What Are the Potential Benefits of Using Bitcoin?
Bitcoin has revolutionized the financial landscape since its creation in 2009. As the first decentralized cryptocurrency, it offers a range of advantages that appeal to individual users, investors, and even governments. Understanding these benefits can help you determine whether integrating Bitcoin into your financial activities makes sense. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the key benefits associated with using Bitcoin.
Financial Advantages of Using Bitcoin
Decentralized Transactions Promote Transparency and Security
One of Bitcoin’s core features is its decentralized nature. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers worldwide. This transparency ensures that all transactions are verifiable and tamper-proof, significantly reducing fraud risks. Unlike traditional banking systems that rely on centralized authorities, Bitcoin operates without intermediaries—meaning users have direct control over their funds.
Lower Transaction Fees for Cross-Border Payments
Traditional international money transfers often involve hefty fees charged by banks or remittance services. In contrast, Bitcoin transactions typically incur lower costs because they bypass middlemen and currency conversion fees. This efficiency makes it especially attractive for cross-border payments or remittances where high fees can eat into transferred amounts.
24/7 Market Accessibility
Unlike stock markets or banking hours limited to specific times during weekdays, Bitcoin markets operate around the clock—24 hours a day, seven days a week. This continuous trading cycle allows users to make transactions whenever needed without waiting for market openings or closures—a significant advantage for businesses requiring quick payments or individuals managing urgent transfers.
Hedge Against Inflation Due to Limited Supply
Bitcoin’s supply cap is set at 21 million coins—a feature embedded in its protocol from inception. Unlike fiat currencies subject to inflation through monetary policy decisions like printing more money, Bitcoin's scarcity provides an inherent hedge against inflationary pressures prevalent in traditional currencies such as USD or EUR.
Investment Opportunities with Bitcoin
Portfolio Diversification Benefits
Adding Bitcoin to an investment portfolio can enhance diversification because its price movements often do not correlate directly with stocks or bonds. This means that when traditional assets decline in value due to economic downturns or market shocks, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin may behave differently—potentially reducing overall portfolio risk.
High Return Potential Amid Volatility
Bitcoin has demonstrated remarkable growth over recent years despite significant price swings along the way. Its volatility presents opportunities for traders seeking high returns; however, this also entails substantial risks if investments are not managed carefully. Investors should approach with caution and consider long-term strategies aligned with their risk tolerance.
Growing Institutional Adoption
Increasing interest from institutional investors—including hedge funds, asset managers, and even some governments—has contributed to higher demand for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Such adoption signals mainstream acceptance and could drive prices upward as demand continues rising over time.
Role in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
While DeFi primarily revolves around Ethereum-based projects; nonetheless, many platforms incorporate aspects involving BTC through wrapped tokens (like WBTC). These integrations enable users to access lending protocols and other financial services without relying on traditional banks—further expanding how individuals can leverage their cryptocurrency holdings within innovative financial ecosystems.
Recent Developments Shaping the Future of Cryptocurrency Use
Recent initiatives highlight growing global interest in blockchain technology:
- The Maldives government announced plans for an $8.8 billion blockchain hub aimed at easing national debt while attracting foreign investment.
- Major firms such as Cantor Fitzgerald partnered with Tether and SoftBank launched Twenty One Capital—a firm holding over 42 thousand bitcoins making it one of the largest bitcoin treasuries globally.
- Companies like XTRA Blockchain Inc., along with Web Blockchain Media Inc., continue gaining attention due to their market activity reflecting broader industry trends toward mainstream adoption.
These developments suggest increasing institutional involvement which could stabilize prices while fostering innovation across sectors utilizing blockchain technology.
Risks Associated With Using Cryptocurrency
Despite numerous benefits—and ongoing positive developments—it’s essential also to recognize potential pitfalls:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear regulations across jurisdictions creates volatility risks; future legal changes might restrict usage.
- Security Concerns: While blockchain itself remains secure due to cryptography principles; individual exchanges or wallets remain vulnerable targets for hacking.
- Market Volatility: Rapid price fluctuations mean investments could lead either toward substantial gains—or losses if not carefully managed by informed investors.
Understanding these challenges helps ensure responsible use aligned with personal risk appetite while staying informed about evolving regulatory landscapes worldwide.
How To Make Informed Decisions About Using Bitcoins
Before incorporating bitcoin into your finances:
- Conduct thorough research about current market conditions.2.. Stay updated on regulatory changes affecting cryptocurrency use locally and globally.3.. Use reputable wallets/exchanges emphasizing security measures.4.. Consider long-term versus short-term investment goals based on your risk tolerance.5.. Diversify holdings within different asset classes alongside cryptocurrencies.
By doing so you align your strategy with best practices rooted in transparency—and build confidence as you navigate this dynamic digital economy.
In summary, using bitcoin offers compelling advantages—from lower transaction costs and enhanced security features to diversification opportunities within investment portfolios—and reflects ongoing technological innovations shaping modern finance today.However, potential risks related to regulation stability and security breaches underscore why cautious engagement backed by continuous education remains vital.As adoption accelerates globally—with new projects emerging regularly—the landscape continues evolving rapidly. Staying informed will empower you both as a user seeking efficient payment methods—and as an investor aiming for strategic growth amid this transformative era_.


Lo
2025-05-06 08:16
What are the potential benefits of using Bitcoin?
What Are the Potential Benefits of Using Bitcoin?
Bitcoin has revolutionized the financial landscape since its creation in 2009. As the first decentralized cryptocurrency, it offers a range of advantages that appeal to individual users, investors, and even governments. Understanding these benefits can help you determine whether integrating Bitcoin into your financial activities makes sense. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the key benefits associated with using Bitcoin.
Financial Advantages of Using Bitcoin
Decentralized Transactions Promote Transparency and Security
One of Bitcoin’s core features is its decentralized nature. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers worldwide. This transparency ensures that all transactions are verifiable and tamper-proof, significantly reducing fraud risks. Unlike traditional banking systems that rely on centralized authorities, Bitcoin operates without intermediaries—meaning users have direct control over their funds.
Lower Transaction Fees for Cross-Border Payments
Traditional international money transfers often involve hefty fees charged by banks or remittance services. In contrast, Bitcoin transactions typically incur lower costs because they bypass middlemen and currency conversion fees. This efficiency makes it especially attractive for cross-border payments or remittances where high fees can eat into transferred amounts.
24/7 Market Accessibility
Unlike stock markets or banking hours limited to specific times during weekdays, Bitcoin markets operate around the clock—24 hours a day, seven days a week. This continuous trading cycle allows users to make transactions whenever needed without waiting for market openings or closures—a significant advantage for businesses requiring quick payments or individuals managing urgent transfers.
Hedge Against Inflation Due to Limited Supply
Bitcoin’s supply cap is set at 21 million coins—a feature embedded in its protocol from inception. Unlike fiat currencies subject to inflation through monetary policy decisions like printing more money, Bitcoin's scarcity provides an inherent hedge against inflationary pressures prevalent in traditional currencies such as USD or EUR.
Investment Opportunities with Bitcoin
Portfolio Diversification Benefits
Adding Bitcoin to an investment portfolio can enhance diversification because its price movements often do not correlate directly with stocks or bonds. This means that when traditional assets decline in value due to economic downturns or market shocks, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin may behave differently—potentially reducing overall portfolio risk.
High Return Potential Amid Volatility
Bitcoin has demonstrated remarkable growth over recent years despite significant price swings along the way. Its volatility presents opportunities for traders seeking high returns; however, this also entails substantial risks if investments are not managed carefully. Investors should approach with caution and consider long-term strategies aligned with their risk tolerance.
Growing Institutional Adoption
Increasing interest from institutional investors—including hedge funds, asset managers, and even some governments—has contributed to higher demand for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Such adoption signals mainstream acceptance and could drive prices upward as demand continues rising over time.
Role in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
While DeFi primarily revolves around Ethereum-based projects; nonetheless, many platforms incorporate aspects involving BTC through wrapped tokens (like WBTC). These integrations enable users to access lending protocols and other financial services without relying on traditional banks—further expanding how individuals can leverage their cryptocurrency holdings within innovative financial ecosystems.
Recent Developments Shaping the Future of Cryptocurrency Use
Recent initiatives highlight growing global interest in blockchain technology:
- The Maldives government announced plans for an $8.8 billion blockchain hub aimed at easing national debt while attracting foreign investment.
- Major firms such as Cantor Fitzgerald partnered with Tether and SoftBank launched Twenty One Capital—a firm holding over 42 thousand bitcoins making it one of the largest bitcoin treasuries globally.
