test Across Devices Regularly: Use emulators or real-device testing environments aligned with each platform's specifications.
By aligning development strategies accordingly—and staying updated with evolving standards—you can provide users with an optimal experience regardless of device type or operating system environment.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:Mobile-responsive websites | Cross-platform compatibility | PWA support | Responsive design best practices | Device-specific optimization | User experience consistency | Web accessibility standards | Browser compatibility tools
This comprehensive understanding underscores why each platform’s approach matters profoundly when striving toward true mobile-web parity—a critical factor influencing user satisfaction , engagement metrics ,and ultimately business success .


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-26 19:31
What is each platform’s mobile-web parity?
What Is Each Platform’s Approach to Mobile-Web Parity?
Understanding how different digital platforms support and promote mobile-web parity is essential for businesses aiming to deliver consistent user experiences across devices. Each platform—Google, Apple, Microsoft, Mozilla—has its own set of tools, guidelines, and initiatives designed to facilitate this goal. Recognizing these differences helps developers and organizations optimize their websites effectively for all users.
Google’s Role in Promoting Mobile-Web Parity
Google has been a pioneer in advocating for mobile-web parity through various initiatives that influence search rankings and web development standards. Its push toward mobile-first indexing means that Google primarily uses the mobile version of a website for indexing and ranking purposes. This shift emphasizes the importance of having a fully functional, responsive site on mobile devices.
One of Google’s significant contributions is the development of Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP), which aim to deliver fast-loading content optimized specifically for mobile users. Additionally, Google supports Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), enabling websites to function like native apps with offline capabilities, push notifications, and smooth performance on smartphones. These tools help ensure that websites are not only accessible but also engaging across platforms.
Apple’s Focus on Native Design Guidelines
Apple emphasizes seamless integration between hardware and software through its iOS ecosystem. Its Safari browser supports PWAs but with certain limitations compared to other browsers; nonetheless, Apple encourages developers to adhere to its Human Interface Guidelines (HIG). These guidelines focus heavily on creating intuitive interfaces tailored for iPhone and iPad screens while ensuring accessibility features are integrated.
Recent updates from Apple have reinforced the importance of optimizing web experiences within their ecosystem by providing detailed design recommendations that prioritize touch interactions, fast load times, and visual consistency across devices. While Apple does not directly control web standards as extensively as Google does with search algorithms, it influences best practices through its developer resources aimed at achieving better web performance on iOS devices.
Microsoft’s Support Through Developer Tools
Microsoft's approach centers around supporting universal Windows platform (UWP) applications alongside traditional websites optimized for Edge browser compatibility. With Microsoft Edge adopting Chromium-based architecture similar to Chrome—another major player supporting robust PWA features—the company promotes cross-platform consistency.
Microsoft offers comprehensive developer tools within Visual Studio Code and Azure cloud services that assist in testing responsiveness across multiple device types. Their emphasis lies in ensuring enterprise-level applications can be accessed seamlessly whether via desktop or mobile without sacrificing functionality or security protocols.
Mozilla's Contributions Toward Consistent Web Experiences
Mozilla Firefox champions open standards compliance by encouraging adherence to HTML5/CSS3 specifications vital for responsive design implementation. The organization actively participates in developing web APIs that enhance cross-browser compatibility—a key factor in maintaining uniform experiences regardless of platform choice.
Firefox also supports PWAs robustly by allowing installation directly from the browser interface while emphasizing privacy controls alongside performance enhancements tailored specifically for diverse device environments—including smartphones running Android or iOS via compatible browsers.
Industry Trends Shaping Platform Strategies
Over recent years—especially during 2020–2022—the industry has seen an accelerated push toward achieving true mobile-web parity driven largely by external factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic's impact on digital engagement levels[5]. E-commerce giants like Amazon have invested heavily into optimizing their sites' responsiveness because they recognize poor mobile experiences lead directly to lost sales[6].
Furthermore, major players continuously update their guidelines: Google's enhanced support for PWAs reinforces this trend[3], while Apple's updated design principles emphasize faster load times and better touch interactions[4]. These collective efforts underscore a shared industry understanding: delivering consistent user experience is critical not just from a usability perspective but also from a business growth standpoint.
Implications For Businesses And Developers
For organizations aiming at competitive advantage online—and especially those operating multi-platform digital assets—it is crucial first-to understand each platform's unique approach toward achieving mobility parity:
- Leverage Platform-Specific Features: Use Google's AMP technology where appropriate; adopt Apple's HIG recommendations; utilize Microsoft's developer tools.
- Prioritize Responsive Design: Ensure your website adapts seamlessly across screen sizes using flexible layouts.
- Implement Progressive Web Apps: Take advantage of PWA capabilities supported broadly today—for offline access or push notifications.
- Test Across Devices Regularly: Use emulators or real-device testing environments aligned with each platform's specifications.
By aligning development strategies accordingly—and staying updated with evolving standards—you can provide users with an optimal experience regardless of device type or operating system environment.
Semantic & LSI Keywords:Mobile-responsive websites | Cross-platform compatibility | PWA support | Responsive design best practices | Device-specific optimization | User experience consistency | Web accessibility standards | Browser compatibility tools
This comprehensive understanding underscores why each platform’s approach matters profoundly when striving toward true mobile-web parity—a critical factor influencing user satisfaction , engagement metrics ,and ultimately business success .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Role of a Node in a Blockchain Network?
Understanding the fundamental components of blockchain technology is essential for grasping how decentralized systems operate securely and efficiently. Among these components, nodes play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity, security, and decentralization of blockchain networks. This article explores what blockchain nodes are, their functions within the network, recent developments affecting them, and potential challenges they face.
What Is a Blockchain Node?
A blockchain node is essentially a computer running specific software that connects to the broader blockchain network. Unlike traditional centralized systems where data resides on single servers controlled by one entity, nodes distribute data across multiple locations worldwide. Each node maintains an identical copy of the entire blockchain ledger—comprising all transactions and blocks—ensuring transparency and resilience.
Nodes serve as both participants and guardians within this decentralized environment. They validate new transactions, propagate information across the network, and help enforce consensus rules that keep everyone on the same page regarding transaction history.
Key Functions of Blockchain Nodes
Transaction Validation
One primary responsibility of nodes is verifying transactions before they are added to the blockchain. When someone initiates a transfer or contract execution, their transaction must be checked against existing rules—such as ensuring digital signatures are valid or that funds are available. Nodes perform these checks based on predefined consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), which establish trust without relying on central authorities.
Maintaining Full Ledger Copies
Every full node stores an exact replica of all historical data within the blockchain. This comprehensive record allows any participant to independently verify transaction legitimacy without relying solely on other entities’ claims. Such redundancy enhances security by making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter past records undetected.
Participating in Consensus Processes
Consensus mechanisms enable nodes to agree upon which transactions should be added next to prevent conflicts such as double-spending or forks in chain history. Depending on whether a network uses PoW (like Bitcoin) or PoS (like Ethereum 2.0), nodes contribute computational power or stake tokens respectively to validate new blocks reliably.
Supporting Decentralization & Security
The distributed nature of nodes ensures no single point controls or manipulates the system—a core principle known as decentralization. The more geographically dispersed and diverse these nodes are, the harder it becomes for bad actors to compromise entire networks through attacks like 51% control or censorship attempts.
Recent Developments Impacting Blockchain Nodes
Scalability Solutions: Sharding & Layer 2 Technologies
As blockchains grow in popularity with increasing transaction volumes, scalability becomes critical for performance optimization. Technologies such as sharding split large blockchains into smaller partitions processed simultaneously by different groups of nodes; this reduces congestion and improves throughput significantly.
Layer 2 solutions—including state channels and sidechains—operate outside main chains but still rely heavily on full-node validation when necessary while enabling faster processing times at lower costs for users.
Transition from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake
Ethereum’s move toward Ethereum 2.0 exemplifies shifts aimed at reducing energy consumption associated with PoW systems while maintaining security standards through staking-based validation methods involving fewer computational resources—a change that influences how many types of nodes participate actively in consensus processes.
Variations in Node Types: Full vs Light Nodes
Not all nodes perform identical roles; some maintain complete copies (full nodes) essential for validating every transaction independently; others (light clients) store only headers—the summarized version—and depend upon full nodes for detailed verification tasks—improving accessibility but potentially impacting decentralization if light clients dominate certain networks.
Concerns Over Centralized Nodes
While decentralization remains idealized conceptually—and vital from an E-A-T perspective—it faces real-world challenges such as centralized hosting services controlling large numbers of high-performance full nodes—which can threaten overall network resilience if compromised or colluded with malicious intent.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Nodes Today
Despite their critical importance, several issues impact node operation:
Security Risks: Centralized hosting providers can become targets for cyberattacks aiming at controlling significant portions—or even majority—of active validators.
Scalability Limitations: As more users join networks requiring validation services from numerous full nodes worldwide, maintaining high performance becomes increasingly complex.
Environmental Concerns: Energy-intensive proof-of-work protocols have drawn criticism due to their substantial carbon footprint; shifting toward eco-friendlier consensus algorithms aims at mitigating this issue.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments exploring regulations around cryptocurrencies could influence how operators run validator infrastructure—for example restricting access or imposing compliance requirements.
How Blockchain Nodes Shape Ecosystem Security & Trustworthiness
Nodes underpin trustless interactions by enabling independent verification without reliance on third parties—a core advantage highlighted under E-A-T principles (Expertise–Authoritativeness–Trustworthiness). Their widespread distribution fosters resilience against censorship attempts while promoting transparency through open ledger maintenance accessible globally.
Furthermore, incentives like transaction fees motivate operators worldwide to run reliable hardware continuously contributing towards robust decentralization efforts—all crucial factors reinforcing user confidence over time.
By understanding what roles blockchain nodes fulfill—from validating transactions and supporting consensus mechanisms to maintaining decentralized security—you gain insight into why they form foundational pillars behind modern cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum alike.
This knowledge also highlights ongoing technological innovations aimed at improving scalability while addressing environmental concerns—all vital considerations shaping future developments within this rapidly evolving space.
In summary: Whether you’re an investor seeking clarity about underlying infrastructure risks—or developer interested in building scalable dApps—the role played by individual nodes remains central—and understanding their dynamics helps navigate today’s complex yet promising landscape effectively.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-22 15:52
What is the role of a "node" in a blockchain network?
What Is the Role of a Node in a Blockchain Network?
Understanding the fundamental components of blockchain technology is essential for grasping how decentralized systems operate securely and efficiently. Among these components, nodes play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity, security, and decentralization of blockchain networks. This article explores what blockchain nodes are, their functions within the network, recent developments affecting them, and potential challenges they face.
What Is a Blockchain Node?
A blockchain node is essentially a computer running specific software that connects to the broader blockchain network. Unlike traditional centralized systems where data resides on single servers controlled by one entity, nodes distribute data across multiple locations worldwide. Each node maintains an identical copy of the entire blockchain ledger—comprising all transactions and blocks—ensuring transparency and resilience.
Nodes serve as both participants and guardians within this decentralized environment. They validate new transactions, propagate information across the network, and help enforce consensus rules that keep everyone on the same page regarding transaction history.
Key Functions of Blockchain Nodes
Transaction Validation
One primary responsibility of nodes is verifying transactions before they are added to the blockchain. When someone initiates a transfer or contract execution, their transaction must be checked against existing rules—such as ensuring digital signatures are valid or that funds are available. Nodes perform these checks based on predefined consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), which establish trust without relying on central authorities.
Maintaining Full Ledger Copies
Every full node stores an exact replica of all historical data within the blockchain. This comprehensive record allows any participant to independently verify transaction legitimacy without relying solely on other entities’ claims. Such redundancy enhances security by making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter past records undetected.
Participating in Consensus Processes
Consensus mechanisms enable nodes to agree upon which transactions should be added next to prevent conflicts such as double-spending or forks in chain history. Depending on whether a network uses PoW (like Bitcoin) or PoS (like Ethereum 2.0), nodes contribute computational power or stake tokens respectively to validate new blocks reliably.
Supporting Decentralization & Security
The distributed nature of nodes ensures no single point controls or manipulates the system—a core principle known as decentralization. The more geographically dispersed and diverse these nodes are, the harder it becomes for bad actors to compromise entire networks through attacks like 51% control or censorship attempts.
Recent Developments Impacting Blockchain Nodes
Scalability Solutions: Sharding & Layer 2 Technologies
As blockchains grow in popularity with increasing transaction volumes, scalability becomes critical for performance optimization. Technologies such as sharding split large blockchains into smaller partitions processed simultaneously by different groups of nodes; this reduces congestion and improves throughput significantly.
Layer 2 solutions—including state channels and sidechains—operate outside main chains but still rely heavily on full-node validation when necessary while enabling faster processing times at lower costs for users.
Transition from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake
Ethereum’s move toward Ethereum 2.0 exemplifies shifts aimed at reducing energy consumption associated with PoW systems while maintaining security standards through staking-based validation methods involving fewer computational resources—a change that influences how many types of nodes participate actively in consensus processes.
Variations in Node Types: Full vs Light Nodes
Not all nodes perform identical roles; some maintain complete copies (full nodes) essential for validating every transaction independently; others (light clients) store only headers—the summarized version—and depend upon full nodes for detailed verification tasks—improving accessibility but potentially impacting decentralization if light clients dominate certain networks.
Concerns Over Centralized Nodes
While decentralization remains idealized conceptually—and vital from an E-A-T perspective—it faces real-world challenges such as centralized hosting services controlling large numbers of high-performance full nodes—which can threaten overall network resilience if compromised or colluded with malicious intent.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Nodes Today
Despite their critical importance, several issues impact node operation:
Security Risks: Centralized hosting providers can become targets for cyberattacks aiming at controlling significant portions—or even majority—of active validators.
Scalability Limitations: As more users join networks requiring validation services from numerous full nodes worldwide, maintaining high performance becomes increasingly complex.
Environmental Concerns: Energy-intensive proof-of-work protocols have drawn criticism due to their substantial carbon footprint; shifting toward eco-friendlier consensus algorithms aims at mitigating this issue.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments exploring regulations around cryptocurrencies could influence how operators run validator infrastructure—for example restricting access or imposing compliance requirements.
How Blockchain Nodes Shape Ecosystem Security & Trustworthiness
Nodes underpin trustless interactions by enabling independent verification without reliance on third parties—a core advantage highlighted under E-A-T principles (Expertise–Authoritativeness–Trustworthiness). Their widespread distribution fosters resilience against censorship attempts while promoting transparency through open ledger maintenance accessible globally.
Furthermore, incentives like transaction fees motivate operators worldwide to run reliable hardware continuously contributing towards robust decentralization efforts—all crucial factors reinforcing user confidence over time.
By understanding what roles blockchain nodes fulfill—from validating transactions and supporting consensus mechanisms to maintaining decentralized security—you gain insight into why they form foundational pillars behind modern cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum alike.
This knowledge also highlights ongoing technological innovations aimed at improving scalability while addressing environmental concerns—all vital considerations shaping future developments within this rapidly evolving space.
In summary: Whether you’re an investor seeking clarity about underlying infrastructure risks—or developer interested in building scalable dApps—the role played by individual nodes remains central—and understanding their dynamics helps navigate today’s complex yet promising landscape effectively.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Role Do Cash Flow Projections Play in Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Models?
Understanding the core of financial valuation methods is essential for investors, analysts, and business owners alike. Among these methods, Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) models stand out as a fundamental approach to estimating a company's intrinsic value. At the heart of DCF analysis are cash flow projections—forecasts of future cash inflows and outflows—that serve as the foundation for valuation. This article explores the critical role that cash flow projections play within DCF models, recent developments influencing their use, and best practices to ensure accurate and realistic valuations.
The Significance of Cash Flow Projections in Valuation
Cash flow projections are essentially educated estimates about how much money a company will generate or spend over a specific period. These forecasts typically include operating cash flows—such as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), depreciation expenses, and changes in working capital—as well as non-operating cash flows like dividends or interest payments.
In DCF models, these projected cash flows serve multiple purposes:
- Estimating Future Company Value: By projecting future cash flows over several years, analysts can gauge what the company might be worth at different points in time.
- Calculating Present Value: Since money today is worth more than money tomorrow due to inflation and risk factors, future cash flows are discounted back to their present value using an appropriate discount rate.
- Determining Terminal Value: Beyond explicit forecast periods—usually 5 to 10 years—a terminal value estimates ongoing cash flows into perpetuity using assumptions about long-term growth rates.
Accurate forecasting is vital because even small errors can significantly impact valuation outcomes. Overly optimistic projections may lead investors to overpay for assets; conversely, overly conservative forecasts could undervalue promising investments.
Recent Trends: Emphasizing Conservative Assumptions
Recent financial research underscores the importance of adopting conservative assumptions when developing cash flow projections within DCF models. Experts recommend cautious approaches particularly concerning terminal growth rates—the assumed rate at which a company's free cash flows will grow indefinitely beyond forecast horizons—and discount rates that reflect investment risk.
Why does this matter? Because overly aggressive assumptions tend to inflate valuations artificially. For example:
- Using high terminal growth rates without sufficient justification can lead to exaggerated long-term company values.
- Underestimating discount rates may make future prospects seem more attractive than they realistically are.
Recent analyses from 2025 highlight that employing modest or conservative terminal growth assumptions helps prevent overvaluation pitfalls while providing more reliable estimates aligned with market realities[1][2].
Key Factors Influencing Cash Flow Projection Accuracy
Several elements influence how precise your projected figures will be:
- Assumption Quality: The credibility of your forecasts hinges on realistic expectations about revenue growth, profit margins, capital expenditures, and working capital needs.
- Market Conditions: Economic trends such as inflation rates or industry-specific shifts should inform your outlooks.
- Company-Specific Data: Historical performance data provides valuable insights but must be adjusted for anticipated changes.
- Risk Considerations: Incorporate appropriate discount rates reflecting operational risks; higher uncertainty warrants higher discounting.
Adopting conservative assumptions across these factors ensures that valuations remain grounded in reality rather than inflated by overly optimistic predictions.
Potential Risks from Misapplied Cash Flow Projections
Failing to incorporate prudent assumptions can have serious consequences:
Overestimating future earnings leads investors astray by valuing companies above their true worth—a common cause of market bubbles or corrections when expectations aren't met.
Conversely, excessively cautious forecasts might cause undervaluation opportunities where potential exists but isn't recognized due to overly conservative estimates.
Striking a balance between optimism and realism is crucial for credible valuation results that guide sound investment decisions.
Best Practices for Developing Reliable Cash Flow Forecasts
To enhance accuracy in your DCF analysis through better projection techniques:
Use historical data as a baseline but adjust based on current market conditions and strategic plans.
Apply sensitivity analysis by testing various scenarios with different growth rates or discount factors; this helps understand potential valuation ranges under varying circumstances.
Keep terminal growth rates modest—generally aligning with long-term economic growth—to avoid unrealistic perpetuity assumptions[1].
Regularly update forecasts with new information such as quarterly earnings reports or macroeconomic indicators ensuring relevance over time[2].
By adhering to these practices rooted in recent research findings—and emphasizing conservatism—you improve both the reliability and credibility of your valuations.
Implications for Investors and Analysts
For those relying on DCF models for investment decisions—or conducting corporate valuations—the quality of underlying cash flow projections directly impacts outcomes. Conservative yet realistic forecasts help mitigate risks associated with overvaluation while capturing genuine opportunities missed by overly cautious approaches alone.
Furthermore,
- Transparent assumption-setting enhances trustworthiness among stakeholders,
- Regular model updates reflect changing conditions,
- Clear communication regarding projection methodologies fosters better decision-making processes,
ultimately leading toward more informed investment choices aligned with actual market dynamics.
References
1. Recent analysis emphasizes adopting modest terminal growth rates within DCF models (2025).
2. Experts highlight the importance of conservative assumptions especially regarding discount rate selection (2025).


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 14:44
What role do cash flow projections play in DCF models?
What Role Do Cash Flow Projections Play in Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Models?
Understanding the core of financial valuation methods is essential for investors, analysts, and business owners alike. Among these methods, Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) models stand out as a fundamental approach to estimating a company's intrinsic value. At the heart of DCF analysis are cash flow projections—forecasts of future cash inflows and outflows—that serve as the foundation for valuation. This article explores the critical role that cash flow projections play within DCF models, recent developments influencing their use, and best practices to ensure accurate and realistic valuations.
The Significance of Cash Flow Projections in Valuation
Cash flow projections are essentially educated estimates about how much money a company will generate or spend over a specific period. These forecasts typically include operating cash flows—such as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), depreciation expenses, and changes in working capital—as well as non-operating cash flows like dividends or interest payments.
In DCF models, these projected cash flows serve multiple purposes:
- Estimating Future Company Value: By projecting future cash flows over several years, analysts can gauge what the company might be worth at different points in time.
- Calculating Present Value: Since money today is worth more than money tomorrow due to inflation and risk factors, future cash flows are discounted back to their present value using an appropriate discount rate.
- Determining Terminal Value: Beyond explicit forecast periods—usually 5 to 10 years—a terminal value estimates ongoing cash flows into perpetuity using assumptions about long-term growth rates.
Accurate forecasting is vital because even small errors can significantly impact valuation outcomes. Overly optimistic projections may lead investors to overpay for assets; conversely, overly conservative forecasts could undervalue promising investments.
Recent Trends: Emphasizing Conservative Assumptions
Recent financial research underscores the importance of adopting conservative assumptions when developing cash flow projections within DCF models. Experts recommend cautious approaches particularly concerning terminal growth rates—the assumed rate at which a company's free cash flows will grow indefinitely beyond forecast horizons—and discount rates that reflect investment risk.
Why does this matter? Because overly aggressive assumptions tend to inflate valuations artificially. For example:
- Using high terminal growth rates without sufficient justification can lead to exaggerated long-term company values.
- Underestimating discount rates may make future prospects seem more attractive than they realistically are.
Recent analyses from 2025 highlight that employing modest or conservative terminal growth assumptions helps prevent overvaluation pitfalls while providing more reliable estimates aligned with market realities[1][2].
Key Factors Influencing Cash Flow Projection Accuracy
Several elements influence how precise your projected figures will be:
- Assumption Quality: The credibility of your forecasts hinges on realistic expectations about revenue growth, profit margins, capital expenditures, and working capital needs.
- Market Conditions: Economic trends such as inflation rates or industry-specific shifts should inform your outlooks.
- Company-Specific Data: Historical performance data provides valuable insights but must be adjusted for anticipated changes.
- Risk Considerations: Incorporate appropriate discount rates reflecting operational risks; higher uncertainty warrants higher discounting.
Adopting conservative assumptions across these factors ensures that valuations remain grounded in reality rather than inflated by overly optimistic predictions.
Potential Risks from Misapplied Cash Flow Projections
Failing to incorporate prudent assumptions can have serious consequences:
Overestimating future earnings leads investors astray by valuing companies above their true worth—a common cause of market bubbles or corrections when expectations aren't met.
Conversely, excessively cautious forecasts might cause undervaluation opportunities where potential exists but isn't recognized due to overly conservative estimates.
Striking a balance between optimism and realism is crucial for credible valuation results that guide sound investment decisions.
Best Practices for Developing Reliable Cash Flow Forecasts
To enhance accuracy in your DCF analysis through better projection techniques:
Use historical data as a baseline but adjust based on current market conditions and strategic plans.
Apply sensitivity analysis by testing various scenarios with different growth rates or discount factors; this helps understand potential valuation ranges under varying circumstances.
Keep terminal growth rates modest—generally aligning with long-term economic growth—to avoid unrealistic perpetuity assumptions[1].
Regularly update forecasts with new information such as quarterly earnings reports or macroeconomic indicators ensuring relevance over time[2].
By adhering to these practices rooted in recent research findings—and emphasizing conservatism—you improve both the reliability and credibility of your valuations.
Implications for Investors and Analysts
For those relying on DCF models for investment decisions—or conducting corporate valuations—the quality of underlying cash flow projections directly impacts outcomes. Conservative yet realistic forecasts help mitigate risks associated with overvaluation while capturing genuine opportunities missed by overly cautious approaches alone.
Furthermore,
- Transparent assumption-setting enhances trustworthiness among stakeholders,
- Regular model updates reflect changing conditions,
- Clear communication regarding projection methodologies fosters better decision-making processes,
ultimately leading toward more informed investment choices aligned with actual market dynamics.
References
1. Recent analysis emphasizes adopting modest terminal growth rates within DCF models (2025).
2. Experts highlight the importance of conservative assumptions especially regarding discount rate selection (2025).
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Are Exchange Transaction Fees Calculated in Cryptocurrency?
Understanding how exchange transaction fees are calculated is essential for cryptocurrency users and investors alike. These fees directly impact the cost of trading, influence user behavior, and can vary significantly across different platforms and blockchain networks. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the methods used to determine transaction fees in the crypto space, highlighting key factors that influence fee structures.
What Are Cryptocurrency Exchange Transaction Fees?
Cryptocurrency exchange transaction fees are charges imposed on users when they buy, sell, or transfer digital assets through an exchange platform. These fees serve multiple purposes: they help maintain network security by incentivizing validators (miners or nodes), manage network congestion during high traffic periods, and generate revenue for exchanges to support their operations.
These fees are typically paid in the same cryptocurrency being transacted but can sometimes be paid using other tokens or fiat currency depending on the platform's policies. The structure and calculation method of these fees vary widely based on several factors including blockchain protocol specifics, exchange policies, and market conditions.
Factors Influencing How Transaction Fees Are Calculated
Several key elements determine how transaction fees are calculated within different blockchain networks and exchanges:
- Network Protocols: Different blockchains have unique mechanisms for fee calculation—Ethereum uses gas prices; Bitcoin relies on satoshis per byte.
- Transaction Complexity: More complex transactions (e.g., smart contract interactions) generally require higher fees due to increased computational resources.
- Network Congestion: During peak times with high demand for block space, fee rates tend to rise as users compete to have their transactions processed quickly.
- User Preferences: Some exchanges offer options like priority processing at higher costs or standard processing at lower costs.
- Fee Models Adopted by Exchanges: Fixed fee structures versus dynamic sliding scales based on transaction size or urgency.
Understanding these factors helps clarify why some transactions incur higher costs than others under similar conditions.
How Gas Fees Work in Ethereum
Ethereum’s fee system is one of the most well-known examples of dynamic fee calculation through gas prices. Gas refers to a unit measuring computational effort required to execute operations such as transfers or smart contract interactions. Users specify a gas price (in Gwei) they’re willing to pay per unit of gas; miners prioritize transactions offering higher gas prices because they earn more from those transactions.
The total fee paid equals:
Gas Limit × Gas Price
where Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gas a user is willing to spend on a specific transaction. During periods of high network congestion—such as after Ethereum's London Hard Fork introduced EIP-1559—the base fee adjusts automatically based on network demand. This mechanism aims to stabilize average transaction costs while burning part of the base fee reduces miner rewards over time.
Fixed vs Variable Fee Structures
Different exchanges adopt various models for calculating transaction fees:
Fixed Fees
Some platforms charge a flat rate regardless of trade size or network conditions—for example:
- $5 per withdrawal
- 0.1% per trade
Fixed models provide simplicity but may not reflect real-time network load variations.
Sliding Scale / Dynamic Fees
More sophisticated exchanges implement variable pricing strategies that adjust according to:
- Transaction urgency
- Network congestion levels
- Trade volume
For instance, during busy periods, users opting for faster confirmation might pay higher percentages compared with standard processing times which cost less but take longer.
Hybrid Approaches
Certain platforms combine fixed minimums with dynamic adjustments—offering predictable baseline charges while allowing surcharges during peak times.
Recent Innovations Impacting Fee Calculation
Recent developments aim at making crypto trading more affordable while maintaining security standards:
- EIP-1559 (Ethereum): Introduced in August 2021 via London's hard fork; it changed how gas prices are set by implementing an automatic base fee that burns part of each transaction’s cost—reducing overall supply pressure.
- Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Polygon and Arbitrum process many transactions off-chain before settling them onto main chains at reduced costs.
- Fee Reduction Mechanisms: BNB Smart Chain implemented measures reducing average transactional costs in 2022 aimed at attracting more traders amid rising competition among blockchains.
These innovations demonstrate ongoing efforts toward balancing low-cost usability with robust security protocols essential for decentralization integrity.
Why Accurate Fee Calculation Matters
For traders and investors, understanding how these calculations work ensures transparency regarding potential expenses associated with each trade or transfer — crucial when planning large investments or frequent trading activities. Overpaying due to ignorance about current rates can erode profit margins; underestimating could lead to failed transactions if insufficient funds cover both principal amounts plus applicable charges.
Moreover, awareness about fluctuating network conditions helps optimize timing—for example executing trades during off-peak hours when lower fees apply enhances overall efficiency without sacrificing speed unnecessarily.
By grasping how cryptocurrency exchange transaction fees are calculated—from basic principles like fixed versus variable models through advanced mechanisms such as Ethereum's gas system—you gain better control over your trading expenses while contributing positively toward sustainable blockchain ecosystems that balance scalability with decentralization integrity.
Keywords: cryptocurrency exchange fees calculation | crypto transaction costs | Ethereum gas price | fixed vs variable cryptoFees | layer 2 scaling solutions | blockchain network congestion


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-15 01:07
How are exchange transaction fees calculated?
How Are Exchange Transaction Fees Calculated in Cryptocurrency?
Understanding how exchange transaction fees are calculated is essential for cryptocurrency users and investors alike. These fees directly impact the cost of trading, influence user behavior, and can vary significantly across different platforms and blockchain networks. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the methods used to determine transaction fees in the crypto space, highlighting key factors that influence fee structures.
What Are Cryptocurrency Exchange Transaction Fees?
Cryptocurrency exchange transaction fees are charges imposed on users when they buy, sell, or transfer digital assets through an exchange platform. These fees serve multiple purposes: they help maintain network security by incentivizing validators (miners or nodes), manage network congestion during high traffic periods, and generate revenue for exchanges to support their operations.
These fees are typically paid in the same cryptocurrency being transacted but can sometimes be paid using other tokens or fiat currency depending on the platform's policies. The structure and calculation method of these fees vary widely based on several factors including blockchain protocol specifics, exchange policies, and market conditions.
Factors Influencing How Transaction Fees Are Calculated
Several key elements determine how transaction fees are calculated within different blockchain networks and exchanges:
- Network Protocols: Different blockchains have unique mechanisms for fee calculation—Ethereum uses gas prices; Bitcoin relies on satoshis per byte.
- Transaction Complexity: More complex transactions (e.g., smart contract interactions) generally require higher fees due to increased computational resources.
- Network Congestion: During peak times with high demand for block space, fee rates tend to rise as users compete to have their transactions processed quickly.
- User Preferences: Some exchanges offer options like priority processing at higher costs or standard processing at lower costs.
- Fee Models Adopted by Exchanges: Fixed fee structures versus dynamic sliding scales based on transaction size or urgency.
Understanding these factors helps clarify why some transactions incur higher costs than others under similar conditions.
How Gas Fees Work in Ethereum
Ethereum’s fee system is one of the most well-known examples of dynamic fee calculation through gas prices. Gas refers to a unit measuring computational effort required to execute operations such as transfers or smart contract interactions. Users specify a gas price (in Gwei) they’re willing to pay per unit of gas; miners prioritize transactions offering higher gas prices because they earn more from those transactions.
The total fee paid equals:
Gas Limit × Gas Price
where Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gas a user is willing to spend on a specific transaction. During periods of high network congestion—such as after Ethereum's London Hard Fork introduced EIP-1559—the base fee adjusts automatically based on network demand. This mechanism aims to stabilize average transaction costs while burning part of the base fee reduces miner rewards over time.
Fixed vs Variable Fee Structures
Different exchanges adopt various models for calculating transaction fees:
Fixed Fees
Some platforms charge a flat rate regardless of trade size or network conditions—for example:
- $5 per withdrawal
- 0.1% per trade
Fixed models provide simplicity but may not reflect real-time network load variations.
Sliding Scale / Dynamic Fees
More sophisticated exchanges implement variable pricing strategies that adjust according to:
- Transaction urgency
- Network congestion levels
- Trade volume
For instance, during busy periods, users opting for faster confirmation might pay higher percentages compared with standard processing times which cost less but take longer.
Hybrid Approaches
Certain platforms combine fixed minimums with dynamic adjustments—offering predictable baseline charges while allowing surcharges during peak times.
Recent Innovations Impacting Fee Calculation
Recent developments aim at making crypto trading more affordable while maintaining security standards:
- EIP-1559 (Ethereum): Introduced in August 2021 via London's hard fork; it changed how gas prices are set by implementing an automatic base fee that burns part of each transaction’s cost—reducing overall supply pressure.
- Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like Polygon and Arbitrum process many transactions off-chain before settling them onto main chains at reduced costs.