- Companies like XTRA Blockchain Inc., along with Web Blockchain Media Inc., continue gaining attention due to their market activity reflecting broader industry trends toward mainstream adoption.
These developments suggest increasing institutional involvement which could stabilize prices while fostering innovation across sectors utilizing blockchain technology.
Risks Associated With Using Cryptocurrency
Despite numerous benefits—and ongoing positive developments—it’s essential also to recognize potential pitfalls:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Lack of clear regulations across jurisdictions creates volatility risks; future legal changes might restrict usage.
- Security Concerns: While blockchain itself remains secure due to cryptography principles; individual exchanges or wallets remain vulnerable targets for hacking.
- Market Volatility: Rapid price fluctuations mean investments could lead either toward substantial gains—or losses if not carefully managed by informed investors.
Understanding these challenges helps ensure responsible use aligned with personal risk appetite while staying informed about evolving regulatory landscapes worldwide.
How To Make Informed Decisions About Using Bitcoins
Before incorporating bitcoin into your finances:
- Conduct thorough research about current market conditions.2.. Stay updated on regulatory changes affecting cryptocurrency use locally and globally.3.. Use reputable wallets/exchanges emphasizing security measures.4.. Consider long-term versus short-term investment goals based on your risk tolerance.5.. Diversify holdings within different asset classes alongside cryptocurrencies.
By doing so you align your strategy with best practices rooted in transparency—and build confidence as you navigate this dynamic digital economy.
In summary, using bitcoin offers compelling advantages—from lower transaction costs and enhanced security features to diversification opportunities within investment portfolios—and reflects ongoing technological innovations shaping modern finance today.However, potential risks related to regulation stability and security breaches underscore why cautious engagement backed by continuous education remains vital.As adoption accelerates globally—with new projects emerging regularly—the landscape continues evolving rapidly. Staying informed will empower you both as a user seeking efficient payment methods—and as an investor aiming for strategic growth amid this transformative era_.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Crypto Rich — when Bitcoin hits 100k and she’s celebrating 🧮 But your bags didn’t make it. You're calculating exit liquidity that never came 💼 That face says it all 😵


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:08
Crypto Rich 🤑 | Until You Check the Wallet
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Market Trends Influence Altcoin Performance
Understanding how market trends impact altcoins is essential for investors, traders, and enthusiasts navigating the volatile world of cryptocurrencies. Altcoins—any digital currency other than Bitcoin—are particularly sensitive to shifts in broader market conditions. This article explores the key factors that drive altcoin performance, recent developments shaping the landscape, and practical insights into how these trends can influence investment decisions.
The Role of Bitcoin in Shaping Altcoin Markets
Bitcoin remains the dominant force in cryptocurrency markets, often setting the tone for overall sentiment and price movements. When Bitcoin experiences significant gains or declines, it tends to ripple through altcoins due to their high correlation with Bitcoin's price. For instance, on May 22, 2025, Bitcoin hit a record high of $111,878 driven by institutional demand via ETFs. Such surges typically boost investor confidence across the crypto space and lift prices of many altcoins.
Conversely, resistance levels around $106,000 have been observed recently as Bitcoin struggles to break higher. These resistance points can act as psychological barriers that influence trader behavior not only for Bitcoin but also for alternative cryptocurrencies.
This interconnectedness underscores why monitoring Bitcoin’s performance is crucial when assessing potential movements within altcoin markets. A strong upward trend in Bitcoin often signals bullish momentum across various projects; however, if it stalls or declines sharply, many altcoins tend to follow suit.
Market Volatility and Its Impact on Altcoins
Cryptocurrency markets are renowned for their volatility—a characteristic that can lead to rapid price swings within short periods. Such fluctuations are driven by multiple factors including macroeconomic events or geopolitical developments.
For example, recent political announcements like former President Trump’s Federal Reserve pick have introduced uncertainty into financial markets globally. This uncertainty spills over into crypto assets as investors reassess risk appetite amid fluctuating economic outlooks.
Volatility creates both opportunities and risks: while sharp upward moves can generate substantial profits during bullish phases; sudden downturns may cause significant losses if traders are unprepared or overly exposed. For altcoins specifically—many with lower liquidity compared to Bitcoin—the impact of volatility can be even more pronounced due to thinner trading volumes and less mature ecosystems.
Investors should therefore stay informed about macroeconomic indicators such as inflation rates or interest rate changes since these elements heavily influence overall market sentiment and consequently affect altcoin prices.
Mining Industry Challenges Affecting Cryptocurrency Prices
Mining remains a foundational component of blockchain networks like Ethereum (prior to its transition) and others relying on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms. However recent developments highlight challenges faced by miners which indirectly impact broader market dynamics.
In 2025’s first quarter alone, BitFuFu Inc., a major mining service provider reported a net loss of $16.9 million—a stark reversal from previous profitability levels indicating sector-wide difficulties such as rising energy costs or equipment shortages.
Mining woes reduce network security confidence temporarily but also reflect underlying economic pressures that could lead miners either consolidating operations or exiting certain networks altogether—factors which might decrease supply stability for some coins while increasing scarcity-driven value propositions elsewhere.
Furthermore, energy consumption concerns linked with AI technologies surpassing those associated with traditional mining operations add another layer of complexity affecting operational costs globally—a factor influencing profitability margins across different projects impacting their long-term viability and investor perception.
Technological Advancements Drive Market Sentiment
Innovation within blockchain technology continues at a rapid pace—improving scalability (like layer-2 solutions), enhancing security protocols (such as zero-knowledge proofs), or introducing new use cases (DeFi platforms). These technological breakthroughs often serve as catalysts boosting specific altcoin valuations when successfully implemented.
Projects demonstrating strong development progress tend to attract positive investor sentiment because they promise better usability or solve existing issues more efficiently than competitors do. Conversely; delays in technological upgrades may dampen enthusiasm leading to stagnation or decline in respective tokens’ values.
Key Factors Influencing Altcoin Performance:
- Market Sentiment: Positive news cycles foster buying pressure; negative news triggers sell-offs.
- Regulatory Environment: Clearer regulations tend to stabilize markets; restrictive policies may suppress growth.
- Global Economic Conditions: Inflation fears push investors toward digital assets perceived as hedges.
- Technological Innovation: Upgrades improve utility & security attracting new users/investors.
By keeping abreast of technological trends alongside regulatory updates—and understanding how they interplay with macroeconomic factors—market participants can better anticipate potential shifts affecting specific coins’ performance.
The Interplay Between Economic Indicators & Cryptocurrency Markets
Global economic indicators such as inflation rates、interest rates、and GDP growth significantly influence cryptocurrency investments—including altcoins。 During times of economic instability或high inflation,investors often seek alternative assets like cryptocurrencies,which are viewed both as speculative investments和potential hedges。
Interest rate adjustments made by central banks directly affect liquidity levels available for investment activities。 Higher interest rates typically make traditional savings options more attractive,reducing capital flow into riskier assets like cryptos。 Conversely,lower interest rates might encourage increased exposure,driving up prices across various tokens。
Moreover,broader economic health impacts investor confidence:a stable economy fosters steady growth expectations;while recession fears could trigger flight-to-safety behaviors impacting all asset classes—including digital currencies.
How Investor Sentiment Shapes Price Movements
Market sentiment—the collective mood among traders—is perhaps one of the most influential yet unpredictable drivers behind short-term price fluctuations in alts. Positive sentiment fueled by favorable news、adoption milestones、or institutional involvement tends to push prices higher. Negative sentiments arising from regulatory crackdowns、security breaches、or macroeconomic uncertainties exert downward pressure。
Social media platforms、news outlets、and community forums play vital roles here—they rapidly disseminate information that influences perceptions almost instantaneously. As such,monitoring sentiment indicators alongside technical analysis provides valuable insights into potential future movements。
Practical Tips for Navigating Market Trends:
1.Stay updated on major news events affecting cryptocurrencies.2.Follow regulatory developments worldwide.3.Observe technological upgrades announced by project teams.4.Monitor global economic data releases regularly.5.Use social media analytics tools cautiously but consistently.
By integrating these strategies into your research process,你可以更好地理解市场趋势对特定altcoins的潜在影响,从而做出更明智的投资决策。
Final Thoughts: Navigating an Evolving Landscape
The relationship between market trends and altcoin performance is complex yet critical knowledge for anyone involved in cryptocurrency investing today。 From bitcoin’s dominance influencing broader sentiments,到 technological innovations推动项目价值,再到宏观经济环境塑造投资者行为,每个因素都在塑造着市场的未来方向。
Keeping informed about current developments—from record-breaking bitcoin highs和矿业行业挑战,到监管变化和技术进步——能帮助你把握机会,同时规避潜在风险。在这个快速变化的生态系统中,有效分析市场趋势是实现成功投资的重要关键。
By understanding these dynamics deeply rooted in real-world factors,你可以更有信心地应对加密货币市场的波动,实现你的财务目标。


kai
2025-06-09 05:37
How do market trends affect altcoin performance?
How Market Trends Influence Altcoin Performance
Understanding how market trends impact altcoins is essential for investors, traders, and enthusiasts navigating the volatile world of cryptocurrencies. Altcoins—any digital currency other than Bitcoin—are particularly sensitive to shifts in broader market conditions. This article explores the key factors that drive altcoin performance, recent developments shaping the landscape, and practical insights into how these trends can influence investment decisions.
The Role of Bitcoin in Shaping Altcoin Markets
Bitcoin remains the dominant force in cryptocurrency markets, often setting the tone for overall sentiment and price movements. When Bitcoin experiences significant gains or declines, it tends to ripple through altcoins due to their high correlation with Bitcoin's price. For instance, on May 22, 2025, Bitcoin hit a record high of $111,878 driven by institutional demand via ETFs. Such surges typically boost investor confidence across the crypto space and lift prices of many altcoins.
Conversely, resistance levels around $106,000 have been observed recently as Bitcoin struggles to break higher. These resistance points can act as psychological barriers that influence trader behavior not only for Bitcoin but also for alternative cryptocurrencies.
This interconnectedness underscores why monitoring Bitcoin’s performance is crucial when assessing potential movements within altcoin markets. A strong upward trend in Bitcoin often signals bullish momentum across various projects; however, if it stalls or declines sharply, many altcoins tend to follow suit.
Market Volatility and Its Impact on Altcoins
Cryptocurrency markets are renowned for their volatility—a characteristic that can lead to rapid price swings within short periods. Such fluctuations are driven by multiple factors including macroeconomic events or geopolitical developments.
For example, recent political announcements like former President Trump’s Federal Reserve pick have introduced uncertainty into financial markets globally. This uncertainty spills over into crypto assets as investors reassess risk appetite amid fluctuating economic outlooks.
Volatility creates both opportunities and risks: while sharp upward moves can generate substantial profits during bullish phases; sudden downturns may cause significant losses if traders are unprepared or overly exposed. For altcoins specifically—many with lower liquidity compared to Bitcoin—the impact of volatility can be even more pronounced due to thinner trading volumes and less mature ecosystems.
Investors should therefore stay informed about macroeconomic indicators such as inflation rates or interest rate changes since these elements heavily influence overall market sentiment and consequently affect altcoin prices.
Mining Industry Challenges Affecting Cryptocurrency Prices
Mining remains a foundational component of blockchain networks like Ethereum (prior to its transition) and others relying on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms. However recent developments highlight challenges faced by miners which indirectly impact broader market dynamics.
In 2025’s first quarter alone, BitFuFu Inc., a major mining service provider reported a net loss of $16.9 million—a stark reversal from previous profitability levels indicating sector-wide difficulties such as rising energy costs or equipment shortages.
Mining woes reduce network security confidence temporarily but also reflect underlying economic pressures that could lead miners either consolidating operations or exiting certain networks altogether—factors which might decrease supply stability for some coins while increasing scarcity-driven value propositions elsewhere.
Furthermore, energy consumption concerns linked with AI technologies surpassing those associated with traditional mining operations add another layer of complexity affecting operational costs globally—a factor influencing profitability margins across different projects impacting their long-term viability and investor perception.
Technological Advancements Drive Market Sentiment
Innovation within blockchain technology continues at a rapid pace—improving scalability (like layer-2 solutions), enhancing security protocols (such as zero-knowledge proofs), or introducing new use cases (DeFi platforms). These technological breakthroughs often serve as catalysts boosting specific altcoin valuations when successfully implemented.
Projects demonstrating strong development progress tend to attract positive investor sentiment because they promise better usability or solve existing issues more efficiently than competitors do. Conversely; delays in technological upgrades may dampen enthusiasm leading to stagnation or decline in respective tokens’ values.
Key Factors Influencing Altcoin Performance:
- Market Sentiment: Positive news cycles foster buying pressure; negative news triggers sell-offs.
- Regulatory Environment: Clearer regulations tend to stabilize markets; restrictive policies may suppress growth.
- Global Economic Conditions: Inflation fears push investors toward digital assets perceived as hedges.
- Technological Innovation: Upgrades improve utility & security attracting new users/investors.
By keeping abreast of technological trends alongside regulatory updates—and understanding how they interplay with macroeconomic factors—market participants can better anticipate potential shifts affecting specific coins’ performance.
The Interplay Between Economic Indicators & Cryptocurrency Markets
Global economic indicators such as inflation rates、interest rates、and GDP growth significantly influence cryptocurrency investments—including altcoins。 During times of economic instability或high inflation,investors often seek alternative assets like cryptocurrencies,which are viewed both as speculative investments和potential hedges。
Interest rate adjustments made by central banks directly affect liquidity levels available for investment activities。 Higher interest rates typically make traditional savings options more attractive,reducing capital flow into riskier assets like cryptos。 Conversely,lower interest rates might encourage increased exposure,driving up prices across various tokens。
Moreover,broader economic health impacts investor confidence:a stable economy fosters steady growth expectations;while recession fears could trigger flight-to-safety behaviors impacting all asset classes—including digital currencies.
How Investor Sentiment Shapes Price Movements
Market sentiment—the collective mood among traders—is perhaps one of the most influential yet unpredictable drivers behind short-term price fluctuations in alts. Positive sentiment fueled by favorable news、adoption milestones、or institutional involvement tends to push prices higher. Negative sentiments arising from regulatory crackdowns、security breaches、or macroeconomic uncertainties exert downward pressure。
Social media platforms、news outlets、and community forums play vital roles here—they rapidly disseminate information that influences perceptions almost instantaneously. As such,monitoring sentiment indicators alongside technical analysis provides valuable insights into potential future movements。
Practical Tips for Navigating Market Trends:
1.Stay updated on major news events affecting cryptocurrencies.2.Follow regulatory developments worldwide.3.Observe technological upgrades announced by project teams.4.Monitor global economic data releases regularly.5.Use social media analytics tools cautiously but consistently.
By integrating these strategies into your research process,你可以更好地理解市场趋势对特定altcoins的潜在影响,从而做出更明智的投资决策。
Final Thoughts: Navigating an Evolving Landscape
The relationship between market trends and altcoin performance is complex yet critical knowledge for anyone involved in cryptocurrency investing today。 From bitcoin’s dominance influencing broader sentiments,到 technological innovations推动项目价值,再到宏观经济环境塑造投资者行为,每个因素都在塑造着市场的未来方向。
Keeping informed about current developments—from record-breaking bitcoin highs和矿业行业挑战,到监管变化和技术进步——能帮助你把握机会,同时规避潜在风险。在这个快速变化的生态系统中,有效分析市场趋势是实现成功投资的重要关键。
By understanding these dynamics deeply rooted in real-world factors,你可以更有信心地应对加密货币市场的波动,实现你的财务目标。
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Can I Earn Interest on My USDC Holdings?
Earning interest on USDC (USD Coin) has become an attractive option for cryptocurrency investors looking to generate passive income while maintaining stability. As a widely used stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, USDC offers a reliable way to participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional financial services. This article explores the various methods available for earning interest on your USDC holdings, recent market developments, and important considerations for managing associated risks.
Understanding USDC and Its Role in Cryptocurrency
USDC is a stablecoin issued by the Centre consortium, which includes Circle and Coinbase. It is designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the USD, providing stability amid volatile crypto markets. Because of its liquidity and transparency—backed by regular audits—USDC has become popular among traders, institutions, and retail investors alike.
In addition to serving as a medium of exchange or store of value within crypto ecosystems, earning interest on USDC allows holders to maximize their assets without selling or converting into other cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies. This dual utility makes it an appealing component of diversified investment strategies.
Methods for Earning Interest on USDC
There are multiple avenues through which you can earn interest on your stablecoin holdings. Each method varies in terms of risk profile, accessibility, and potential returns:
1. Lending Platforms
Decentralized lending protocols have revolutionized how users earn interest from their crypto assets. These platforms connect lenders with borrowers directly via smart contracts.