- Fee Reduction Mechanisms: BNB Smart Chain implemented measures reducing average transactional costs in 2022 aimed at attracting more traders amid rising competition among blockchains.
These innovations demonstrate ongoing efforts toward balancing low-cost usability with robust security protocols essential for decentralization integrity.
Why Accurate Fee Calculation Matters
For traders and investors, understanding how these calculations work ensures transparency regarding potential expenses associated with each trade or transfer — crucial when planning large investments or frequent trading activities. Overpaying due to ignorance about current rates can erode profit margins; underestimating could lead to failed transactions if insufficient funds cover both principal amounts plus applicable charges.
Moreover, awareness about fluctuating network conditions helps optimize timing—for example executing trades during off-peak hours when lower fees apply enhances overall efficiency without sacrificing speed unnecessarily.
By grasping how cryptocurrency exchange transaction fees are calculated—from basic principles like fixed versus variable models through advanced mechanisms such as Ethereum's gas system—you gain better control over your trading expenses while contributing positively toward sustainable blockchain ecosystems that balance scalability with decentralization integrity.
Keywords: cryptocurrency exchange fees calculation | crypto transaction costs | Ethereum gas price | fixed vs variable cryptoFees | layer 2 scaling solutions | blockchain network congestion
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do I Use Investing.com’s Economic Calendar?
Understanding how to effectively utilize Investing.com’s Economic Calendar can significantly enhance your trading and investment strategies. This powerful tool provides real-time updates on upcoming economic events, helping you anticipate market movements and make informed decisions. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to leverage this resource for maximum benefit.
What Is the Investing.com Economic Calendar?
The Investing.com Economic Calendar is an essential resource for traders, investors, and financial analysts. It offers a detailed schedule of upcoming economic releases from around the world, including key indicators such as GDP growth rates, inflation figures, employment data, interest rate decisions, and central bank statements. The calendar consolidates data from reputable sources like government agencies and financial institutions to ensure accuracy.
This tool not only displays when these events will occur but also provides context about their potential impact on markets. By monitoring these scheduled releases, users can better understand market sentiment and prepare for possible volatility.
Why Is the Economic Calendar Important for Investors?
Market participants rely heavily on economic calendars because they highlight moments when asset prices might experience significant fluctuations due to new information entering the market. For example:
- An unexpected increase in unemployment rates could lead to a decline in stock prices.
- A surprise rate hike by a central bank might strengthen or weaken a currency.
- Strong GDP data may boost investor confidence in an economy.
By staying informed about these events beforehand through the calendar, investors can adjust their positions accordingly—either by taking advantage of anticipated moves or by reducing exposure during volatile periods.
How To Access and Navigate the Calendar
Accessing the calendar is straightforward via Investing.com’s website or mobile app. Once there:
- Select Your Region or Market: Customize your view based on geographic focus—such as US economy, Eurozone countries, or emerging markets—to filter relevant events.
- Review Event Details: Each scheduled event includes:
- Date and time (with timezone adjustments)
- Expected release (forecast)
- Previous results
- Actual results once released
- Understand Impact Indicators: Many entries feature impact icons indicating whether an event is likely to have low, medium, or high influence on markets.
- Use Filters: Narrow down your view by selecting specific event types like employment reports or interest rate decisions that align with your trading strategy.
The platform's user-friendly interface makes it easy even for beginners to find relevant information quickly while offering advanced options for experienced traders seeking detailed analysis.
Customizing Your Experience
One of the key advantages of Investing.com's calendar is its customization features:
- Focus Regions: Filter events based on specific countries or regions that are part of your investment portfolio.
- Event Types: Choose particular categories such as inflation reports or trade balance announcements.
- Time Settings: Adjust time zones according to your location so you don’t miss critical updates during off-hours.
Customizing ensures you receive targeted alerts aligned with your trading hours and strategic interests—saving time while enhancing decision-making precision.
Interpreting Data & Forecasts
While viewing scheduled releases is helpful; understanding what they mean requires some knowledge:
- Look at forecast figures versus previous results; large deviations often trigger market reactions.
- Pay attention to impact indicators—high-impact events tend to cause more volatility than low-impact ones.
Many calendars include brief analyses predicting potential outcomes based on current economic conditions—a valuable feature that helps interpret raw data within broader macroeconomic contexts.
However, always cross-reference forecasts with multiple sources before making trades; no single indicator guarantees market direction.
Using Additional Tools Alongside The Calendar
To maximize insights gained from investing in economic releases:
- Combine calendar alerts with technical analysis charts available on Investing.com—for example:
- Support/resistance levels
- Moving averages
- Trend lines
This integrated approach allows you not only anticipate when significant news will arrive but also understand how it might influence price action within existing trends.
Additionally,
- Follow related news feeds linked directly within each event entry,
- Set up notifications so you’re alerted ahead of major releases,
- Use historical data provided alongside upcoming schedules for trend analysis over time.
Managing Risks During Major Releases
Economic announcements often lead to increased volatility which can result in rapid price swings—both upward and downward—that may catch unprepared traders off guard. To mitigate risks:
- Avoid opening new positions immediately before high-impact events unless you have a clear strategy,
- Consider tightening stop-loss orders around scheduled release times,
- Stay updated through live news feeds during important announcements,4.. Be cautious about holding leveraged positions during volatile periods since margin calls could be triggered unexpectedly.
Staying Updated With Real-Time Changes
Economic calendars are dynamic; actual results sometimes differ significantly from forecasts causing sudden shifts in markets post-release — known as “surprise” outcomes which can be highly profitable if correctly interpreted but risky otherwise.
Investing.com offers real-time updates once data is released along with immediate chart reactions so traders can respond swiftly rather than relying solely on pre-event expectations.
Final Tips For Effective Use Of The Economic Calendar
To get consistent value out of this tool:
– Regularly review upcoming schedules aligned with your trading hours
– Develop a routine where checking key indicators becomes part of daily analysis
– Keep abreast of geopolitical developments that may influence certain reports
– Combine calendar insights with fundamental analysis techniques
By integrating these practices into your workflow — supported by accurate scheduling information from investing.com — you'll improve decision-making quality while managing risk more effectively across different asset classes such as stocks, forex pairs, commodities,and bonds.
Leveraging Expertise & Building Confidence
Using investing.com's economic calendar effectively requires understanding macroeconomic principles alongside technical skills—and continuously updating knowledge about global financial trends enhances E-A-T (Expertise-Authoritativeness-Trustrworthiness). Relying solely on raw data without contextual interpretation increases risk; therefore combining reliable sources like official government publications along with professional analyses strengthens credibility.
In summary,
Mastering how to use Investings.com's Economic Calendar empowers investors at all levels—from beginners learning basic concepts to seasoned professionals refining strategies—to navigate complex markets confidently while minimizing surprises caused by unforeseen economic developments.


kai
2025-05-27 00:12
How do I use Investing.com’s economic calendar?
How Do I Use Investing.com’s Economic Calendar?
Understanding how to effectively utilize Investing.com’s Economic Calendar can significantly enhance your trading and investment strategies. This powerful tool provides real-time updates on upcoming economic events, helping you anticipate market movements and make informed decisions. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to leverage this resource for maximum benefit.
What Is the Investing.com Economic Calendar?
The Investing.com Economic Calendar is an essential resource for traders, investors, and financial analysts. It offers a detailed schedule of upcoming economic releases from around the world, including key indicators such as GDP growth rates, inflation figures, employment data, interest rate decisions, and central bank statements. The calendar consolidates data from reputable sources like government agencies and financial institutions to ensure accuracy.
This tool not only displays when these events will occur but also provides context about their potential impact on markets. By monitoring these scheduled releases, users can better understand market sentiment and prepare for possible volatility.
Why Is the Economic Calendar Important for Investors?
Market participants rely heavily on economic calendars because they highlight moments when asset prices might experience significant fluctuations due to new information entering the market. For example:
- An unexpected increase in unemployment rates could lead to a decline in stock prices.
- A surprise rate hike by a central bank might strengthen or weaken a currency.
- Strong GDP data may boost investor confidence in an economy.
By staying informed about these events beforehand through the calendar, investors can adjust their positions accordingly—either by taking advantage of anticipated moves or by reducing exposure during volatile periods.
How To Access and Navigate the Calendar
Accessing the calendar is straightforward via Investing.com’s website or mobile app. Once there:
- Select Your Region or Market: Customize your view based on geographic focus—such as US economy, Eurozone countries, or emerging markets—to filter relevant events.
- Review Event Details: Each scheduled event includes:
- Date and time (with timezone adjustments)
- Expected release (forecast)
- Previous results
- Actual results once released
- Understand Impact Indicators: Many entries feature impact icons indicating whether an event is likely to have low, medium, or high influence on markets.
- Use Filters: Narrow down your view by selecting specific event types like employment reports or interest rate decisions that align with your trading strategy.
The platform's user-friendly interface makes it easy even for beginners to find relevant information quickly while offering advanced options for experienced traders seeking detailed analysis.
Customizing Your Experience
One of the key advantages of Investing.com's calendar is its customization features:
- Focus Regions: Filter events based on specific countries or regions that are part of your investment portfolio.
- Event Types: Choose particular categories such as inflation reports or trade balance announcements.
- Time Settings: Adjust time zones according to your location so you don’t miss critical updates during off-hours.
Customizing ensures you receive targeted alerts aligned with your trading hours and strategic interests—saving time while enhancing decision-making precision.
Interpreting Data & Forecasts
While viewing scheduled releases is helpful; understanding what they mean requires some knowledge:
- Look at forecast figures versus previous results; large deviations often trigger market reactions.
- Pay attention to impact indicators—high-impact events tend to cause more volatility than low-impact ones.
Many calendars include brief analyses predicting potential outcomes based on current economic conditions—a valuable feature that helps interpret raw data within broader macroeconomic contexts.
However, always cross-reference forecasts with multiple sources before making trades; no single indicator guarantees market direction.
Using Additional Tools Alongside The Calendar
To maximize insights gained from investing in economic releases:
- Combine calendar alerts with technical analysis charts available on Investing.com—for example:
- Support/resistance levels
- Moving averages
- Trend lines
This integrated approach allows you not only anticipate when significant news will arrive but also understand how it might influence price action within existing trends.
Additionally,
- Follow related news feeds linked directly within each event entry,
- Set up notifications so you’re alerted ahead of major releases,
- Use historical data provided alongside upcoming schedules for trend analysis over time.
Managing Risks During Major Releases
Economic announcements often lead to increased volatility which can result in rapid price swings—both upward and downward—that may catch unprepared traders off guard. To mitigate risks:
- Avoid opening new positions immediately before high-impact events unless you have a clear strategy,
- Consider tightening stop-loss orders around scheduled release times,
- Stay updated through live news feeds during important announcements,4.. Be cautious about holding leveraged positions during volatile periods since margin calls could be triggered unexpectedly.
Staying Updated With Real-Time Changes
Economic calendars are dynamic; actual results sometimes differ significantly from forecasts causing sudden shifts in markets post-release — known as “surprise” outcomes which can be highly profitable if correctly interpreted but risky otherwise.
Investing.com offers real-time updates once data is released along with immediate chart reactions so traders can respond swiftly rather than relying solely on pre-event expectations.
Final Tips For Effective Use Of The Economic Calendar
To get consistent value out of this tool:
– Regularly review upcoming schedules aligned with your trading hours
– Develop a routine where checking key indicators becomes part of daily analysis
– Keep abreast of geopolitical developments that may influence certain reports
– Combine calendar insights with fundamental analysis techniques
By integrating these practices into your workflow — supported by accurate scheduling information from investing.com — you'll improve decision-making quality while managing risk more effectively across different asset classes such as stocks, forex pairs, commodities,and bonds.
Leveraging Expertise & Building Confidence
Using investing.com's economic calendar effectively requires understanding macroeconomic principles alongside technical skills—and continuously updating knowledge about global financial trends enhances E-A-T (Expertise-Authoritativeness-Trustrworthiness). Relying solely on raw data without contextual interpretation increases risk; therefore combining reliable sources like official government publications along with professional analyses strengthens credibility.
In summary,
Mastering how to use Investings.com's Economic Calendar empowers investors at all levels—from beginners learning basic concepts to seasoned professionals refining strategies—to navigate complex markets confidently while minimizing surprises caused by unforeseen economic developments.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Three-Method Pattern? An In-Depth Explanation
Understanding the concept of a "three-method pattern" can be challenging because, as of current knowledge, it is not a widely recognized or established term in programming, software development, cryptography, or investment strategies. Despite its apparent simplicity—implying a pattern involving three methods—there is no standard definition or common usage in technical literature or industry best practices. This lack of recognition suggests that the term might be niche, context-specific, or possibly misinterpreted from other concepts.
In this article, we will explore what such a pattern could theoretically involve and clarify why it remains largely undefined in professional circles. We will also discuss related concepts and best practices to help you understand where this idea might fit within broader development and strategic frameworks.
The Absence of an Official Definition
The phrase "three-method pattern" does not correspond to any formal design pattern like Singleton, Factory Method, Observer, or Decorator that are well-documented within software engineering. Design patterns typically have clear definitions and are widely referenced in literature such as the "Gang of Four" book (Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software). Since no such standard exists for a three-method approach, it’s safe to say that if someone references this term, they may be describing their own methodology rather than an industry-standard practice.
Similarly, in cryptography and investment strategies—fields where structured methodologies are common—the notion of a "three-method" approach is not prevalent. Cryptographic protocols tend to focus on algorithms like RSA or AES rather than multi-step patterns named by number alone. Investment techniques often involve multiple analysis methods but rarely formalize them into named patterns based solely on count.
Possible Interpretations Across Fields
While there’s no official recognition for the "three-method pattern," we can consider how similar concepts appear across different domains:
Software Development:
Developers sometimes implement multi-step processes involving distinct methods—for example:- Input validation
- Data processing
- Output formatting
These steps could loosely be seen as three separate methods working together but aren’t collectively called a “pattern.”
Cryptography:
Cryptographic systems often combine multiple algorithms (e.g., hashing + encryption + digital signatures), but these combinations aren’t referred to as “patterns” based on their method count.Investment Strategies:
Investors may use three core approaches—fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and quantitative models—but again these aren’t grouped under one specific name like “three-method.”
Why Might Someone Refer to Such a Pattern?
If you encounter references to a "three-method pattern," it could stem from:
- A proprietary methodology used internally within an organization.
- A simplified way some practitioners describe layered approaches involving three distinct techniques.
- Misinterpretation or informal naming without widespread adoption.
In all cases though—the key takeaway is that this isn’t an established terminology with broad acceptance.
Related Concepts That Are Recognized
Instead of focusing on an unrecognized term like the "three-method pattern," it's more productive to look at well-known frameworks that emphasize multiple approaches:
- Layered Security Models: Combining several security measures (firewalls + encryption + access controls).
- Three-Legged Stool Analogy: In finance and management—balancing three core components.
- Triadic Methods in Problem Solving: Using three different perspectives for comprehensive analysis (e.g., SWOT analysis).
These examples demonstrate how combining multiple techniques enhances robustness but do not necessarily form standardized patterns labeled by number alone.
Best Practices When Applying Multiple Methods
Whether you're designing software solutions or developing strategic plans:
- Clearly define each method's purpose.
- Ensure methods complement each other without redundancy.
- Maintain flexibility for adjustments based on results.
- Document each step thoroughly for clarity and future reference.
This approach aligns with principles found in modular design and systematic problem-solving frameworks known across industries—not tied specifically to any so-called “three-method” model but rooted firmly in proven practices.
Why Clarity Matters When Discussing Methodologies
Using precise language when describing your process helps avoid confusion among team members and stakeholders alike—and ensures alignment with recognized standards when necessary—for example:
- Following established design patterns when developing code.
- Adhering to proven cryptographic protocols for security implementations.
- Applying validated investment strategies backed by research data.
Misusing vague terms like “pattern” without proper context can lead to misunderstandings about your methodology's validity or effectiveness.
Emerging Trends & Future Perspectives
While currently nonexistent as an official concept—or at least lacking widespread acknowledgment—the idea behind something called the "three-method pattern" hints at combining diverse approaches into cohesive workflows—a principle central across many fields today amid increasing complexity demands robust solutions built from multiple layers/methods/techniques.
As industries evolve toward more integrated systems—such as hybrid cloud architectures combining various security tools; multi-faceted AI models; layered financial risk assessments—it’s conceivable that future frameworks might formalize similar triadic structures under new terminologies aligned with emerging standards rather than vague labels like “pattern.”