Compound: A leading DeFi protocol that enables users to lend their USDC in exchange for COMP tokens as rewards. The platform operates transparently with open-source code.
Aave: Similar to Compound but offering additional features like flash loans; users lend their USDC at variable or fixed rates and receive AAVE tokens as incentives.
Nexo: A centralized platform that provides high-yield savings accounts denominated in fiat currency or cryptocurrencies including USDC; interest is paid regularly without requiring active management from the user.
Lending platforms typically pay out interest daily or weekly based on supply-demand dynamics within each protocol's liquidity pools.
2. Staking Stablecoins
Staking involves locking up your assets in specific protocols that support staking programs designed explicitly for stablecoins like USDC.
For example:
- Circle’s U.S.-based staking program allows users to stake their USDC directly through Circle’s ecosystem.
While less common than traditional staking involving proof-of-stake networks (like Ethereum), these programs often offer predictable returns with minimal risk if managed properly.
3. Yield Farming Strategies
Yield farming entails deploying your USDC into various DeFi protocols—such as liquidity pools—to earn higher yields through complex strategies involving multiple tokens or protocols simultaneously.
This approach can generate substantial returns but comes with increased risks:
- Impermanent loss
- Smart contract vulnerabilities
- Market volatility affecting underlying assets
Yield farmers often move funds across different platforms seeking optimal APYs (Annual Percentage Yields).
4. Traditional Banking Options
Some financial institutions now offer accounts where you can deposit stablecoins like USDC and earn interest similar to savings accounts at banks—but usually at higher rates due to fewer regulatory constraints involved in crypto services compared to traditional banking systems.
However, these options are less widespread and may involve higher fees or minimum deposit requirements compared with DeFi alternatives.
Recent Trends Impacting Interest Rates on Stablecoins
The landscape surrounding earning interests from stablecoins like USDC continues evolving rapidly due to technological advancements and regulatory developments:
Meta’s Exploration of Stablecoin Payments
In May 2025, Meta announced plans exploring integration of stablecoins such as USD Coin into its social media platforms aimed at facilitating cross-border payments among content creators worldwide[1]. Such initiatives could significantly increase demand for stablecoins like USDC—and consequently influence the supply-and-demand dynamics that determine lending rates across DeFi platforms.
Regulatory Environment Changes
Regulatory clarity remains crucial for sustainable growth within this sector:
- In March 2023, SEC officials emphasized the need for clearer rules around digital assets including stablecoins.
Stricter regulations could impact how lending platforms operate—potentially reducing yields if compliance costs rise—or lead some providers out of business altogether if they cannot meet new standards.
Risks Associated With Earning Interest Using Stablecoins
While earning interest offers compelling benefits—including passive income—it also involves notable risks:
Regulatory Risks
Uncertain legal frameworks could restrict access or impose restrictions that limit yield opportunities—for example,regulations targeting unregistered securities offerings might affect certain DeFi products’ legality[2].
Market Volatility
Although-US DC itself remains relatively stable compared with other cryptos—the broader market's volatility influences demand levels:a downturn might reduce borrowing activity leading lenders’ yields lower accordingly[3].
Security Concerns
DeFi protocols are vulnerable:smart contract bugs,hacks,or exploits can result in significant losses—sometimes total loss—in worst-case scenarios[4].
It’s essential always conduct thorough due diligence before engaging with any platform.
Managing Risks When Earning Interest On Your U.S.D.C Holdings
To mitigate potential downsides while maximizing gains:
- Diversify across multiple lending protocols rather than relying solely on one platform.
- Stay informed about regulatory updates affecting digital asset markets.
- Use reputable platforms known for security audits.
- Consider setting stop-loss limits when participating in yield farming activities.
Additionally, understanding each protocol's terms—including lock-up periods & withdrawal conditions—is vital before committing funds.
Final Thoughts: Is Earning Interest On U.S.D.C Worth It?
Earning interest on your USD Coin holdings presents an excellent opportunity within today’s evolving financial landscape—but it requires careful consideration regarding associated risks versus potential rewards. As technology advances alongside increasing institutional adoption—and regulators clarify rules—the environment becomes more conducive yet still unpredictable.
By staying informed about current trends—from Meta's payment initiatives influencing demand—to assessing security measures—you can make smarter decisions aligned with your investment goals while safeguarding your capital against unforeseen challenges.
References
[1] Meta Announces Exploration Into Stablecoin Payments – May 2025
[2] Regulatory Developments Impacting Crypto Lending – March 2023
[3] Market Dynamics Affecting Stablecoin Yields – Ongoing Analysis
[4] Security Risks & Best Practices For DeFi Participation – Industry Reports


kai
2025-05-29 09:13
How can I earn interest on my USDC holdings?
How Can I Earn Interest on My USDC Holdings?
Earning interest on USDC (USD Coin) has become an attractive option for cryptocurrency investors looking to generate passive income while maintaining stability. As a widely used stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, USDC offers a reliable way to participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) and traditional financial services. This article explores the various methods available for earning interest on your USDC holdings, recent market developments, and important considerations for managing associated risks.
Understanding USDC and Its Role in Cryptocurrency
USDC is a stablecoin issued by the Centre consortium, which includes Circle and Coinbase. It is designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the USD, providing stability amid volatile crypto markets. Because of its liquidity and transparency—backed by regular audits—USDC has become popular among traders, institutions, and retail investors alike.
In addition to serving as a medium of exchange or store of value within crypto ecosystems, earning interest on USDC allows holders to maximize their assets without selling or converting into other cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies. This dual utility makes it an appealing component of diversified investment strategies.
Methods for Earning Interest on USDC
There are multiple avenues through which you can earn interest on your stablecoin holdings. Each method varies in terms of risk profile, accessibility, and potential returns:
1. Lending Platforms
Decentralized lending protocols have revolutionized how users earn interest from their crypto assets. These platforms connect lenders with borrowers directly via smart contracts.
Compound: A leading DeFi protocol that enables users to lend their USDC in exchange for COMP tokens as rewards. The platform operates transparently with open-source code.
Aave: Similar to Compound but offering additional features like flash loans; users lend their USDC at variable or fixed rates and receive AAVE tokens as incentives.
Nexo: A centralized platform that provides high-yield savings accounts denominated in fiat currency or cryptocurrencies including USDC; interest is paid regularly without requiring active management from the user.
Lending platforms typically pay out interest daily or weekly based on supply-demand dynamics within each protocol's liquidity pools.
2. Staking Stablecoins
Staking involves locking up your assets in specific protocols that support staking programs designed explicitly for stablecoins like USDC.
For example:
- Circle’s U.S.-based staking program allows users to stake their USDC directly through Circle’s ecosystem.
While less common than traditional staking involving proof-of-stake networks (like Ethereum), these programs often offer predictable returns with minimal risk if managed properly.
3. Yield Farming Strategies
Yield farming entails deploying your USDC into various DeFi protocols—such as liquidity pools—to earn higher yields through complex strategies involving multiple tokens or protocols simultaneously.
This approach can generate substantial returns but comes with increased risks:
- Impermanent loss
- Smart contract vulnerabilities
- Market volatility affecting underlying assets
Yield farmers often move funds across different platforms seeking optimal APYs (Annual Percentage Yields).
4. Traditional Banking Options
Some financial institutions now offer accounts where you can deposit stablecoins like USDC and earn interest similar to savings accounts at banks—but usually at higher rates due to fewer regulatory constraints involved in crypto services compared to traditional banking systems.
However, these options are less widespread and may involve higher fees or minimum deposit requirements compared with DeFi alternatives.
Recent Trends Impacting Interest Rates on Stablecoins
The landscape surrounding earning interests from stablecoins like USDC continues evolving rapidly due to technological advancements and regulatory developments:
Meta’s Exploration of Stablecoin Payments
In May 2025, Meta announced plans exploring integration of stablecoins such as USD Coin into its social media platforms aimed at facilitating cross-border payments among content creators worldwide[1]. Such initiatives could significantly increase demand for stablecoins like USDC—and consequently influence the supply-and-demand dynamics that determine lending rates across DeFi platforms.
Regulatory Environment Changes
Regulatory clarity remains crucial for sustainable growth within this sector:
- In March 2023, SEC officials emphasized the need for clearer rules around digital assets including stablecoins.
Stricter regulations could impact how lending platforms operate—potentially reducing yields if compliance costs rise—or lead some providers out of business altogether if they cannot meet new standards.
Risks Associated With Earning Interest Using Stablecoins
While earning interest offers compelling benefits—including passive income—it also involves notable risks:
Regulatory Risks
Uncertain legal frameworks could restrict access or impose restrictions that limit yield opportunities—for example,regulations targeting unregistered securities offerings might affect certain DeFi products’ legality[2].
Market Volatility
Although-US DC itself remains relatively stable compared with other cryptos—the broader market's volatility influences demand levels:a downturn might reduce borrowing activity leading lenders’ yields lower accordingly[3].
Security Concerns
DeFi protocols are vulnerable:smart contract bugs,hacks,or exploits can result in significant losses—sometimes total loss—in worst-case scenarios[4].
It’s essential always conduct thorough due diligence before engaging with any platform.
Managing Risks When Earning Interest On Your U.S.D.C Holdings
To mitigate potential downsides while maximizing gains:
- Diversify across multiple lending protocols rather than relying solely on one platform.
- Stay informed about regulatory updates affecting digital asset markets.
- Use reputable platforms known for security audits.
- Consider setting stop-loss limits when participating in yield farming activities.
Additionally, understanding each protocol's terms—including lock-up periods & withdrawal conditions—is vital before committing funds.
Final Thoughts: Is Earning Interest On U.S.D.C Worth It?
Earning interest on your USD Coin holdings presents an excellent opportunity within today’s evolving financial landscape—but it requires careful consideration regarding associated risks versus potential rewards. As technology advances alongside increasing institutional adoption—and regulators clarify rules—the environment becomes more conducive yet still unpredictable.
By staying informed about current trends—from Meta's payment initiatives influencing demand—to assessing security measures—you can make smarter decisions aligned with your investment goals while safeguarding your capital against unforeseen challenges.
References
[1] Meta Announces Exploration Into Stablecoin Payments – May 2025
[2] Regulatory Developments Impacting Crypto Lending – March 2023
[3] Market Dynamics Affecting Stablecoin Yields – Ongoing Analysis
[4] Security Risks & Best Practices For DeFi Participation – Industry Reports
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Web3 and How Does It Relate to Cryptocurrency?
Web3 is transforming the way we think about the internet, shifting from centralized platforms to a more decentralized digital landscape. This evolution is closely linked with cryptocurrencies, which serve as both a technological backbone and an economic incentive within this new ecosystem. Understanding Web3’s core principles, its connection to blockchain technology, and recent developments can help users grasp its potential impact on digital privacy, security, and financial systems.
The Origins of Web3: A Brief Historical Perspective
The concept of Web3 was first introduced by Gavin Wood in 2014 through his paper "Envisioning Blockchain and Web 3.0: From Visions to Reality." Initially rooted in blockchain innovation, the idea gained momentum around 2017 with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These technologies demonstrated that decentralized networks could facilitate secure transactions without traditional intermediaries—paving the way for a more user-empowered internet.
Over time, developers envisioned a web where users would have control over their data rather than relying on large corporations that often monetize personal information. This shift aimed at creating an internet that is not only more transparent but also resistant to censorship or single points of failure.
Core Principles Driving Web3 Development
Web3's foundation rests on several key principles designed to foster decentralization and user sovereignty:
Decentralization: Moving away from centralized servers controlled by corporations toward distributed networks ensures greater resilience against outages or malicious attacks.
Blockchain Technology: Serving as the backbone for transparency and security, blockchains record transactions across multiple nodes without a single point of failure.
Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automate agreements based on predefined rules—eliminating middlemen in processes like payments or voting.
User Control Over Data: Unlike traditional web models where data is stored centrally by service providers, Web3 aims for individuals to own their digital assets securely.
These principles collectively aim at creating an internet environment where users are empowered rather than exploited—a fundamental shift aligned with broader trends toward data privacy and digital rights.
How Blockchain Technology Powers Web3
At its core, blockchain technology underpins many aspects of Web3 by providing a secure ledger system that records all transactions transparently across multiple computers (or nodes). Unlike traditional databases managed by central authorities such as banks or tech giants, blockchains are inherently tamper-proof due to cryptographic validation mechanisms.
There are different types of blockchains:
Public Blockchains, like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH), allow anyone to participate openly.
Private Blockchains, used mainly within organizations for internal purposes.
Hybrid Blockchains, combining features from both public and private variants for specific use cases.
This diversity enables various applications—from peer-to-peer payments via cryptocurrencies to complex smart contract deployments—making blockchain versatile enough for numerous industries beyond finance.
Cryptocurrencies as Integral Components
Cryptocurrencies are often considered synonymous with blockchain but serve specific roles within the broader ecosystem. They function as digital currencies secured through cryptography; most operate independently from governments or central banks. Notable examples include Bitcoin (BTC), regarded as digital gold; Ethereum (ETH), which facilitates smart contracts; Litecoin (LTC); Monero (XMR) emphasizing privacy features; among others.
In addition to serving as mediums of exchange or stores of value, cryptocurrencies incentivize network participation—for example, miners validating transactions receive tokens in return. This mechanism encourages decentralization while fostering innovation across sectors such as gaming, supply chain management—and increasingly within decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offering lending & borrowing services without traditional banks.
Recent Trends Shaping the Future of Web3
The development trajectory over recent years highlights significant advancements:
Upgrades Like Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum’s transition towards Ethereum 2.0 aims at improving scalability through sharding techniques combined with proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms—reducing energy consumption while increasing transaction throughput significantly.
Interoperability Protocols
Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos focus on enabling different blockchains’ communication—creating interconnected ecosystems rather than isolated networks—which enhances usability across diverse platforms while fostering innovation through cross-chain applications.
Growth in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi has emerged rapidly within the Web3 space by offering financial services such as lending pools , asset swaps , yield farming , all built atop smart contract protocols without reliance on centralized institutions like banks or brokers .
Market Dynamics & Regulatory Environment
As cryptocurrency markets experience high volatility driven by investor sentiment—and regulatory landscapes evolve globally—the sector faces challenges related mostly to legal clarity around taxation , anti-money laundering measures , consumer protection policies . While some countries adopt favorable policies encouraging adoption , others impose restrictions that could slow growth prospects temporarily .
Security remains paramount despite blockchain’s inherent robustness; hacking incidents targeting exchanges remind stakeholders about ongoing risks requiring continuous improvements in cybersecurity practices . Scalability issues also persist — current infrastructure sometimes struggles under heavy load — prompting ongoing research into solutions capable of supporting mass adoption .
The Impact Of Web3 On Digital Privacy And User Empowerment
One primary motivation behind developing Web3 is enhancing individual control over personal data—a stark contrast against conventional models where tech giants monetize user information extensively. With decentralized identity solutions (DID)and encrypted storage options,users can decide what information they share online. Moreover,blockchain-based voting systems promise increased transparency in governance processes.*
This paradigm shift aligns well with growing concerns about surveillance capitalism*, data breaches*,and censorship. As these technologies mature,users will likely enjoy safer browsing experienceswith greater ownership over their online identities.*
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption Of Web3 Technologies
Despite promising developments,several hurdles remain before mainstream acceptance becomes commonplace:
Scalability: Current infrastructure needs enhancement so it can handle millions—or billions—of users efficiently.*
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide grapple with establishing clear frameworks regulating crypto assets and decentralized applications.
Security Risks: While blockchain itself offers strong security features,smart contract bugsand exchange hacks pose ongoing threats.*
4.User Experience: Simplifying interfacesto make onboarding accessible even for non-tech-savvy audiences remains critical.
Addressing these issues requires collaborative efforts among developers,s regulators,and industry stakeholders committedto building resilient,decentralized systems accessible worldwide.*
By understanding what constitutes Web3—and how it integrates cryptocurrency—you gain insight into one of today’s most transformative technological shifts.* As this space continues evolving—with innovations addressing current limitations—the potential benefits include enhanced privacy,safety,and democratized access—to our increasingly digitized world.*


kai
2025-05-22 19:21
What is "Web3," and how does it relate to cryptocurrency?
What Is Web3 and How Does It Relate to Cryptocurrency?
Web3 is transforming the way we think about the internet, shifting from centralized platforms to a more decentralized digital landscape. This evolution is closely linked with cryptocurrencies, which serve as both a technological backbone and an economic incentive within this new ecosystem. Understanding Web3’s core principles, its connection to blockchain technology, and recent developments can help users grasp its potential impact on digital privacy, security, and financial systems.
The Origins of Web3: A Brief Historical Perspective
The concept of Web3 was first introduced by Gavin Wood in 2014 through his paper "Envisioning Blockchain and Web 3.0: From Visions to Reality." Initially rooted in blockchain innovation, the idea gained momentum around 2017 with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These technologies demonstrated that decentralized networks could facilitate secure transactions without traditional intermediaries—paving the way for a more user-empowered internet.