Key Takeaways About The Three-Method Pattern
To summarize:
– The term isn't officially recognized within programming languages’ documentation nor cryptography/investment literature.– It likely refers informally—or hypothetically—to processes involving exactly three methods/steps/approaches working together.– Effective implementation involves understanding each method's role while ensuring they complement one another seamlessly.– Emphasizing clarity over ambiguous terminology improves communication among professionals across disciplines.
Understanding what works best depends heavily on context-specific needs rather than relying solely on generic labels such as “the three-method pattern.” Instead focus on proven methodologies tailored explicitly toward your project goals whether coding architecture designs; security protocols; financial analyses; or strategic planning efforts—all grounded firmly in industry standards designed through rigorous testing and validation processes.
By maintaining awareness about existing recognized practices—and avoiding reliance on unverified terminology—you ensure your work remains credible while leveraging effective techniques rooted firmly in expert consensus across relevant fields.


Lo
2025-05-20 04:00
What’s a three-method pattern?
What Is the Three-Method Pattern? An In-Depth Explanation
Understanding the concept of a "three-method pattern" can be challenging because, as of current knowledge, it is not a widely recognized or established term in programming, software development, cryptography, or investment strategies. Despite its apparent simplicity—implying a pattern involving three methods—there is no standard definition or common usage in technical literature or industry best practices. This lack of recognition suggests that the term might be niche, context-specific, or possibly misinterpreted from other concepts.
In this article, we will explore what such a pattern could theoretically involve and clarify why it remains largely undefined in professional circles. We will also discuss related concepts and best practices to help you understand where this idea might fit within broader development and strategic frameworks.
The Absence of an Official Definition
The phrase "three-method pattern" does not correspond to any formal design pattern like Singleton, Factory Method, Observer, or Decorator that are well-documented within software engineering. Design patterns typically have clear definitions and are widely referenced in literature such as the "Gang of Four" book (Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software). Since no such standard exists for a three-method approach, it’s safe to say that if someone references this term, they may be describing their own methodology rather than an industry-standard practice.
Similarly, in cryptography and investment strategies—fields where structured methodologies are common—the notion of a "three-method" approach is not prevalent. Cryptographic protocols tend to focus on algorithms like RSA or AES rather than multi-step patterns named by number alone. Investment techniques often involve multiple analysis methods but rarely formalize them into named patterns based solely on count.
Possible Interpretations Across Fields
While there’s no official recognition for the "three-method pattern," we can consider how similar concepts appear across different domains:
Software Development:
Developers sometimes implement multi-step processes involving distinct methods—for example:- Input validation
- Data processing
- Output formatting
These steps could loosely be seen as three separate methods working together but aren’t collectively called a “pattern.”
Cryptography:
Cryptographic systems often combine multiple algorithms (e.g., hashing + encryption + digital signatures), but these combinations aren’t referred to as “patterns” based on their method count.Investment Strategies:
Investors may use three core approaches—fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and quantitative models—but again these aren’t grouped under one specific name like “three-method.”
Why Might Someone Refer to Such a Pattern?
If you encounter references to a "three-method pattern," it could stem from:
- A proprietary methodology used internally within an organization.
- A simplified way some practitioners describe layered approaches involving three distinct techniques.
- Misinterpretation or informal naming without widespread adoption.
In all cases though—the key takeaway is that this isn’t an established terminology with broad acceptance.
Related Concepts That Are Recognized
Instead of focusing on an unrecognized term like the "three-method pattern," it's more productive to look at well-known frameworks that emphasize multiple approaches:
- Layered Security Models: Combining several security measures (firewalls + encryption + access controls).
- Three-Legged Stool Analogy: In finance and management—balancing three core components.
- Triadic Methods in Problem Solving: Using three different perspectives for comprehensive analysis (e.g., SWOT analysis).
These examples demonstrate how combining multiple techniques enhances robustness but do not necessarily form standardized patterns labeled by number alone.
Best Practices When Applying Multiple Methods
Whether you're designing software solutions or developing strategic plans:
- Clearly define each method's purpose.
- Ensure methods complement each other without redundancy.
- Maintain flexibility for adjustments based on results.
- Document each step thoroughly for clarity and future reference.
This approach aligns with principles found in modular design and systematic problem-solving frameworks known across industries—not tied specifically to any so-called “three-method” model but rooted firmly in proven practices.
Why Clarity Matters When Discussing Methodologies
Using precise language when describing your process helps avoid confusion among team members and stakeholders alike—and ensures alignment with recognized standards when necessary—for example:
- Following established design patterns when developing code.
- Adhering to proven cryptographic protocols for security implementations.
- Applying validated investment strategies backed by research data.
Misusing vague terms like “pattern” without proper context can lead to misunderstandings about your methodology's validity or effectiveness.
Emerging Trends & Future Perspectives
While currently nonexistent as an official concept—or at least lacking widespread acknowledgment—the idea behind something called the "three-method pattern" hints at combining diverse approaches into cohesive workflows—a principle central across many fields today amid increasing complexity demands robust solutions built from multiple layers/methods/techniques.
As industries evolve toward more integrated systems—such as hybrid cloud architectures combining various security tools; multi-faceted AI models; layered financial risk assessments—it’s conceivable that future frameworks might formalize similar triadic structures under new terminologies aligned with emerging standards rather than vague labels like “pattern.”
Key Takeaways About The Three-Method Pattern
To summarize:
– The term isn't officially recognized within programming languages’ documentation nor cryptography/investment literature.– It likely refers informally—or hypothetically—to processes involving exactly three methods/steps/approaches working together.– Effective implementation involves understanding each method's role while ensuring they complement one another seamlessly.– Emphasizing clarity over ambiguous terminology improves communication among professionals across disciplines.
Understanding what works best depends heavily on context-specific needs rather than relying solely on generic labels such as “the three-method pattern.” Instead focus on proven methodologies tailored explicitly toward your project goals whether coding architecture designs; security protocols; financial analyses; or strategic planning efforts—all grounded firmly in industry standards designed through rigorous testing and validation processes.
By maintaining awareness about existing recognized practices—and avoiding reliance on unverified terminology—you ensure your work remains credible while leveraging effective techniques rooted firmly in expert consensus across relevant fields.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the McClellan Summation Index?
The McClellan Summation Index is a technical analysis tool used by traders and investors to assess the overall health and momentum of the stock market. Developed in the 1970s by Sherman and Marian McClellan, this indicator provides insights into long-term market trends, helping users identify potential turning points before they occur. Unlike short-term oscillators that focus on immediate price movements, the Summation Index offers a broader perspective, making it especially valuable for those interested in understanding sustained market directions.
At its core, the McClellan Summation Index builds upon the McClellan Oscillator—a momentum indicator that measures the difference between advancing and declining stocks within a given period. By integrating this oscillator with a long-term moving average (typically 40 days), it creates an aggregated view of market momentum over time. This combination allows traders to see whether bullish or bearish forces are gaining strength or waning across extended periods.
How Is It Calculated?
Understanding how the McClellan Summation Index is calculated can help traders interpret its signals more effectively. The process involves two main components:
- McClellan Oscillator: This is computed daily by subtracting a 19-day exponential moving average (EMA) of advancing issues from a similar EMA of declining issues.
- Summation Process: The oscillator value is multiplied by 10 (or another scaling factor), then added cumulatively to form the index.
Mathematically:
McClellan Summation Index = Previous Value + (McClellan Oscillator × Scaling Factor)Typically, analysts use a 40-day simple moving average as part of their interpretation framework to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends.
Why Do Traders Use It?
The primary appeal of the McClellan Summation Index lies in its ability to reveal underlying market strength or weakness over extended periods. When plotted on charts, rising values indicate sustained bullish momentum—suggesting that most stocks are advancing—and can signal ongoing upward trends. Conversely, falling values point toward bearish conditions where declining stocks dominate.
This indicator helps identify several key trading signals:
- Trend Confirmation: A consistently rising index confirms strong bullish sentiment.
- Divergence Detection: When prices move higher but the index declines or flattens, it may signal weakening momentum—potentially warning of an upcoming reversal.
- Market Extremes: Extremely high or low readings can suggest overbought or oversold conditions—areas where reversals might be imminent.
Because it synthesizes data across many stocks into one comprehensive measure, it’s particularly useful for assessing broad-market health rather than individual securities.
Historical Significance and Usage
Since its introduction in the 1970s, investors have relied on the McClellan Summation Index as part of their technical toolkit for analyzing stock markets like NYSE and NASDAQ indices. Its ability to provide early warnings about trend changes has made it popular among professional traders who seek confirmation before executing buy or sell decisions.
During significant historical events such as economic downturns or bull markets—including during recent crises like COVID-19—the index has helped interpret underlying shifts amid heightened volatility. For example, during March-April 2020 when markets experienced unprecedented swings due to pandemic fears, many analysts used changes in this index alongside other indicators for better timing strategies.
Recent Developments & Modern Applications
In recent years, technological advancements have expanded how traders incorporate tools like the McClellan Summation Index into their strategies:
Market Volatility Analysis: During volatile periods such as COVID-19 pandemic-induced swings between fear and optimism—this index provided valuable insights into whether underlying momentum supported rally attempts or signaled impending corrections.
Integration with Other Indicators: Many modern trading systems combine this index with RSI (Relative Strength Indicator), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), Bollinger Bands—and even fundamental data—to develop more robust decision-making frameworks.
Application Beyond Stocks: Although originally designed for traditional equities markets like NYSE/NASDAQ indices, some analysts are experimenting with applying similar principles to cryptocurrency markets—though these applications remain experimental due to differing asset behaviors.
Limitations & Risks
While powerful when used correctly, reliance solely on any single technical indicator—including the McClellan Summation Index—is risky:
Overdependence may lead traders astray if broader fundamentals aren’t considered.
Market complexity means external factors such as geopolitical events or macroeconomic shifts can override signals generated solely from technical tools.
Therefore, combining this indicator with fundamental analysis and other technical signals enhances reliability while reducing false positives/negatives.
How Can Investors Use It Effectively?
To maximize its benefits:
- Monitor trend confirmations — look for consistent upward movement indicating strong bullish sentiment; downward movement suggests bearishness.
- Watch for divergence — when price action diverges from what your summation index indicates; these moments often precede reversals.
- Identify extremes — very high readings could mean overbought conditions; very low readings might signal oversold scenarios ripe for rebounds.
- Combine with other tools — use alongside volume analysis or chart patterns for more comprehensive insights into potential entry/exit points.
Practical Tips:
- Regularly review historical peaks/troughs within your chosen timeframe
- Use multiple timeframes—for example daily vs weekly—to confirm signals
- Stay updated on macroeconomic news that could influence overall market direction
By integrating these practices into your trading routine—with proper risk management—you can leverage what makes this tool valuable while avoiding common pitfalls associated with relying solely on technical indicators.
By understanding what exactly drives its calculations—and how seasoned investors interpret those movements—the McCLELLAN Summation Index remains an essential component in navigating complex financial markets today.. Whether you're aiming at long-term trend identification or seeking early signs of reversals amidst volatility—the knowledge about this indicator empowers you towards smarter investment decisions grounded in proven analytical methods..


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-20 03:33
What’s the McClellan Summation Index?
What Is the McClellan Summation Index?
The McClellan Summation Index is a technical analysis tool used by traders and investors to assess the overall health and momentum of the stock market. Developed in the 1970s by Sherman and Marian McClellan, this indicator provides insights into long-term market trends, helping users identify potential turning points before they occur. Unlike short-term oscillators that focus on immediate price movements, the Summation Index offers a broader perspective, making it especially valuable for those interested in understanding sustained market directions.
At its core, the McClellan Summation Index builds upon the McClellan Oscillator—a momentum indicator that measures the difference between advancing and declining stocks within a given period. By integrating this oscillator with a long-term moving average (typically 40 days), it creates an aggregated view of market momentum over time. This combination allows traders to see whether bullish or bearish forces are gaining strength or waning across extended periods.
How Is It Calculated?
Understanding how the McClellan Summation Index is calculated can help traders interpret its signals more effectively. The process involves two main components:
- McClellan Oscillator: This is computed daily by subtracting a 19-day exponential moving average (EMA) of advancing issues from a similar EMA of declining issues.
- Summation Process: The oscillator value is multiplied by 10 (or another scaling factor), then added cumulatively to form the index.
Mathematically:
McClellan Summation Index = Previous Value + (McClellan Oscillator × Scaling Factor)Typically, analysts use a 40-day simple moving average as part of their interpretation framework to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends.
Why Do Traders Use It?
The primary appeal of the McClellan Summation Index lies in its ability to reveal underlying market strength or weakness over extended periods. When plotted on charts, rising values indicate sustained bullish momentum—suggesting that most stocks are advancing—and can signal ongoing upward trends. Conversely, falling values point toward bearish conditions where declining stocks dominate.
This indicator helps identify several key trading signals:
- Trend Confirmation: A consistently rising index confirms strong bullish sentiment.
- Divergence Detection: When prices move higher but the index declines or flattens, it may signal weakening momentum—potentially warning of an upcoming reversal.
- Market Extremes: Extremely high or low readings can suggest overbought or oversold conditions—areas where reversals might be imminent.
Because it synthesizes data across many stocks into one comprehensive measure, it’s particularly useful for assessing broad-market health rather than individual securities.
Historical Significance and Usage
Since its introduction in the 1970s, investors have relied on the McClellan Summation Index as part of their technical toolkit for analyzing stock markets like NYSE and NASDAQ indices. Its ability to provide early warnings about trend changes has made it popular among professional traders who seek confirmation before executing buy or sell decisions.
During significant historical events such as economic downturns or bull markets—including during recent crises like COVID-19—the index has helped interpret underlying shifts amid heightened volatility. For example, during March-April 2020 when markets experienced unprecedented swings due to pandemic fears, many analysts used changes in this index alongside other indicators for better timing strategies.
Recent Developments & Modern Applications
In recent years, technological advancements have expanded how traders incorporate tools like the McClellan Summation Index into their strategies:
Market Volatility Analysis: During volatile periods such as COVID-19 pandemic-induced swings between fear and optimism—this index provided valuable insights into whether underlying momentum supported rally attempts or signaled impending corrections.
Integration with Other Indicators: Many modern trading systems combine this index with RSI (Relative Strength Indicator), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), Bollinger Bands—and even fundamental data—to develop more robust decision-making frameworks.
Application Beyond Stocks: Although originally designed for traditional equities markets like NYSE/NASDAQ indices, some analysts are experimenting with applying similar principles to cryptocurrency markets—though these applications remain experimental due to differing asset behaviors.
Limitations & Risks
While powerful when used correctly, reliance solely on any single technical indicator—including the McClellan Summation Index—is risky:
Overdependence may lead traders astray if broader fundamentals aren’t considered.
Market complexity means external factors such as geopolitical events or macroeconomic shifts can override signals generated solely from technical tools.
Therefore, combining this indicator with fundamental analysis and other technical signals enhances reliability while reducing false positives/negatives.
How Can Investors Use It Effectively?
To maximize its benefits:
- Monitor trend confirmations — look for consistent upward movement indicating strong bullish sentiment; downward movement suggests bearishness.
- Watch for divergence — when price action diverges from what your summation index indicates; these moments often precede reversals.
- Identify extremes — very high readings could mean overbought conditions; very low readings might signal oversold scenarios ripe for rebounds.
- Combine with other tools — use alongside volume analysis or chart patterns for more comprehensive insights into potential entry/exit points.
Practical Tips:
- Regularly review historical peaks/troughs within your chosen timeframe
- Use multiple timeframes—for example daily vs weekly—to confirm signals
- Stay updated on macroeconomic news that could influence overall market direction
By integrating these practices into your trading routine—with proper risk management—you can leverage what makes this tool valuable while avoiding common pitfalls associated with relying solely on technical indicators.
By understanding what exactly drives its calculations—and how seasoned investors interpret those movements—the McCLELLAN Summation Index remains an essential component in navigating complex financial markets today.. Whether you're aiming at long-term trend identification or seeking early signs of reversals amidst volatility—the knowledge about this indicator empowers you towards smarter investment decisions grounded in proven analytical methods..
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is the Debt-to-Equity Ratio?
The debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio is a fundamental financial metric that helps investors, analysts, and company management understand how a business finances its operations. It measures the proportion of debt used relative to shareholders’ equity, providing insight into the company's leverage and financial stability. The formula for calculating this ratio is straightforward:
[ \text{Debt-to-Equity Ratio} = \frac{\text{Total Liabilities}}{\text{Shareholder Equity}} ]
Total liabilities include both short-term and long-term debts, while shareholder equity reflects the residual interest in assets after deducting liabilities. This ratio is typically expressed as a decimal or a multiple (e.g., 1.5 or 150%).
Understanding this metric allows stakeholders to assess whether a company relies heavily on borrowed funds or maintains a more conservative capital structure. A balanced approach can support growth without exposing the company to excessive risk.
Why Is the Debt-to-Equity Ratio Important?
The D/E ratio plays an essential role in evaluating a company's financial health and risk profile. A high D/E ratio indicates that a larger portion of financing comes from debt, which can amplify returns during good times but also increases vulnerability during downturns.
For investors, analyzing this ratio helps determine whether a company has an appropriate level of leverage aligned with its industry standards and growth prospects. For example, capital-intensive industries like utilities often operate with higher ratios due to stable cash flows that support debt repayment.
Conversely, companies with low D/E ratios tend to be less risky but might also miss out on opportunities for expansion if they are overly cautious about taking on debt. Therefore, understanding industry benchmarks alongside specific company figures provides better context for interpretation.
Regulators and credit rating agencies also scrutinize these ratios when assessing creditworthiness or setting lending terms. Excessive leverage may lead to higher borrowing costs or restrictions on future financing options.
How To Calculate Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Calculating the D/E ratio involves two key components: total liabilities and shareholder equity—both found on the company's balance sheet.
Step-by-step process:
- Gather Financial Statements: Obtain recent balance sheets from annual reports or quarterly filings.
- Identify Total Liabilities: Sum up all current liabilities (due within one year) and long-term liabilities (due beyond one year).
- Determine Shareholder Equity: This includes common stock, retained earnings, additional paid-in capital, minus treasury stock.
- Apply Formula: Divide total liabilities by shareholder equity using:
[ \text{D/E Ratio} = \frac{\text{Total Liabilities}}{\text{Shareholder Equity}} ]
Example Calculation:
Suppose Company XYZ has:
- Total liabilities: $500 million
- Shareholder equity: $250 million
Then,
[ \frac{$500,\text{million}}{$250,\text{million}} = 2 ]
This indicates that Company XYZ's debt level is twice its equity base—a relatively high leverage position depending on industry norms.
Interpreting Different Debt-to-Equity Ratios
A key aspect of using this metric effectively involves contextual interpretation:
Low Ratios (<0.5): Suggest conservative financing; companies rely more on internal funds than borrowed money—generally viewed as less risky.
Moderate Ratios (0.5–1): Indicate balanced leverage suitable for many industries aiming for growth without excessive risk exposure.
High Ratios (>1): Reflect significant reliance on debt; while potentially boosting returns during favorable conditions, it raises concerns about solvency risks if cash flows decline.
It's crucial not to evaluate ratios in isolation but compare them against industry averages because what’s considered high in one sector might be standard in another—such as utilities versus tech startups.
Impact of Industry Trends & Market Conditions
Industry-specific factors influence acceptable levels of leverage significantly:
Sector Variations
Utilities often operate comfortably with higher D/E ratios due to predictable revenue streams and regulated rates supporting steady repayments — sometimes exceeding 2 or even 3 times their equity base.In contrast, technology firms tend toward lower ratios because their revenues are more volatile; excessive debt could threaten their survival if market conditions shift unexpectedly.
Recent Developments
Recent years have seen shifts towards more conservative capital structures across many sectors driven by regulatory scrutiny post-financial crises like COVID-19's economic impact starting in 2020 — prompting companies to reduce reliance on external borrowing for resilience purposes.Furthermore, ESG investing emphasizes sustainable practices including prudent financial management—companies are increasingly transparent about their leverage levels as part of broader governance strategies.
Cryptocurrency & New Markets
While cryptocurrencies themselves don’t have traditional balance sheets involving debts/equities like conventional firms do; some crypto exchanges and lending platforms now monitor similar metrics internally—to manage collateralization risks associated with crypto-backed loans—and ensure operational stability amid volatile markets.
Risks Associated With High Leverage
Maintaining an excessively high debt-to-equity ratio can pose serious risks:
- Increased interest obligations may strain cash flow,
- Elevated default risk during economic downturns,
- Limited flexibility when seeking new funding,
- Potential dilution of existing shareholders' value if distressed assets need liquidation,
- Higher borrowing costs due to perceived increased risk by lenders,
During periods where interest rates rise globally—as seen historically—the cost burden intensifies further for highly leveraged firms leading possibly toward insolvency if not managed carefully.
Regulatory Environment & Transparency Standards
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) have historically emphasized transparency around corporate indebtedness since laws enacted in 1934 mandated detailed disclosures about capital structures—including debts owed by public companies.Recent reforms under acts like Dodd–Frank (2010) continue reinforcing these standards through enhanced reporting requirements aimed at protecting investors from undue risks associated with over-leverage.As markets evolve—with increasing focus on sustainability metrics—the importance placed upon clear disclosure regarding leverage levels continues growing among regulators worldwide.
How Investors Use Debt-to-Equity Data
Investors analyze D/E ratios alongside other financial indicators such as return-on-equity (ROE), profit margins,and cash flow statements before making investment decisions:
- A low D/E combined with strong profitability signals stability,
- High leverage might indicate aggressive growth strategies but warrants caution,
- Comparing across peers helps identify undervalued opportunities or red flags,
Business valuation models incorporate this data when estimating enterprise value—especially within discounted cash flow analyses where assumptions around future borrowings influence projections.
By understanding how to compute—and interpret—the debt-to-equity ratio accurately you gain valuable insights into corporate health and strategic positioning within your investment portfolio or managerial decision-making processes.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-19 13:35
How to compute debt-to-equity ratio and its implications?
What Is the Debt-to-Equity Ratio?
The debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio is a fundamental financial metric that helps investors, analysts, and company management understand how a business finances its operations. It measures the proportion of debt used relative to shareholders’ equity, providing insight into the company's leverage and financial stability. The formula for calculating this ratio is straightforward:
[ \text{Debt-to-Equity Ratio} = \frac{\text{Total Liabilities}}{\text{Shareholder Equity}} ]
Total liabilities include both short-term and long-term debts, while shareholder equity reflects the residual interest in assets after deducting liabilities. This ratio is typically expressed as a decimal or a multiple (e.g., 1.5 or 150%).
Understanding this metric allows stakeholders to assess whether a company relies heavily on borrowed funds or maintains a more conservative capital structure. A balanced approach can support growth without exposing the company to excessive risk.
Why Is the Debt-to-Equity Ratio Important?
The D/E ratio plays an essential role in evaluating a company's financial health and risk profile. A high D/E ratio indicates that a larger portion of financing comes from debt, which can amplify returns during good times but also increases vulnerability during downturns.
For investors, analyzing this ratio helps determine whether a company has an appropriate level of leverage aligned with its industry standards and growth prospects. For example, capital-intensive industries like utilities often operate with higher ratios due to stable cash flows that support debt repayment.
Conversely, companies with low D/E ratios tend to be less risky but might also miss out on opportunities for expansion if they are overly cautious about taking on debt. Therefore, understanding industry benchmarks alongside specific company figures provides better context for interpretation.
Regulators and credit rating agencies also scrutinize these ratios when assessing creditworthiness or setting lending terms. Excessive leverage may lead to higher borrowing costs or restrictions on future financing options.
How To Calculate Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Calculating the D/E ratio involves two key components: total liabilities and shareholder equity—both found on the company's balance sheet.
Step-by-step process:
- Gather Financial Statements: Obtain recent balance sheets from annual reports or quarterly filings.
- Identify Total Liabilities: Sum up all current liabilities (due within one year) and long-term liabilities (due beyond one year).
- Determine Shareholder Equity: This includes common stock, retained earnings, additional paid-in capital, minus treasury stock.
- Apply Formula: Divide total liabilities by shareholder equity using:
[ \text{D/E Ratio} = \frac{\text{Total Liabilities}}{\text{Shareholder Equity}} ]
Example Calculation:
Suppose Company XYZ has:
- Total liabilities: $500 million
- Shareholder equity: $250 million
Then,
[ \frac{$500,\text{million}}{$250,\text{million}} = 2 ]
This indicates that Company XYZ's debt level is twice its equity base—a relatively high leverage position depending on industry norms.
Interpreting Different Debt-to-Equity Ratios
A key aspect of using this metric effectively involves contextual interpretation:
Low Ratios (<0.5): Suggest conservative financing; companies rely more on internal funds than borrowed money—generally viewed as less risky.
Moderate Ratios (0.5–1): Indicate balanced leverage suitable for many industries aiming for growth without excessive risk exposure.
High Ratios (>1): Reflect significant reliance on debt; while potentially boosting returns during favorable conditions, it raises concerns about solvency risks if cash flows decline.
It's crucial not to evaluate ratios in isolation but compare them against industry averages because what’s considered high in one sector might be standard in another—such as utilities versus tech startups.
Impact of Industry Trends & Market Conditions
Industry-specific factors influence acceptable levels of leverage significantly:
Sector Variations
Utilities often operate comfortably with higher D/E ratios due to predictable revenue streams and regulated rates supporting steady repayments — sometimes exceeding 2 or even 3 times their equity base.In contrast, technology firms tend toward lower ratios because their revenues are more volatile; excessive debt could threaten their survival if market conditions shift unexpectedly.
Recent Developments
Recent years have seen shifts towards more conservative capital structures across many sectors driven by regulatory scrutiny post-financial crises like COVID-19's economic impact starting in 2020 — prompting companies to reduce reliance on external borrowing for resilience purposes.Furthermore, ESG investing emphasizes sustainable practices including prudent financial management—companies are increasingly transparent about their leverage levels as part of broader governance strategies.
Cryptocurrency & New Markets
While cryptocurrencies themselves don’t have traditional balance sheets involving debts/equities like conventional firms do; some crypto exchanges and lending platforms now monitor similar metrics internally—to manage collateralization risks associated with crypto-backed loans—and ensure operational stability amid volatile markets.
Risks Associated With High Leverage
Maintaining an excessively high debt-to-equity ratio can pose serious risks:
- Increased interest obligations may strain cash flow,
- Elevated default risk during economic downturns,
- Limited flexibility when seeking new funding,
- Potential dilution of existing shareholders' value if distressed assets need liquidation,
- Higher borrowing costs due to perceived increased risk by lenders,
During periods where interest rates rise globally—as seen historically—the cost burden intensifies further for highly leveraged firms leading possibly toward insolvency if not managed carefully.
Regulatory Environment & Transparency Standards
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) have historically emphasized transparency around corporate indebtedness since laws enacted in 1934 mandated detailed disclosures about capital structures—including debts owed by public companies.Recent reforms under acts like Dodd–Frank (2010) continue reinforcing these standards through enhanced reporting requirements aimed at protecting investors from undue risks associated with over-leverage.As markets evolve—with increasing focus on sustainability metrics—the importance placed upon clear disclosure regarding leverage levels continues growing among regulators worldwide.
How Investors Use Debt-to-Equity Data
Investors analyze D/E ratios alongside other financial indicators such as return-on-equity (ROE), profit margins,and cash flow statements before making investment decisions:
- A low D/E combined with strong profitability signals stability,
- High leverage might indicate aggressive growth strategies but warrants caution,
- Comparing across peers helps identify undervalued opportunities or red flags,
Business valuation models incorporate this data when estimating enterprise value—especially within discounted cash flow analyses where assumptions around future borrowings influence projections.
By understanding how to compute—and interpret—the debt-to-equity ratio accurately you gain valuable insights into corporate health and strategic positioning within your investment portfolio or managerial decision-making processes.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Real-World Asset Tokens?
Real-world asset tokens (RWATs) are digital representations of tangible or intangible assets that exist outside the blockchain. These tokens leverage blockchain technology to facilitate secure, transparent, and efficient transactions. By converting physical assets such as real estate, commodities, or art into digital tokens through a process called tokenization, investors can access new opportunities for liquidity and diversification.
Understanding the Concept of Tokenization
Tokenization involves transforming traditional assets into digital tokens that can be traded on blockchain platforms. This process typically requires creating a smart contract that represents ownership rights over the underlying asset. Once tokenized, these assets become divisible and tradable in smaller units compared to their physical counterparts. For example, a single property worth millions can be divided into multiple tokens, allowing investors to buy fractions rather than entire properties.
This innovation addresses several limitations associated with conventional asset markets—such as high transaction costs and limited liquidity—by enabling faster settlement times and broader access for investors worldwide.
Key Benefits of Real-World Asset Tokens
Blockchain technology underpins RWATs by providing an immutable ledger that records all transactions transparently. This ensures trustworthiness in ownership transfers while reducing fraud risks associated with counterfeit or disputed titles.
Security is another critical advantage; smart contracts automate compliance checks and enforce transfer rules without intermediaries. Additionally, tokenization enhances market liquidity because it simplifies buying and selling processes across borders—making previously illiquid assets more accessible to a global investor base.
Moreover, regulatory developments are gradually shaping the landscape for RWATs. Some jurisdictions have introduced frameworks governing their issuance and trading—adding legal clarity that boosts investor confidence while safeguarding market integrity.
Recent Trends in Real-World Asset Tokenization
The industry has seen notable growth driven by companies expanding into this space:
Amber International Holding Ltd has been actively involved in tokenizing real-world assets within regulated Asian and Middle Eastern markets—a move aligned with increasing institutional interest.
Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have issued guidelines clarifying how security tokens—which often represent equity or debt instruments linked to real-world assets—should be issued and traded.
Market adoption is accelerating as more firms recognize benefits such as capital raising efficiency, enhanced transparency, and broader investor participation.
These trends indicate a maturing ecosystem where traditional finance increasingly intersects with blockchain innovations.
Risks Associated With Real-World Asset Tokens
Despite promising prospects, RWATs come with inherent risks:
Market Volatility: The value of these tokens can fluctuate significantly due to macroeconomic factors or shifts in investor sentiment—a common trait shared with other crypto-assets.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Inconsistent regulations across different jurisdictions may pose compliance challenges for issuers—and create barriers for cross-border trading.
Security Concerns: While blockchain offers robust security features, vulnerabilities remain—particularly around smart contract bugs or hacking incidents targeting exchanges or custodians handling these tokens.
Investors should conduct thorough due diligence before engaging in RWAT markets—and stay informed about evolving legal frameworks to mitigate potential pitfalls effectively.
The Future Outlook for Real-World Asset Tokens
As awareness grows among both institutional players and retail investors alike—and regulatory clarity improves—the adoption of RWATs is expected to expand further. Their ability to unlock liquidity from traditionally illiquid markets could revolutionize sectors like real estate investment trusts (REITs), art collections management, commodity trading—including precious metals—and intellectual property rights management.
However—as market volatility persists—and regulators continue refining policies—the path forward will require balancing innovation with risk mitigation strategies such as enhanced cybersecurity measures and clear legal standards.
Key Takeaways
Real-world asset tokens are digital representations of physical or intangible assets created via blockchain-based tokenization.
They offer benefits including increased liquidity, reduced transaction costs, enhanced security through decentralization—all underpinned by transparent recordkeeping on immutable ledgers.
Recent developments highlight growing industry interest but also underline ongoing challenges related to regulation risk management.
By understanding both their potential advantagesand associated risks—with attention paidto evolving legal landscapes—investorsand stakeholderscan better navigate this transformative segmentof modern finance poised at the intersectionof traditionalassetsand innovativeblockchain solutions


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 02:13
What are real-world asset tokens?
What Are Real-World Asset Tokens?
Real-world asset tokens (RWATs) are digital representations of tangible or intangible assets that exist outside the blockchain. These tokens leverage blockchain technology to facilitate secure, transparent, and efficient transactions. By converting physical assets such as real estate, commodities, or art into digital tokens through a process called tokenization, investors can access new opportunities for liquidity and diversification.
Understanding the Concept of Tokenization
Tokenization involves transforming traditional assets into digital tokens that can be traded on blockchain platforms. This process typically requires creating a smart contract that represents ownership rights over the underlying asset. Once tokenized, these assets become divisible and tradable in smaller units compared to their physical counterparts. For example, a single property worth millions can be divided into multiple tokens, allowing investors to buy fractions rather than entire properties.
This innovation addresses several limitations associated with conventional asset markets—such as high transaction costs and limited liquidity—by enabling faster settlement times and broader access for investors worldwide.