Over time, developers envisioned a web where users would have control over their data rather than relying on large corporations that often monetize personal information. This shift aimed at creating an internet that is not only more transparent but also resistant to censorship or single points of failure.
Core Principles Driving Web3 Development
Web3's foundation rests on several key principles designed to foster decentralization and user sovereignty:
Decentralization: Moving away from centralized servers controlled by corporations toward distributed networks ensures greater resilience against outages or malicious attacks.
Blockchain Technology: Serving as the backbone for transparency and security, blockchains record transactions across multiple nodes without a single point of failure.
Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automate agreements based on predefined rules—eliminating middlemen in processes like payments or voting.
User Control Over Data: Unlike traditional web models where data is stored centrally by service providers, Web3 aims for individuals to own their digital assets securely.
These principles collectively aim at creating an internet environment where users are empowered rather than exploited—a fundamental shift aligned with broader trends toward data privacy and digital rights.
How Blockchain Technology Powers Web3
At its core, blockchain technology underpins many aspects of Web3 by providing a secure ledger system that records all transactions transparently across multiple computers (or nodes). Unlike traditional databases managed by central authorities such as banks or tech giants, blockchains are inherently tamper-proof due to cryptographic validation mechanisms.
There are different types of blockchains:
Public Blockchains, like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH), allow anyone to participate openly.
Private Blockchains, used mainly within organizations for internal purposes.
Hybrid Blockchains, combining features from both public and private variants for specific use cases.
This diversity enables various applications—from peer-to-peer payments via cryptocurrencies to complex smart contract deployments—making blockchain versatile enough for numerous industries beyond finance.
Cryptocurrencies as Integral Components
Cryptocurrencies are often considered synonymous with blockchain but serve specific roles within the broader ecosystem. They function as digital currencies secured through cryptography; most operate independently from governments or central banks. Notable examples include Bitcoin (BTC), regarded as digital gold; Ethereum (ETH), which facilitates smart contracts; Litecoin (LTC); Monero (XMR) emphasizing privacy features; among others.
In addition to serving as mediums of exchange or stores of value, cryptocurrencies incentivize network participation—for example, miners validating transactions receive tokens in return. This mechanism encourages decentralization while fostering innovation across sectors such as gaming, supply chain management—and increasingly within decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offering lending & borrowing services without traditional banks.
Recent Trends Shaping the Future of Web3
The development trajectory over recent years highlights significant advancements:
Upgrades Like Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum’s transition towards Ethereum 2.0 aims at improving scalability through sharding techniques combined with proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms—reducing energy consumption while increasing transaction throughput significantly.
Interoperability Protocols
Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos focus on enabling different blockchains’ communication—creating interconnected ecosystems rather than isolated networks—which enhances usability across diverse platforms while fostering innovation through cross-chain applications.
Growth in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi has emerged rapidly within the Web3 space by offering financial services such as lending pools , asset swaps , yield farming , all built atop smart contract protocols without reliance on centralized institutions like banks or brokers .
Market Dynamics & Regulatory Environment
As cryptocurrency markets experience high volatility driven by investor sentiment—and regulatory landscapes evolve globally—the sector faces challenges related mostly to legal clarity around taxation , anti-money laundering measures , consumer protection policies . While some countries adopt favorable policies encouraging adoption , others impose restrictions that could slow growth prospects temporarily .
Security remains paramount despite blockchain’s inherent robustness; hacking incidents targeting exchanges remind stakeholders about ongoing risks requiring continuous improvements in cybersecurity practices . Scalability issues also persist — current infrastructure sometimes struggles under heavy load — prompting ongoing research into solutions capable of supporting mass adoption .
The Impact Of Web3 On Digital Privacy And User Empowerment
One primary motivation behind developing Web3 is enhancing individual control over personal data—a stark contrast against conventional models where tech giants monetize user information extensively. With decentralized identity solutions (DID)and encrypted storage options,users can decide what information they share online. Moreover,blockchain-based voting systems promise increased transparency in governance processes.*
This paradigm shift aligns well with growing concerns about surveillance capitalism*, data breaches*,and censorship. As these technologies mature,users will likely enjoy safer browsing experienceswith greater ownership over their online identities.*
Challenges Facing Widespread Adoption Of Web3 Technologies
Despite promising developments,several hurdles remain before mainstream acceptance becomes commonplace:
Scalability: Current infrastructure needs enhancement so it can handle millions—or billions—of users efficiently.*
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide grapple with establishing clear frameworks regulating crypto assets and decentralized applications.
Security Risks: While blockchain itself offers strong security features,smart contract bugsand exchange hacks pose ongoing threats.*
4.User Experience: Simplifying interfacesto make onboarding accessible even for non-tech-savvy audiences remains critical.
Addressing these issues requires collaborative efforts among developers,s regulators,and industry stakeholders committedto building resilient,decentralized systems accessible worldwide.*
By understanding what constitutes Web3—and how it integrates cryptocurrency—you gain insight into one of today’s most transformative technological shifts.* As this space continues evolving—with innovations addressing current limitations—the potential benefits include enhanced privacy,safety,and democratized access—to our increasingly digitized world.*
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Altcoins and Why Did They Emerge After Bitcoin?
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the financial landscape, with Bitcoin (BTC) leading the charge as the first decentralized digital currency. However, as Bitcoin gained popularity and market dominance, a wave of alternative cryptocurrencies—commonly known as altcoins—began to surface. Understanding what altcoins are and why they emerged after Bitcoin is essential for investors, developers, and enthusiasts looking to navigate the evolving crypto ecosystem.
Defining Altcoins: The Alternative Cryptocurrencies
Altcoins refer to any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. The term "altcoin" was first introduced around 2011 when numerous new digital assets started appearing on various exchanges. These coins aim to improve upon or differentiate themselves from Bitcoin by offering unique features such as faster transaction speeds, lower fees, enhanced privacy protocols, or specialized use cases.
Unlike Bitcoin’s primary focus on being a decentralized store of value and medium of exchange, many altcoins serve specific functions within their ecosystems—ranging from enabling smart contracts to facilitating decentralized finance (DeFi) applications or supporting non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Examples include Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), Ripple (XRP), Chainlink (LINK), and Binance Coin (BNB).
Why Did Altcoins Emerge After Bitcoin?
The emergence of altcoins was driven by multiple factors rooted in technological innovation, investor demand for diversification, community initiatives, and evolving use cases within blockchain technology.
Diversification in Investment Portfolios
As early investors recognized the potential risks associated with holding only Bitcoin due to its volatility or market saturation, they sought alternatives that could offer higher returns or different risk profiles. Creating new cryptocurrencies allowed investors to diversify their holdings across various projects tailored for specific purposes.
Technological Innovation & Development
Bitcoin's underlying blockchain inspired developers worldwide to experiment with new features that could enhance performance or security. For instance:
- Faster Transaction Times: Litecoin was created in 2011 aiming for quicker confirmation times.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Some altcoins focused on reducing costs associated with transfers.
- Enhanced Privacy & Security: Projects like Monero prioritized user anonymity through advanced cryptographic techniques.
- Smart Contracts & Decentralized Applications: Ethereum introduced programmable contracts that opened up possibilities beyond simple transactions.
This wave of innovation led entrepreneurs and communities to develop coins suited for particular niches within blockchain technology.
Community Driven Projects & Governance Models
Many altcoins originated from community-led initiatives seeking more democratic governance structures compared to Bitcoin’s relatively centralized development process. These projects often aimed at implementing specific governance models or addressing perceived limitations in existing cryptocurrencies.
For example:
- Namecoin introduced decentralized domain registration.
- Peercoin incorporated proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms.
Such projects reflected a desire among communities for greater control over project direction while exploring diverse use cases beyond mere currency transfer.
Early Milestones in Altcoin Development
The history of altcoins begins with pioneering projects that set foundational standards:
Namecoin: Launched in April 2011; it pioneered decentralized domain name registration using blockchain technology.
Litecoin: Introduced later in October 2011; designed as “silver” compared to Bitcoin’s “gold,” focusing on faster transactions and lower fees helped establish it as one of the first successful alternative coins.
By 2013, the number of available cryptocurrencies had surged past 100 listings across exchanges worldwide—a clear sign of growing interest among developers and users alike.
The launch of Ethereum in 2015 marked a turning point by introducing smart contracts—a revolutionary feature enabling programmable agreements—and creating an entire ecosystem supporting dApps (decentralized applications). This development significantly expanded what cryptocurrencies could achieve beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers.
Recent Trends Fueling Altcoin Growth
In recent years—particularly between 2020 and 2023—the popularity of altcoins skyrocketed due mainly to innovations like DeFi platforms and NFTs. These developments attracted mainstream attention toward alternative tokens such as Binance Coin (BNB), Chainlink (LINK), Polkadot (DOT), along with stablecoins like USDT and USDC which provide stability amid volatile markets.
Decentralized finance has democratized access to financial services such as lending, borrowing,and trading without traditional intermediaries—all powered by various alttokens facilitating these activities efficiently across blockchains globally.
Challenges Facing Altcoin Ecosystem
Despite their growth potential ,altcoind face several hurdles that can impact their long-term viability:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrency activities due partlyto concerns over money launderingand fraud.The lackof uniform regulations creates uncertaintyfor investorsand developers alike,and some jurisdictions may impose bansor restrictionson certain typesof tokens .
Market Volatility
Altcoinstypically exhibit high price swings drivenby speculative tradingand market sentiment.This volatility can leadto significant gains but also substantial losses,making them less suitableas stable investments comparedto traditional assets .
Security Risks
As newer technologies,manyaltcoinnetworksare vulnerableto hacking incidentsor smart contract exploits.Security breaches have resultedin losssof fundsand diminished trustin certain projects .
Competition & Market Saturation
With thousandsof different coinsavailable,the competitionis fierce.Manyprojects strugglefor adoptionor funding,resultingin consolidationwhere weaker ones fade awayor get absorbedby stronger competitors .
Navigating an Evolving Landscape
Understanding why altcoins emerged after bitcoin helps clarify their role within broader financial systems.They offer innovative solutions tailored toward diverse needs—from privacy enhancements,to complex financial instruments—and foster community-driven development models . However ,investors should remain cautious given regulatory uncertainties ,market volatility ,security vulnerabilities,and intense competition . Staying informed about ongoing developments is crucialfor making sound decisions amid this dynamic environment.
Keywords: what are altcoins | reasons for emergence | cryptocurrency diversification | blockchain innovation | DeFi tokens | NFT platforms | crypto regulation challenges


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-22 09:00
What are altcoins and why did they emerge after Bitcoin (BTC)?
What Are Altcoins and Why Did They Emerge After Bitcoin?
Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the financial landscape, with Bitcoin (BTC) leading the charge as the first decentralized digital currency. However, as Bitcoin gained popularity and market dominance, a wave of alternative cryptocurrencies—commonly known as altcoins—began to surface. Understanding what altcoins are and why they emerged after Bitcoin is essential for investors, developers, and enthusiasts looking to navigate the evolving crypto ecosystem.
Defining Altcoins: The Alternative Cryptocurrencies
Altcoins refer to any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. The term "altcoin" was first introduced around 2011 when numerous new digital assets started appearing on various exchanges. These coins aim to improve upon or differentiate themselves from Bitcoin by offering unique features such as faster transaction speeds, lower fees, enhanced privacy protocols, or specialized use cases.
Unlike Bitcoin’s primary focus on being a decentralized store of value and medium of exchange, many altcoins serve specific functions within their ecosystems—ranging from enabling smart contracts to facilitating decentralized finance (DeFi) applications or supporting non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Examples include Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), Ripple (XRP), Chainlink (LINK), and Binance Coin (BNB).
Why Did Altcoins Emerge After Bitcoin?
The emergence of altcoins was driven by multiple factors rooted in technological innovation, investor demand for diversification, community initiatives, and evolving use cases within blockchain technology.
Diversification in Investment Portfolios
As early investors recognized the potential risks associated with holding only Bitcoin due to its volatility or market saturation, they sought alternatives that could offer higher returns or different risk profiles. Creating new cryptocurrencies allowed investors to diversify their holdings across various projects tailored for specific purposes.
Technological Innovation & Development
Bitcoin's underlying blockchain inspired developers worldwide to experiment with new features that could enhance performance or security. For instance:
- Faster Transaction Times: Litecoin was created in 2011 aiming for quicker confirmation times.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Some altcoins focused on reducing costs associated with transfers.
- Enhanced Privacy & Security: Projects like Monero prioritized user anonymity through advanced cryptographic techniques.
- Smart Contracts & Decentralized Applications: Ethereum introduced programmable contracts that opened up possibilities beyond simple transactions.
This wave of innovation led entrepreneurs and communities to develop coins suited for particular niches within blockchain technology.
Community Driven Projects & Governance Models
Many altcoins originated from community-led initiatives seeking more democratic governance structures compared to Bitcoin’s relatively centralized development process. These projects often aimed at implementing specific governance models or addressing perceived limitations in existing cryptocurrencies.
For example:
- Namecoin introduced decentralized domain registration.
- Peercoin incorporated proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms.
Such projects reflected a desire among communities for greater control over project direction while exploring diverse use cases beyond mere currency transfer.
Early Milestones in Altcoin Development
The history of altcoins begins with pioneering projects that set foundational standards:
Namecoin: Launched in April 2011; it pioneered decentralized domain name registration using blockchain technology.
Litecoin: Introduced later in October 2011; designed as “silver” compared to Bitcoin’s “gold,” focusing on faster transactions and lower fees helped establish it as one of the first successful alternative coins.
By 2013, the number of available cryptocurrencies had surged past 100 listings across exchanges worldwide—a clear sign of growing interest among developers and users alike.
The launch of Ethereum in 2015 marked a turning point by introducing smart contracts—a revolutionary feature enabling programmable agreements—and creating an entire ecosystem supporting dApps (decentralized applications). This development significantly expanded what cryptocurrencies could achieve beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers.
Recent Trends Fueling Altcoin Growth
In recent years—particularly between 2020 and 2023—the popularity of altcoins skyrocketed due mainly to innovations like DeFi platforms and NFTs. These developments attracted mainstream attention toward alternative tokens such as Binance Coin (BNB), Chainlink (LINK), Polkadot (DOT), along with stablecoins like USDT and USDC which provide stability amid volatile markets.
Decentralized finance has democratized access to financial services such as lending, borrowing,and trading without traditional intermediaries—all powered by various alttokens facilitating these activities efficiently across blockchains globally.
Challenges Facing Altcoin Ecosystem
Despite their growth potential ,altcoind face several hurdles that can impact their long-term viability:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Governments worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing cryptocurrency activities due partlyto concerns over money launderingand fraud.The lackof uniform regulations creates uncertaintyfor investorsand developers alike,and some jurisdictions may impose bansor restrictionson certain typesof tokens .
Market Volatility
Altcoinstypically exhibit high price swings drivenby speculative tradingand market sentiment.This volatility can leadto significant gains but also substantial losses,making them less suitableas stable investments comparedto traditional assets .
Security Risks
As newer technologies,manyaltcoinnetworksare vulnerableto hacking incidentsor smart contract exploits.Security breaches have resultedin losssof fundsand diminished trustin certain projects .
Competition & Market Saturation
With thousandsof different coinsavailable,the competitionis fierce.Manyprojects strugglefor adoptionor funding,resultingin consolidationwhere weaker ones fade awayor get absorbedby stronger competitors .
Navigating an Evolving Landscape
Understanding why altcoins emerged after bitcoin helps clarify their role within broader financial systems.They offer innovative solutions tailored toward diverse needs—from privacy enhancements,to complex financial instruments—and foster community-driven development models . However ,investors should remain cautious given regulatory uncertainties ,market volatility ,security vulnerabilities,and intense competition . Staying informed about ongoing developments is crucialfor making sound decisions amid this dynamic environment.
Keywords: what are altcoins | reasons for emergence | cryptocurrency diversification | blockchain innovation | DeFi tokens | NFT platforms | crypto regulation challenges
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is a Renko Chart?
Renko charts are a distinctive type of technical analysis tool used by traders to visualize price movements in financial markets, including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional charts such as candlestick or line charts that display data over time, Renko charts focus solely on the magnitude of price changes. This unique approach helps traders filter out market noise and identify clear trends more effectively.
At its core, a Renko chart consists of bricks or boxes that are plotted based on specific price movement thresholds rather than time intervals. Each brick appears only when the price moves beyond a predetermined amount—called the brick size—either upward or downward. This means that if the market remains relatively stable within certain ranges, no new bricks will be formed until significant movement occurs. As a result, Renko charts emphasize meaningful shifts in market direction rather than short-term fluctuations.