Key Benefits of Real-World Asset Tokens
Blockchain technology underpins RWATs by providing an immutable ledger that records all transactions transparently. This ensures trustworthiness in ownership transfers while reducing fraud risks associated with counterfeit or disputed titles.
Security is another critical advantage; smart contracts automate compliance checks and enforce transfer rules without intermediaries. Additionally, tokenization enhances market liquidity because it simplifies buying and selling processes across borders—making previously illiquid assets more accessible to a global investor base.
Moreover, regulatory developments are gradually shaping the landscape for RWATs. Some jurisdictions have introduced frameworks governing their issuance and trading—adding legal clarity that boosts investor confidence while safeguarding market integrity.
Recent Trends in Real-World Asset Tokenization
The industry has seen notable growth driven by companies expanding into this space:
Amber International Holding Ltd has been actively involved in tokenizing real-world assets within regulated Asian and Middle Eastern markets—a move aligned with increasing institutional interest.
Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have issued guidelines clarifying how security tokens—which often represent equity or debt instruments linked to real-world assets—should be issued and traded.
Market adoption is accelerating as more firms recognize benefits such as capital raising efficiency, enhanced transparency, and broader investor participation.
These trends indicate a maturing ecosystem where traditional finance increasingly intersects with blockchain innovations.
Risks Associated With Real-World Asset Tokens
Despite promising prospects, RWATs come with inherent risks:
Market Volatility: The value of these tokens can fluctuate significantly due to macroeconomic factors or shifts in investor sentiment—a common trait shared with other crypto-assets.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Inconsistent regulations across different jurisdictions may pose compliance challenges for issuers—and create barriers for cross-border trading.
Security Concerns: While blockchain offers robust security features, vulnerabilities remain—particularly around smart contract bugs or hacking incidents targeting exchanges or custodians handling these tokens.
Investors should conduct thorough due diligence before engaging in RWAT markets—and stay informed about evolving legal frameworks to mitigate potential pitfalls effectively.
The Future Outlook for Real-World Asset Tokens
As awareness grows among both institutional players and retail investors alike—and regulatory clarity improves—the adoption of RWATs is expected to expand further. Their ability to unlock liquidity from traditionally illiquid markets could revolutionize sectors like real estate investment trusts (REITs), art collections management, commodity trading—including precious metals—and intellectual property rights management.
However—as market volatility persists—and regulators continue refining policies—the path forward will require balancing innovation with risk mitigation strategies such as enhanced cybersecurity measures and clear legal standards.
Key Takeaways
Real-world asset tokens are digital representations of physical or intangible assets created via blockchain-based tokenization.
They offer benefits including increased liquidity, reduced transaction costs, enhanced security through decentralization—all underpinned by transparent recordkeeping on immutable ledgers.
Recent developments highlight growing industry interest but also underline ongoing challenges related to regulation risk management.
By understanding both their potential advantagesand associated risks—with attention paidto evolving legal landscapes—investorsand stakeholderscan better navigate this transformative segmentof modern finance poised at the intersectionof traditionalassetsand innovativeblockchain solutions
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Why Do Skewness and Kurtosis Matter in Price Return Distributions?
Understanding the behavior of financial markets requires more than just tracking prices or returns. Two critical statistical measures—skewness and kurtosis—offer deeper insights into the shape and risk profile of return distributions. These metrics are especially relevant in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, where extreme price movements are common. In this article, we explore why skewness and kurtosis matter, how they influence investment decisions, and their role in modern risk management.
What Are Skewness and Kurtosis?
Skewness is a measure of asymmetry within a distribution. When analyzing asset returns, positive skewness indicates that the distribution has a longer tail on the right side—meaning there’s a higher probability of large gains. Conversely, negative skewness suggests a longer left tail, implying potential for significant losses. For investors, understanding skewness helps gauge whether an asset tends to produce more frequent small gains with occasional big wins or vice versa.
Kurtosis describes the "tailedness" or peakedness of a distribution. High kurtosis signifies that extreme values (either very high or very low returns) are more probable than in normal distributions—a phenomenon often observed during market crashes or rapid rallies. Low kurtosis indicates fewer extreme events and generally more stable return patterns.
The Significance in Financial Markets
In financial analysis—including stocks, commodities, forex, and particularly cryptocurrencies—these two metrics provide vital information about risk exposure beyond traditional measures like volatility alone.
- Risk Assessment: Assets with high positive skewness may offer opportunities for outsized gains but come with increased risk due to potential large losses if negatively skewed assets dominate.
- Return Distribution Insights: Kurtosis reveals how likely it is to encounter rare but impactful events—crucial for stress testing portfolios against market shocks.
- Portfolio Diversification: Recognizing assets' skewness and kurtosis helps investors build diversified portfolios that balance risks associated with asymmetric return profiles.
Recent Developments Enhancing Market Analysis
The rise of advanced statistical tools has transformed how traders interpret these measures:
Cryptocurrency Market Volatility: Cryptos are notorious for their unpredictable swings; during bull runs or crashes like those seen in 2022, both skewness and kurtosis tend to spike sharply. This heightened complexity underscores their importance when assessing crypto investments.
Real-Time Data Analysis: Platforms such as QuantConnect or Alpaca now enable traders to incorporate real-time calculations of skewness and kurtosis into automated trading strategies using APIs integrated with machine learning algorithms—all contributing toward smarter decision-making processes.
Regulatory Focus on Risk Management: Regulatory bodies worldwide recognize the importance of monitoring these metrics as part of systemic risk mitigation efforts since abnormal levels can signal underlying vulnerabilities within financial systems.
Investor Sentiment Monitoring
Skewenessand kurtosishave also become tools for gauging investor sentiment:
- Elevated kurtosis might indicate heightened investor optimism (or pessimism), reflecting expectations about future market moves.
- Shifts in these metrics over time can serve as early warning signals for changing attitudes toward specific assets or sectors.
Impacts on Investment Strategies
Ignoring these statistical characteristics can lead to misguided investment choices:
- Underestimating negative skew could cause investors to overlook potential downside risks associated with certain assets.
- Overlooking high kurtosis might result in insufficient preparation for sudden market downturns caused by rare but severe events.
Conversely, incorporating insights from skewness and kurtosis allows investors to optimize portfolio allocations by balancing expected returns against tail risks effectively.
Market Stability Considerations
High levels of kurtosis suggest increased likelihoods of extreme price swings which can destabilize markets if widespread across multiple assets simultaneously—a concern amplified during periods like 2022’s crypto downturns when volatility surged dramatically.
Regulators also monitor these indicators closely because persistent abnormal values may precede systemic crises; thus understanding them aids policymakers aiming at maintaining overall financial stability through proactive measures such as stress testing banks’ resilience under adverse scenarios informed by these statistics.
Technological Advancements Driving Better Risk Management
As machine learning models become increasingly sophisticated—and data availability continues expanding—the capacity to analyze real-time changes in skewenessandkurtosishas improved significantly:
- Automated trading algorithms now incorporate dynamic assessments based on current distribution shapes,
- Risk management frameworks leverage these insights for better hedging strategies,
- Predictive analytics help anticipate future shifts before they materialize into costly market events,
This technological progress enhances our ability not only to understand current risks but also proactively mitigate them before they escalate into crises affecting broader markets.
How Understanding These Metrics Benefits Investors & Regulators
For individual investors seeking long-term growth while managing downside risks effectively—as well as institutional players aiming at systemic stability—grasping what skwenessandkurtosishow about return distributions is essential:
• Accurate assessment prevents misjudgments that could lead either to excessive caution (missing out on gains) or reckless exposure (underestimating tail risks).• It supports strategic diversification tailored towards different asset classes’ unique distribution profiles.• It informs regulatory policies designed around early detection signals indicating rising systemic vulnerabilities linked directly back to unusual distribution shapes.
Tracking Changes Over Time: The Role Of SkewenessandKurtosishas Become More Critical
Monitoring shifts in these statistics over time provides valuable clues about evolving market conditions:
- Rising positive skwenessmight suggest growing investor optimism,
- Increasing negative skwenesscould warn about looming downside dangers,
- Surges in kurtoisis often precede turbulent periods characterized by rapid price swings,
Such trends enable both traders and regulators alike to adapt strategies accordingly—to capitalize on emerging opportunities while safeguarding against impending threats.
Risks Of Ignoring Distribution Shape Metrics
Failing to consider skwenessandkurtosin investment analysis carries notable dangers:
- Underestimating tail risks may leave portfolios vulnerable during black swan events,
- Misinterpreting asymmetries could lead traders astray regarding true profit potentials,
- Ignoring signs from higher moments might result in inadequate capital buffers against shocks,
Therefore integrating these measures into regular analysis enhances resilience amid unpredictable markets.
Advancing Market Resilience Through Better Data Interpretation
As analytical techniques evolve—with AI-driven models providing deeper insights—the ability not only improves individual decision-making but also contributes toward overall market stability by enabling timely responses based on comprehensive understanding rather than reactive moves alone.
By appreciating why skewenessandkurtoshave become central components within modern financial analytics—and applying this knowledge diligently—you position yourself better prepared for navigating complex markets characterized by uncertainty yet rich with opportunity.
Keywords: Skewness,Kurtosis,Risk Management,Cryptocurrency Volatility,Fear Indexes,Moment Analysis,Systemic Risks


kai
2025-05-14 15:38
Why do skewness and kurtosis matter in price return distributions?
Why Do Skewness and Kurtosis Matter in Price Return Distributions?
Understanding the behavior of financial markets requires more than just tracking prices or returns. Two critical statistical measures—skewness and kurtosis—offer deeper insights into the shape and risk profile of return distributions. These metrics are especially relevant in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies, where extreme price movements are common. In this article, we explore why skewness and kurtosis matter, how they influence investment decisions, and their role in modern risk management.
What Are Skewness and Kurtosis?
Skewness is a measure of asymmetry within a distribution. When analyzing asset returns, positive skewness indicates that the distribution has a longer tail on the right side—meaning there’s a higher probability of large gains. Conversely, negative skewness suggests a longer left tail, implying potential for significant losses. For investors, understanding skewness helps gauge whether an asset tends to produce more frequent small gains with occasional big wins or vice versa.
Kurtosis describes the "tailedness" or peakedness of a distribution. High kurtosis signifies that extreme values (either very high or very low returns) are more probable than in normal distributions—a phenomenon often observed during market crashes or rapid rallies. Low kurtosis indicates fewer extreme events and generally more stable return patterns.
The Significance in Financial Markets
In financial analysis—including stocks, commodities, forex, and particularly cryptocurrencies—these two metrics provide vital information about risk exposure beyond traditional measures like volatility alone.
- Risk Assessment: Assets with high positive skewness may offer opportunities for outsized gains but come with increased risk due to potential large losses if negatively skewed assets dominate.
- Return Distribution Insights: Kurtosis reveals how likely it is to encounter rare but impactful events—crucial for stress testing portfolios against market shocks.
- Portfolio Diversification: Recognizing assets' skewness and kurtosis helps investors build diversified portfolios that balance risks associated with asymmetric return profiles.
Recent Developments Enhancing Market Analysis
The rise of advanced statistical tools has transformed how traders interpret these measures:
Cryptocurrency Market Volatility: Cryptos are notorious for their unpredictable swings; during bull runs or crashes like those seen in 2022, both skewness and kurtosis tend to spike sharply. This heightened complexity underscores their importance when assessing crypto investments.
Real-Time Data Analysis: Platforms such as QuantConnect or Alpaca now enable traders to incorporate real-time calculations of skewness and kurtosis into automated trading strategies using APIs integrated with machine learning algorithms—all contributing toward smarter decision-making processes.
Regulatory Focus on Risk Management: Regulatory bodies worldwide recognize the importance of monitoring these metrics as part of systemic risk mitigation efforts since abnormal levels can signal underlying vulnerabilities within financial systems.
Investor Sentiment Monitoring
Skewenessand kurtosishave also become tools for gauging investor sentiment:
- Elevated kurtosis might indicate heightened investor optimism (or pessimism), reflecting expectations about future market moves.
- Shifts in these metrics over time can serve as early warning signals for changing attitudes toward specific assets or sectors.
Impacts on Investment Strategies
Ignoring these statistical characteristics can lead to misguided investment choices:
- Underestimating negative skew could cause investors to overlook potential downside risks associated with certain assets.
- Overlooking high kurtosis might result in insufficient preparation for sudden market downturns caused by rare but severe events.
Conversely, incorporating insights from skewness and kurtosis allows investors to optimize portfolio allocations by balancing expected returns against tail risks effectively.
Market Stability Considerations
High levels of kurtosis suggest increased likelihoods of extreme price swings which can destabilize markets if widespread across multiple assets simultaneously—a concern amplified during periods like 2022’s crypto downturns when volatility surged dramatically.
Regulators also monitor these indicators closely because persistent abnormal values may precede systemic crises; thus understanding them aids policymakers aiming at maintaining overall financial stability through proactive measures such as stress testing banks’ resilience under adverse scenarios informed by these statistics.
Technological Advancements Driving Better Risk Management
As machine learning models become increasingly sophisticated—and data availability continues expanding—the capacity to analyze real-time changes in skewenessandkurtosishas improved significantly:
- Automated trading algorithms now incorporate dynamic assessments based on current distribution shapes,
- Risk management frameworks leverage these insights for better hedging strategies,
- Predictive analytics help anticipate future shifts before they materialize into costly market events,
This technological progress enhances our ability not only to understand current risks but also proactively mitigate them before they escalate into crises affecting broader markets.
How Understanding These Metrics Benefits Investors & Regulators
For individual investors seeking long-term growth while managing downside risks effectively—as well as institutional players aiming at systemic stability—grasping what skwenessandkurtosishow about return distributions is essential:
• Accurate assessment prevents misjudgments that could lead either to excessive caution (missing out on gains) or reckless exposure (underestimating tail risks).• It supports strategic diversification tailored towards different asset classes’ unique distribution profiles.• It informs regulatory policies designed around early detection signals indicating rising systemic vulnerabilities linked directly back to unusual distribution shapes.
Tracking Changes Over Time: The Role Of SkewenessandKurtosishas Become More Critical
Monitoring shifts in these statistics over time provides valuable clues about evolving market conditions:
- Rising positive skwenessmight suggest growing investor optimism,
- Increasing negative skwenesscould warn about looming downside dangers,
- Surges in kurtoisis often precede turbulent periods characterized by rapid price swings,
Such trends enable both traders and regulators alike to adapt strategies accordingly—to capitalize on emerging opportunities while safeguarding against impending threats.
Risks Of Ignoring Distribution Shape Metrics
Failing to consider skwenessandkurtosin investment analysis carries notable dangers:
- Underestimating tail risks may leave portfolios vulnerable during black swan events,
- Misinterpreting asymmetries could lead traders astray regarding true profit potentials,
- Ignoring signs from higher moments might result in inadequate capital buffers against shocks,
Therefore integrating these measures into regular analysis enhances resilience amid unpredictable markets.
Advancing Market Resilience Through Better Data Interpretation
As analytical techniques evolve—with AI-driven models providing deeper insights—the ability not only improves individual decision-making but also contributes toward overall market stability by enabling timely responses based on comprehensive understanding rather than reactive moves alone.
By appreciating why skewenessandkurtoshave become central components within modern financial analytics—and applying this knowledge diligently—you position yourself better prepared for navigating complex markets characterized by uncertainty yet rich with opportunity.
Keywords: Skewness,Kurtosis,Risk Management,Cryptocurrency Volatility,Fear Indexes,Moment Analysis,Systemic Risks
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding the Theoretical Foundations of the Force Index
The Force Index is a technical analysis tool that helps traders gauge the strength behind market movements by combining price action with trading volume. Developed by renowned trader and author Alexander Elder in 1999, this indicator offers valuable insights into whether a trend is supported by significant buying or selling pressure. To fully appreciate its utility, it’s essential to understand its theoretical basis—how it works conceptually and why it can be an effective component of a comprehensive trading strategy.
The Core Concept: Price and Volume as Market Indicators
At its essence, the Force Index operates on the principle that price movements alone do not tell the full story of market dynamics. Instead, volume—the number of shares or contracts traded—serves as an important confirmation signal for price trends. When prices rise on high volume, it suggests strong buying interest; conversely, falling prices accompanied by high volume indicate robust selling pressure.
Alexander Elder’s insight was to combine these two elements into a single metric that quantifies market "power" or "force." By doing so, traders can distinguish between weak moves driven merely by noise or low participation versus genuine shifts backed by substantial trading activity.
Mathematical Foundation: Why Multiply Price and Volume?
The original formula for the Force Index is straightforward:
[ \text{Force Index} = \text{Price} \times \text{Volume} ]
This simple multiplication captures several key ideas:
- Magnitude of Movement: Larger price changes suggest stronger momentum.
- Participation Level: Higher volumes imply more significant trader commitment.
- Combined Strength: Multiplying these factors emphasizes moves supported by both substantial price change and high trading activity.
While some variations incorporate differences in closing prices over multiple periods (such as using current versus previous close), Elder's initial approach focused on immediate data points to provide real-time insights into market strength.
How Does It Reflect Market Sentiment?
The sign (positive or negative) of the Force Index indicates prevailing sentiment:
- A positive value suggests bullish momentum with strong buying interest.
- A negative value indicates bearish sentiment with active selling pressure.
This directional information helps traders confirm whether current trends are likely sustainable or if they might be losing steam. For example, a rising positive Force Index during an uptrend reinforces confidence in continued upward movement; meanwhile, divergence—where prices rise but the Force Index declines—can signal weakening momentum and potential reversals.
Relationship With Other Technical Indicators
The theoretical basis also involves understanding how the Force Index complements other tools like moving averages, trend lines, RSI (Relative Strength Index), or Bollinger Bands. Since it measures force rather than just directionality like traditional trend indicators do, combining these signals provides a more nuanced view of market conditions. For instance:
- Confirming breakouts when both moving averages align with positive force index readings.
- Spotting divergences between RSI and force index to identify potential reversals before they occur.
This synergy enhances decision-making accuracy for traders seeking confirmation from multiple sources within their technical analysis toolkit.
Application in Different Markets
Initially popular among traditional stock traders, especially those focusing on swing trading and trend following strategies during stable markets in early 2000s, recent years have seen increased adoption among cryptocurrency traders. The volatile nature of digital assets makes volume-based indicators like the Force Index particularly relevant because they help differentiate between genuine moves driven by strong participation versus fleeting spikes caused by speculative activity.
In algorithmic trading systems too—the realm where quantitative models dominate—the simplicity yet effectiveness of multiplying price and volume has made this indicator attractive for automated decision-making processes aiming to capture short-term momentum shifts efficiently.
Limitations Rooted in Theory
Despite its strengths grounded in sound principles linking volume with price action, reliance solely on the Force Index can lead to pitfalls if broader context isn’t considered:
- Market Volatility: High volatility environments—especially prevalent in crypto markets—may produce frequent false signals due to exaggerated swings.
- Overreliance: Using only one indicator ignores other critical factors such as macroeconomic news events or fundamental data influencing asset prices.
- Market Sentiment Shifts: Rapid changes driven by news can temporarily distort volume-price relationships without reflecting true underlying strength or weakness.
Therefore, while rooted firmly in logical assumptions about trader behavior reflected through combined price-volume analysis—a core tenet within technical analysis—the practical application demands cautious integration alongside other tools for robust decision-making aligned with user intent: understanding what drives market movements at their core.
How Traders Use Theoretical Insights Into Practice
By grasping why multiplying price times volume effectively measures "market force," traders gain confidence that this indicator reflects genuine conviction behind moves rather than mere speculation or noise. This understanding supports strategic decisions such as entering trades when positive force index readings confirm upward trends—or exiting positions when divergence hints at weakening momentum despite ongoing price increases.
Incorporating Broader Market Context
While foundational theory underscores how combined data points reveal underlying strength levels across different assets—including stocks and cryptocurrencies—it remains crucial for users to interpret signals within broader contexts like overall market sentiment shifts or macroeconomic developments which may override pure technical cues.
Summary
The theoretical basis of the Force Index hinges on integrating two vital aspects: how much money is flowing into (or out of) an asset via trade volumes—and how strongly prices are moving accordingly. Its simplicity belies its powerful ability to reflect real-time trader conviction about ongoing trends across various markets today—from traditional equities to highly volatile cryptocurrencies—all while emphasizing that no single indicator should operate alone but instead form part of a well-rounded analytical approach rooted deeply in behavioral finance principles.
By understanding these core concepts underpinning Alexander Elder’s creation—the combination of supply/demand dynamics captured through volume alongside raw pricing data—you equip yourself better for making informed decisions based on solid theoretical foundations.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 03:12
What is the theoretical basis of the Force Index?
Understanding the Theoretical Foundations of the Force Index
The Force Index is a technical analysis tool that helps traders gauge the strength behind market movements by combining price action with trading volume. Developed by renowned trader and author Alexander Elder in 1999, this indicator offers valuable insights into whether a trend is supported by significant buying or selling pressure. To fully appreciate its utility, it’s essential to understand its theoretical basis—how it works conceptually and why it can be an effective component of a comprehensive trading strategy.
The Core Concept: Price and Volume as Market Indicators
At its essence, the Force Index operates on the principle that price movements alone do not tell the full story of market dynamics. Instead, volume—the number of shares or contracts traded—serves as an important confirmation signal for price trends. When prices rise on high volume, it suggests strong buying interest; conversely, falling prices accompanied by high volume indicate robust selling pressure.
Alexander Elder’s insight was to combine these two elements into a single metric that quantifies market "power" or "force." By doing so, traders can distinguish between weak moves driven merely by noise or low participation versus genuine shifts backed by substantial trading activity.
Mathematical Foundation: Why Multiply Price and Volume?
The original formula for the Force Index is straightforward:
[ \text{Force Index} = \text{Price} \times \text{Volume} ]
This simple multiplication captures several key ideas:
- Magnitude of Movement: Larger price changes suggest stronger momentum.
- Participation Level: Higher volumes imply more significant trader commitment.
- Combined Strength: Multiplying these factors emphasizes moves supported by both substantial price change and high trading activity.
While some variations incorporate differences in closing prices over multiple periods (such as using current versus previous close), Elder's initial approach focused on immediate data points to provide real-time insights into market strength.
How Does It Reflect Market Sentiment?
The sign (positive or negative) of the Force Index indicates prevailing sentiment:
- A positive value suggests bullish momentum with strong buying interest.
- A negative value indicates bearish sentiment with active selling pressure.
This directional information helps traders confirm whether current trends are likely sustainable or if they might be losing steam. For example, a rising positive Force Index during an uptrend reinforces confidence in continued upward movement; meanwhile, divergence—where prices rise but the Force Index declines—can signal weakening momentum and potential reversals.
Relationship With Other Technical Indicators
The theoretical basis also involves understanding how the Force Index complements other tools like moving averages, trend lines, RSI (Relative Strength Index), or Bollinger Bands. Since it measures force rather than just directionality like traditional trend indicators do, combining these signals provides a more nuanced view of market conditions. For instance:
- Confirming breakouts when both moving averages align with positive force index readings.
- Spotting divergences between RSI and force index to identify potential reversals before they occur.
This synergy enhances decision-making accuracy for traders seeking confirmation from multiple sources within their technical analysis toolkit.
Application in Different Markets
Initially popular among traditional stock traders, especially those focusing on swing trading and trend following strategies during stable markets in early 2000s, recent years have seen increased adoption among cryptocurrency traders. The volatile nature of digital assets makes volume-based indicators like the Force Index particularly relevant because they help differentiate between genuine moves driven by strong participation versus fleeting spikes caused by speculative activity.
In algorithmic trading systems too—the realm where quantitative models dominate—the simplicity yet effectiveness of multiplying price and volume has made this indicator attractive for automated decision-making processes aiming to capture short-term momentum shifts efficiently.
Limitations Rooted in Theory
Despite its strengths grounded in sound principles linking volume with price action, reliance solely on the Force Index can lead to pitfalls if broader context isn’t considered:
- Market Volatility: High volatility environments—especially prevalent in crypto markets—may produce frequent false signals due to exaggerated swings.
- Overreliance: Using only one indicator ignores other critical factors such as macroeconomic news events or fundamental data influencing asset prices.
- Market Sentiment Shifts: Rapid changes driven by news can temporarily distort volume-price relationships without reflecting true underlying strength or weakness.
Therefore, while rooted firmly in logical assumptions about trader behavior reflected through combined price-volume analysis—a core tenet within technical analysis—the practical application demands cautious integration alongside other tools for robust decision-making aligned with user intent: understanding what drives market movements at their core.
How Traders Use Theoretical Insights Into Practice
By grasping why multiplying price times volume effectively measures "market force," traders gain confidence that this indicator reflects genuine conviction behind moves rather than mere speculation or noise. This understanding supports strategic decisions such as entering trades when positive force index readings confirm upward trends—or exiting positions when divergence hints at weakening momentum despite ongoing price increases.
Incorporating Broader Market Context
While foundational theory underscores how combined data points reveal underlying strength levels across different assets—including stocks and cryptocurrencies—it remains crucial for users to interpret signals within broader contexts like overall market sentiment shifts or macroeconomic developments which may override pure technical cues.
Summary
The theoretical basis of the Force Index hinges on integrating two vital aspects: how much money is flowing into (or out of) an asset via trade volumes—and how strongly prices are moving accordingly. Its simplicity belies its powerful ability to reflect real-time trader conviction about ongoing trends across various markets today—from traditional equities to highly volatile cryptocurrencies—all while emphasizing that no single indicator should operate alone but instead form part of a well-rounded analytical approach rooted deeply in behavioral finance principles.
By understanding these core concepts underpinning Alexander Elder’s creation—the combination of supply/demand dynamics captured through volume alongside raw pricing data—you equip yourself better for making informed decisions based on solid theoretical foundations.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Best Wallets for Storing Cryptocurrency Safely
Storing cryptocurrency securely is a top priority for investors and users alike. As digital assets grow in value and popularity, the risk of theft, hacking, or loss increases. Choosing the right wallet is essential to protect your funds from potential threats while maintaining easy access when needed. This guide explores the most effective wallets for safe cryptocurrency storage, considering security features, usability, and recent developments.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallets
A cryptocurrency wallet functions as a digital container that stores your public addresses and private keys—crucial components needed to send or receive digital currencies. Unlike traditional bank accounts, crypto wallets do not hold physical coins but instead secure the cryptographic keys that grant access to your assets on the blockchain.
Wallets are categorized into different types based on their form factor and security level:
- Software wallets (applications installed on devices)
- Hardware wallets (physical devices offline)
- Paper wallets (printed keys)
- Exchange wallets (held within trading platforms)
Each type offers distinct advantages and trade-offs concerning security, convenience, and control over funds.
Hardware Wallets: The Most Secure Option
For long-term storage of significant amounts of cryptocurrencies or valuable holdings, hardware wallets are widely regarded as the safest choice. These physical devices store private keys offline—completely disconnected from internet-connected systems—making them highly resistant to hacking attempts.
Popular hardware options include Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor Model T. They typically feature PIN protection, multi-signature support, and secure elements designed to prevent malware or phishing attacks from compromising private keys. While they require an initial investment (~$50-$200), their robust security makes them ideal for safeguarding large portfolios against cyber threats.
However, hardware wallets demand careful handling; losing access to these devices without proper backups can result in permanent loss of funds unless recovery seed phrases are securely stored elsewhere.
Software Wallets: Convenient but Less Secure
Software wallets offer ease of use by installing applications directly onto computers or smartphones. They are suitable for daily transactions or smaller holdings due to their accessibility but come with increased risks if device security is compromised.
Examples include MetaMask (popular among Ethereum users), Electrum (Bitcoin-focused), and MyEtherWallet—a web-based interface often used with hardware integration for added safety. To maximize security when using software wallets:
- Keep your device free from malware
- Use strong passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication where available
- Regularly update wallet software
While convenient for active traders or small-scale investors, software wallets should be complemented with additional safeguards if holding substantial assets.
Paper Wallets: Offline Storage with Risks
Paper wallets involve printing out public addresses along with private keys on paper—an entirely offline method that minimizes online hacking risks during storage. They can be generated using trusted tools like BitAddress.org or MyEtherWallet's offline mode.
Despite their simplicity in concept—and low cost—they carry vulnerabilities such as physical damage (fire/water) or theft if not stored securely in safes or vaults. Additionally,
they require careful handling during creation; generating a paper wallet online without verifying source trust can expose private keys to malicious actors through compromised generators.
In modern practice, paper wallets are less favored due to these risks but remain useful as cold storage options when combined with proper physical security measures.
Exchange Wallets: Ease vs Security Trade-off
Many beginners start by storing cryptocurrencies within exchange accounts like Coinbase or Binance because they offer quick access for trading purposes. However,
these exchange-held funds are generally less secure than personal-controlled solutions because exchanges become attractive targets for hackers—they have experienced multiple high-profile breaches historically.
While some exchanges implement strong internal security protocols—including cold storage reserves—the risk remains that user accounts could be compromised through phishing attacks or weak passwords unless additional protections like two-factor authentication are enabled diligently.
For long-term holding beyond active trading needs—or large sums—it’s advisable to transfer assets into more secure personal custody solutions rather than relying solely on exchange-hosted hot-wallet services.
Recent Developments Impacting Crypto Storage Security
The landscape of crypto storage continues evolving alongside technological advancements and emerging threats:
New Cryptocurrencies & Their Storage Needs
The launch of new tokens such as $TRUMP Coin—a Solana-based meme coin launched in April 2025—underscores ongoing interest in diverse digital assets requiring reliable custody solutions tailored per blockchain standards.Investors must ensure compatibility between their chosen wallet type(s) and specific tokens’ technical requirements while prioritizing safety measures like multi-signature support where applicable.
Cybersecurity Threats & User Vigilance
Cyber threats such as "slopsquatting" — malicious package distribution targeting AI-related software — highlight how attackers exploit trust vulnerabilities across various platforms including those managing crypto operations[2]. Users should always verify sources before downloading any management tools related to cryptocurrencies.Implementing multi-layered defenses—including hardware 2FA tokens—and staying informed about current scams enhances overall safety posture.
Key Features That Enhance Crypto Wallet Security
When selecting a wallet type suitable for your needs consider these critical features:
- Multi-Signature Support: Requires multiple approvals before executing transactions.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Adds an extra layer beyond passwords.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensures protection against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Backup & Recovery Options: Enables restoring access if devices fail.5.. Regulatory Compliance & Trustworthiness: Choose reputable providers adhering to legal standards which bolster confidence in asset management practices.[1]
Always review user feedback regarding reliability; well-established brands tend toward better performance stability over lesser-known alternatives.
Risks Associated With Poor Storage Practices
Failing at proper crypto custody exposes users not only financially but also legally depending on jurisdictional regulations:
- Hacking incidents resulting in stolen funds
- Loss due to forgotten passwords/private key mishandling
- Physical damage destroying paper backups
- Regulatory restrictions impacting certain types of custodial services
Educating oneself about best practices—from creating complex passwords via password managers—to securing seed phrases off-line significantly reduces vulnerability exposure[3].
By understanding different types of cryptocurrency wallets—from highly secure hardware options suited for large holdings—to more accessible software solutions ideal for everyday use—you can tailor your approach based on individual risk tolerance levels while maintaining control over your digital wealth safely amidst evolving cybersecurity challenges.[1][2][3]


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-11 10:12
What wallets work best for storing it safely?
Best Wallets for Storing Cryptocurrency Safely
Storing cryptocurrency securely is a top priority for investors and users alike. As digital assets grow in value and popularity, the risk of theft, hacking, or loss increases. Choosing the right wallet is essential to protect your funds from potential threats while maintaining easy access when needed. This guide explores the most effective wallets for safe cryptocurrency storage, considering security features, usability, and recent developments.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Wallets
A cryptocurrency wallet functions as a digital container that stores your public addresses and private keys—crucial components needed to send or receive digital currencies. Unlike traditional bank accounts, crypto wallets do not hold physical coins but instead secure the cryptographic keys that grant access to your assets on the blockchain.
Wallets are categorized into different types based on their form factor and security level:
- Software wallets (applications installed on devices)
- Hardware wallets (physical devices offline)
- Paper wallets (printed keys)
- Exchange wallets (held within trading platforms)
Each type offers distinct advantages and trade-offs concerning security, convenience, and control over funds.
Hardware Wallets: The Most Secure Option
For long-term storage of significant amounts of cryptocurrencies or valuable holdings, hardware wallets are widely regarded as the safest choice. These physical devices store private keys offline—completely disconnected from internet-connected systems—making them highly resistant to hacking attempts.
Popular hardware options include Ledger Nano S/X and Trezor Model T. They typically feature PIN protection, multi-signature support, and secure elements designed to prevent malware or phishing attacks from compromising private keys. While they require an initial investment (~$50-$200), their robust security makes them ideal for safeguarding large portfolios against cyber threats.
However, hardware wallets demand careful handling; losing access to these devices without proper backups can result in permanent loss of funds unless recovery seed phrases are securely stored elsewhere.
Software Wallets: Convenient but Less Secure
Software wallets offer ease of use by installing applications directly onto computers or smartphones. They are suitable for daily transactions or smaller holdings due to their accessibility but come with increased risks if device security is compromised.
Examples include MetaMask (popular among Ethereum users), Electrum (Bitcoin-focused), and MyEtherWallet—a web-based interface often used with hardware integration for added safety. To maximize security when using software wallets:
- Keep your device free from malware
- Use strong passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication where available
- Regularly update wallet software
While convenient for active traders or small-scale investors, software wallets should be complemented with additional safeguards if holding substantial assets.
Paper Wallets: Offline Storage with Risks
Paper wallets involve printing out public addresses along with private keys on paper—an entirely offline method that minimizes online hacking risks during storage. They can be generated using trusted tools like BitAddress.org or MyEtherWallet's offline mode.
Despite their simplicity in concept—and low cost—they carry vulnerabilities such as physical damage (fire/water) or theft if not stored securely in safes or vaults. Additionally,
they require careful handling during creation; generating a paper wallet online without verifying source trust can expose private keys to malicious actors through compromised generators.
In modern practice, paper wallets are less favored due to these risks but remain useful as cold storage options when combined with proper physical security measures.
Exchange Wallets: Ease vs Security Trade-off
Many beginners start by storing cryptocurrencies within exchange accounts like Coinbase or Binance because they offer quick access for trading purposes. However,
these exchange-held funds are generally less secure than personal-controlled solutions because exchanges become attractive targets for hackers—they have experienced multiple high-profile breaches historically.
While some exchanges implement strong internal security protocols—including cold storage reserves—the risk remains that user accounts could be compromised through phishing attacks or weak passwords unless additional protections like two-factor authentication are enabled diligently.
For long-term holding beyond active trading needs—or large sums—it’s advisable to transfer assets into more secure personal custody solutions rather than relying solely on exchange-hosted hot-wallet services.
Recent Developments Impacting Crypto Storage Security
The landscape of crypto storage continues evolving alongside technological advancements and emerging threats:
New Cryptocurrencies & Their Storage Needs
The launch of new tokens such as $TRUMP Coin—a Solana-based meme coin launched in April 2025—underscores ongoing interest in diverse digital assets requiring reliable custody solutions tailored per blockchain standards.Investors must ensure compatibility between their chosen wallet type(s) and specific tokens’ technical requirements while prioritizing safety measures like multi-signature support where applicable.
Cybersecurity Threats & User Vigilance
Cyber threats such as "slopsquatting" — malicious package distribution targeting AI-related software — highlight how attackers exploit trust vulnerabilities across various platforms including those managing crypto operations[2]. Users should always verify sources before downloading any management tools related to cryptocurrencies.Implementing multi-layered defenses—including hardware 2FA tokens—and staying informed about current scams enhances overall safety posture.
Key Features That Enhance Crypto Wallet Security
When selecting a wallet type suitable for your needs consider these critical features:
- Multi-Signature Support: Requires multiple approvals before executing transactions.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Adds an extra layer beyond passwords.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensures protection against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Backup & Recovery Options: Enables restoring access if devices fail.5.. Regulatory Compliance & Trustworthiness: Choose reputable providers adhering to legal standards which bolster confidence in asset management practices.[1]
Always review user feedback regarding reliability; well-established brands tend toward better performance stability over lesser-known alternatives.
Risks Associated With Poor Storage Practices
Failing at proper crypto custody exposes users not only financially but also legally depending on jurisdictional regulations:
- Hacking incidents resulting in stolen funds
- Loss due to forgotten passwords/private key mishandling
- Physical damage destroying paper backups
- Regulatory restrictions impacting certain types of custodial services
Educating oneself about best practices—from creating complex passwords via password managers—to securing seed phrases off-line significantly reduces vulnerability exposure[3].
By understanding different types of cryptocurrency wallets—from highly secure hardware options suited for large holdings—to more accessible software solutions ideal for everyday use—you can tailor your approach based on individual risk tolerance levels while maintaining control over your digital wealth safely amidst evolving cybersecurity challenges.[1][2][3]
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Market-Making Strategies for USD Coin (USDC) and Their Impact on Bid-Ask Spreads
Understanding Bid-Ask Spreads in Cryptocurrency Markets
Bid-ask spreads are fundamental to understanding liquidity and trading costs in any financial market, including cryptocurrencies. For USD Coin (USDC), a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, maintaining a narrow bid-ask spread is essential for efficient trading. The bid price represents what buyers are willing to pay, while the ask price indicates what sellers want to receive. When these prices are close together, the spread is tight, signaling high liquidity and active market participation.
Tight spreads benefit traders by reducing transaction costs and enabling smoother execution of trades. They also reflect confidence among market participants that USDC can be exchanged quickly without significant price impact. Achieving such conditions requires sophisticated strategies from market makers—entities or algorithms dedicated to providing continuous buy and sell quotes.
Core Market-Making Strategies Ensuring Tight USDC Spreads
Order Book Management: Building Depth and Liquidity
Effective order book management forms the backbone of tight bid-ask spreads. Market makers place both buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders at various price levels around the current market rate. This layered approach creates depth within the order book, increasing the likelihood of matching trades at favorable prices.
Maintaining a deep order book with sufficient volume ensures that there are always counterparties available for transactions across different sizes—particularly large trades—which helps prevent sudden widening of spreads during periods of volatility or low activity.
Dynamic Price Discovery: Real-Time Adjustments Based on Data
Market makers rely heavily on real-time data analysis for setting optimal bid and ask prices. By continuously monitoring factors such as recent trading volumes, historical price trends, macroeconomic indicators, and broader crypto market movements, they can adjust their quotes promptly.
This dynamic pricing process allows them to respond swiftly to changing conditions—whether it’s increased demand during bullish phases or heightened volatility—and keep spreads tight by aligning their quotes closely with prevailing market rates.
Risk Management Techniques: Protecting Profitability While Providing Liquidity
Market making involves inherent risks due to unpredictable price swings or sudden liquidity shortages. To mitigate these risks while maintaining tight spreads:
Position Sizing: Market makers limit exposure by capping how much USDC they hold at any given time.
Hedging Strategies: They often use hedging instruments like futures contracts or options on other assets (e.g., Bitcoin or Ethereum) to offset potential losses from adverse moves in USDC’s value relative to fiat currency or other cryptocurrencies.
These practices help sustain consistent quoting behavior without exposing firms—or individual traders—to excessive risk that could force wider spreads as a protective measure.
Enhancing Liquidity Through Incentives & Tiered Pricing Structures
Liquidity provision can be incentivized through tiered pricing models where larger trades attract better rates—encouraging institutional investors or high-volume traders to participate actively in markets involving USDC. Rebate programs offered by exchanges further motivate liquidity providers; for example:
- Offering fee rebates for high-volume transactions
- Providing preferential treatment during volatile periods
Such incentives increase overall participation levels which directly contribute toward narrower bid-ask spreads by boosting available supply and demand at various levels within the order book.
Collateral Management & Trust Building: Ensuring Stability & Confidence
Since stablecoins like USDC rely heavily on collateral backing—often held in highly liquid assets such as U.S Treasury bonds—the management of collateral quality is critical for maintaining trust among users and participants alike.
High-quality collateral reduces systemic risk concerns that could lead traders away from using USDC due to fears over its peg stability—a factor that influences how tightly market makers can quote prices without risking insolvency if confidence erodes unexpectedly.
Recent Developments Shaping Stablecoin Market Dynamics
The landscape surrounding stablecoins continues evolving rapidly amid strategic corporate moves and regulatory shifts. In 2025, Ripple's attempt—a $5 billion acquisition deal aimed at acquiring Circle—highlighted how competitive this space has become[2]. Although unsuccessful so far, such developments underscore the importance of strategic positioning among major players influencing liquidity pools involving USDC.
Meanwhile, Coinbase's ambitious revenue targets indicate an ongoing focus on expanding cryptocurrency services—including stablecoins—which indirectly impacts their trading volumes[1]. Increased activity tends toward tighter bids-offer margins due to higher competition among market makers seeking opportunities across diverse assets like Bitcoin alongside stablecoins like USDC.
Emerging alternatives such as Ethena USD (ENAUSD) have gained traction recently[3], introducing new competitors into this ecosystem. As more options become available—for instance through innovative features or improved stability—they exert downward pressure on bid-ask spreads because more entities compete over providing liquidity across multiple stablecoin platforms.
Potential Challenges That Could Widen Bid-Ask Spreads
While current strategies promote narrow spreads under normal conditions, several external factors threaten this equilibrium:
Increased Competition: The rise of alternative stablecoins may fragment liquidity pools leading some traders away from USDC; reduced volume can cause wider gaps between bids and asks.
Regulatory Changes: Governments worldwide scrutinize stablecoins more intensely; stricter regulations might impose higher collateral requirements or operational restrictions[2], potentially constraining supply-side activities crucial for keeping spreads tight.
Market Volatility: Sudden shocks—in crypto markets especially—can cause rapid fluctuations in demand/supply dynamics affecting all assets including stablecoins; during turbulent times, widened spread margins serve as risk buffers but reduce efficiency.
How Effective Market-Making Supports Stablecoin Ecosystems
Implementing robust strategies not only benefits individual traders but also sustains broader ecosystem health:
- It enhances overall liquidity which attracts institutional investors seeking reliable settlement options.
- It stabilizes peg integrity by ensuring ample backing through well-managed collateral reserves.
- It fosters transparency when firms publish real-time data about their quoting behaviors — reinforcing user trust based on expertise (“E-A-T”: Experience Authority Trust).
By continuously adapting these techniques amidst evolving technological innovations—and regulatory landscapes—market participants help maintain competitive edge while safeguarding against systemic risks.
This comprehensive overview underscores how strategic approaches—from managing order books effectively through dynamic pricing tactics—to leveraging incentives play vital roles in ensuring narrow bid-ask spreads around USD Coin (USDC). As new competitors emerge alongside shifting regulations globally—and with ongoing developments shaping investor sentiment—the ability of professional market-makers remains central not just for profitability but also for fostering resilient cryptocurrency markets rooted in transparency & trustworthiness


Lo
2025-05-11 08:24
What market-making strategies ensure tight bid-ask spreads for USD Coin (USDC)?
Market-Making Strategies for USD Coin (USDC) and Their Impact on Bid-Ask Spreads
Understanding Bid-Ask Spreads in Cryptocurrency Markets
Bid-ask spreads are fundamental to understanding liquidity and trading costs in any financial market, including cryptocurrencies. For USD Coin (USDC), a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, maintaining a narrow bid-ask spread is essential for efficient trading. The bid price represents what buyers are willing to pay, while the ask price indicates what sellers want to receive. When these prices are close together, the spread is tight, signaling high liquidity and active market participation.
Tight spreads benefit traders by reducing transaction costs and enabling smoother execution of trades. They also reflect confidence among market participants that USDC can be exchanged quickly without significant price impact. Achieving such conditions requires sophisticated strategies from market makers—entities or algorithms dedicated to providing continuous buy and sell quotes.
Core Market-Making Strategies Ensuring Tight USDC Spreads
Order Book Management: Building Depth and Liquidity
Effective order book management forms the backbone of tight bid-ask spreads. Market makers place both buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders at various price levels around the current market rate. This layered approach creates depth within the order book, increasing the likelihood of matching trades at favorable prices.
Maintaining a deep order book with sufficient volume ensures that there are always counterparties available for transactions across different sizes—particularly large trades—which helps prevent sudden widening of spreads during periods of volatility or low activity.
Dynamic Price Discovery: Real-Time Adjustments Based on Data
Market makers rely heavily on real-time data analysis for setting optimal bid and ask prices. By continuously monitoring factors such as recent trading volumes, historical price trends, macroeconomic indicators, and broader crypto market movements, they can adjust their quotes promptly.
This dynamic pricing process allows them to respond swiftly to changing conditions—whether it’s increased demand during bullish phases or heightened volatility—and keep spreads tight by aligning their quotes closely with prevailing market rates.
Risk Management Techniques: Protecting Profitability While Providing Liquidity
Market making involves inherent risks due to unpredictable price swings or sudden liquidity shortages. To mitigate these risks while maintaining tight spreads:
Position Sizing: Market makers limit exposure by capping how much USDC they hold at any given time.
Hedging Strategies: They often use hedging instruments like futures contracts or options on other assets (e.g., Bitcoin or Ethereum) to offset potential losses from adverse moves in USDC’s value relative to fiat currency or other cryptocurrencies.
These practices help sustain consistent quoting behavior without exposing firms—or individual traders—to excessive risk that could force wider spreads as a protective measure.
Enhancing Liquidity Through Incentives & Tiered Pricing Structures
Liquidity provision can be incentivized through tiered pricing models where larger trades attract better rates—encouraging institutional investors or high-volume traders to participate actively in markets involving USDC. Rebate programs offered by exchanges further motivate liquidity providers; for example:
- Offering fee rebates for high-volume transactions
- Providing preferential treatment during volatile periods
Such incentives increase overall participation levels which directly contribute toward narrower bid-ask spreads by boosting available supply and demand at various levels within the order book.
Collateral Management & Trust Building: Ensuring Stability & Confidence
Since stablecoins like USDC rely heavily on collateral backing—often held in highly liquid assets such as U.S Treasury bonds—the management of collateral quality is critical for maintaining trust among users and participants alike.
High-quality collateral reduces systemic risk concerns that could lead traders away from using USDC due to fears over its peg stability—a factor that influences how tightly market makers can quote prices without risking insolvency if confidence erodes unexpectedly.
Recent Developments Shaping Stablecoin Market Dynamics
The landscape surrounding stablecoins continues evolving rapidly amid strategic corporate moves and regulatory shifts. In 2025, Ripple's attempt—a $5 billion acquisition deal aimed at acquiring Circle—highlighted how competitive this space has become[2]. Although unsuccessful so far, such developments underscore the importance of strategic positioning among major players influencing liquidity pools involving USDC.
Meanwhile, Coinbase's ambitious revenue targets indicate an ongoing focus on expanding cryptocurrency services—including stablecoins—which indirectly impacts their trading volumes[1]. Increased activity tends toward tighter bids-offer margins due to higher competition among market makers seeking opportunities across diverse assets like Bitcoin alongside stablecoins like USDC.
Emerging alternatives such as Ethena USD (ENAUSD) have gained traction recently[3], introducing new competitors into this ecosystem. As more options become available—for instance through innovative features or improved stability—they exert downward pressure on bid-ask spreads because more entities compete over providing liquidity across multiple stablecoin platforms.
Potential Challenges That Could Widen Bid-Ask Spreads
While current strategies promote narrow spreads under normal conditions, several external factors threaten this equilibrium:
Increased Competition: The rise of alternative stablecoins may fragment liquidity pools leading some traders away from USDC; reduced volume can cause wider gaps between bids and asks.
Regulatory Changes: Governments worldwide scrutinize stablecoins more intensely; stricter regulations might impose higher collateral requirements or operational restrictions[2], potentially constraining supply-side activities crucial for keeping spreads tight.
Market Volatility: Sudden shocks—in crypto markets especially—can cause rapid fluctuations in demand/supply dynamics affecting all assets including stablecoins; during turbulent times, widened spread margins serve as risk buffers but reduce efficiency.
How Effective Market-Making Supports Stablecoin Ecosystems
Implementing robust strategies not only benefits individual traders but also sustains broader ecosystem health:
- It enhances overall liquidity which attracts institutional investors seeking reliable settlement options.
- It stabilizes peg integrity by ensuring ample backing through well-managed collateral reserves.
- It fosters transparency when firms publish real-time data about their quoting behaviors — reinforcing user trust based on expertise (“E-A-T”: Experience Authority Trust).
By continuously adapting these techniques amidst evolving technological innovations—and regulatory landscapes—market participants help maintain competitive edge while safeguarding against systemic risks.
This comprehensive overview underscores how strategic approaches—from managing order books effectively through dynamic pricing tactics—to leveraging incentives play vital roles in ensuring narrow bid-ask spreads around USD Coin (USDC). As new competitors emerge alongside shifting regulations globally—and with ongoing developments shaping investor sentiment—the ability of professional market-makers remains central not just for profitability but also for fostering resilient cryptocurrency markets rooted in transparency & trustworthiness
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