This characteristic makes them particularly popular among traders seeking to simplify complex data and focus on long-term trend identification. By removing minor price oscillations that often clutter traditional charts, Renko tools provide clearer signals for entry and exit points in trading strategies.
How Do Renko Charts Work?
Understanding how Renko charts function requires grasping their construction principles. Each brick represents an equal amount of price movement—say $1 or $5—set according to the trader’s preference based on their risk appetite and trading style. When prices move upward beyond the last brick's top edge by this set amount, a new upward brick is added; similarly, if prices decline below the previous brick's bottom edge by this threshold, a downward brick appears.
The process ignores time entirely: whether prices move quickly or slowly doesn't influence when bricks are formed; only whether they surpass these predefined thresholds matters. This approach results in blocks aligned vertically without gaps along the x-axis (which does not represent time), creating an easy-to-interpret visual pattern highlighting trend directions.
Because each brick’s size can be customized—from small increments like $1 for short-term trades to larger ones like $10 for longer-term analysis—it offers flexibility tailored to individual trading strategies and asset volatility levels.
Advantages of Using Renko Charts
One primary benefit of employing Renko charts lies in their ability to reduce market noise significantly. Traditional candlestick or bar charts often display many minor fluctuations that can obscure overall trends; these "whipsaws" may lead traders astray with false signals. In contrast, since bricks only form after substantial movements surpassing set thresholds, traders gain cleaner visual cues about genuine trend directions.
Another advantage is enhanced visual clarity: patterns such as support/resistance levels, breakouts, double tops/bottoms become more apparent when viewed through this simplified lens. The straightforward structure allows both novice and experienced traders to quickly interpret potential trade setups without being overwhelmed by extraneous data points.
Furthermore, because users can adjust Brick Size according to their preferred timeframe or asset volatility—for example choosing smaller sizes for volatile cryptocurrencies—they gain control over sensitivity levels within their analysis framework.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite these benefits, there are notable limitations associated with Renko charting techniques that users should consider carefully before integrating them into their trading routines.
Firstly—and perhaps most critically—the absence of a time axis means it’s difficult to determine precisely when certain events occur within real-time markets. For day traders who rely heavily on timing precision for executing quick trades (scalping), this lack of temporal context could hinder decision-making processes.
Secondly—and relatedly—the subjective nature of setting Brick Size introduces variability among different analysts viewing identical data sets: one trader might choose larger bricks leading to fewer signals but smoother trends; another might prefer smaller sizes resulting in more frequent signals but increased noise sensitivity. Such differences can cause discrepancies in interpretation unless standardized guidelines are followed diligently across teams or communities sharing insights online.
Lastly—and importantly—the filtering effect might cause some short-term opportunities to be overlooked if they don't meet threshold criteria initially set by users’ parameters—a potential downside especially during highly volatile periods where rapid swings could generate valuable profit chances if captured timely through other analytical methods alongside Renko tools.
Practical Applications & Trading Strategies
Renko charts have found widespread use across various markets due primarily to their simplicity and effectiveness at trend detection:
- Trend Following: Traders often use them as primary indicators for identifying sustained directional moves.
- Breakout Trading: Clear breakout points emerge from pattern formations like triangles or channels visible on Bricks.
- Reversal Signals: Reversal patterns such as double tops/bottoms become easier discernible once noise is minimized.
Many practitioners combine renown technical indicators—including moving averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), MACD—with reno-based visuals for confirmation purposes before executing trades — enhancing robustness against false signals inherent in single-indicator approaches.
Recent Trends & Adoption
In recent years notably within cryptocurrency markets—which tend toward high volatility—Renko charting has gained popularity among retail investors seeking clearer insights amid chaotic price action environments . Many advanced trading platforms now incorporate customizable reno tools directly into their suite offerings enabling seamless integration with other technical indicators .
Online communities dedicated specifically towards technical analysis frequently discuss best practices involving reno setups—sharing templates optimized for different assets—and strategies designed around breakout confirmation combined with volume analysis . These developments reflect growing recognition of Reno’s utility beyond traditional equities into fast-moving digital assets.
Risks & Considerations When Using Renko Charts
While advantageous features make Renovation appealing , overreliance poses risks:
- Traders may overlook important short-term opportunities due solely to threshold settings filtering out smaller movements.
- Subjectivity involved in selecting Brick Sizes could lead analysts down divergent paths even analyzing identical data sets.
- Lack of temporal information complicates precise timing decisions essential during rapid-market conditions typical with scalping strategies .
Therefore , it remains crucial for users combining Renovation with other analytical methods—including volume studies , oscillators , fundamental news—to mitigate potential blind spots .
Final Thoughts
Renko charts serve as powerful tools offering unique perspectives focused on significant market moves rather than fleeting fluctuations tied strictly to clock timeframes . Their abilityto clarify complex trends makes them invaluable components within comprehensive technical analysis frameworks—but they should complement rather than replace traditional methods given inherent limitations regarding timing precisionand subjective parameter choices . Proper understanding coupled with disciplined application ensures maximum benefit from incorporating Renovation into your overall strategy toolbox.
Note: Always tailor your use case based on your specific asset class volatility profileand risk management preferences while experimenting with different Brick Sizes until optimal settings are identified.


kai
2025-05-19 03:43
What is Renko Chart?
What is a Renko Chart?
Renko charts are a distinctive type of technical analysis tool used by traders to visualize price movements in financial markets, including stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional charts such as candlestick or line charts that display data over time, Renko charts focus solely on the magnitude of price changes. This unique approach helps traders filter out market noise and identify clear trends more effectively.
At its core, a Renko chart consists of bricks or boxes that are plotted based on specific price movement thresholds rather than time intervals. Each brick appears only when the price moves beyond a predetermined amount—called the brick size—either upward or downward. This means that if the market remains relatively stable within certain ranges, no new bricks will be formed until significant movement occurs. As a result, Renko charts emphasize meaningful shifts in market direction rather than short-term fluctuations.
This characteristic makes them particularly popular among traders seeking to simplify complex data and focus on long-term trend identification. By removing minor price oscillations that often clutter traditional charts, Renko tools provide clearer signals for entry and exit points in trading strategies.
How Do Renko Charts Work?
Understanding how Renko charts function requires grasping their construction principles. Each brick represents an equal amount of price movement—say $1 or $5—set according to the trader’s preference based on their risk appetite and trading style. When prices move upward beyond the last brick's top edge by this set amount, a new upward brick is added; similarly, if prices decline below the previous brick's bottom edge by this threshold, a downward brick appears.
The process ignores time entirely: whether prices move quickly or slowly doesn't influence when bricks are formed; only whether they surpass these predefined thresholds matters. This approach results in blocks aligned vertically without gaps along the x-axis (which does not represent time), creating an easy-to-interpret visual pattern highlighting trend directions.
Because each brick’s size can be customized—from small increments like $1 for short-term trades to larger ones like $10 for longer-term analysis—it offers flexibility tailored to individual trading strategies and asset volatility levels.
Advantages of Using Renko Charts
One primary benefit of employing Renko charts lies in their ability to reduce market noise significantly. Traditional candlestick or bar charts often display many minor fluctuations that can obscure overall trends; these "whipsaws" may lead traders astray with false signals. In contrast, since bricks only form after substantial movements surpassing set thresholds, traders gain cleaner visual cues about genuine trend directions.
Another advantage is enhanced visual clarity: patterns such as support/resistance levels, breakouts, double tops/bottoms become more apparent when viewed through this simplified lens. The straightforward structure allows both novice and experienced traders to quickly interpret potential trade setups without being overwhelmed by extraneous data points.
Furthermore, because users can adjust Brick Size according to their preferred timeframe or asset volatility—for example choosing smaller sizes for volatile cryptocurrencies—they gain control over sensitivity levels within their analysis framework.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite these benefits, there are notable limitations associated with Renko charting techniques that users should consider carefully before integrating them into their trading routines.
Firstly—and perhaps most critically—the absence of a time axis means it’s difficult to determine precisely when certain events occur within real-time markets. For day traders who rely heavily on timing precision for executing quick trades (scalping), this lack of temporal context could hinder decision-making processes.
Secondly—and relatedly—the subjective nature of setting Brick Size introduces variability among different analysts viewing identical data sets: one trader might choose larger bricks leading to fewer signals but smoother trends; another might prefer smaller sizes resulting in more frequent signals but increased noise sensitivity. Such differences can cause discrepancies in interpretation unless standardized guidelines are followed diligently across teams or communities sharing insights online.
Lastly—and importantly—the filtering effect might cause some short-term opportunities to be overlooked if they don't meet threshold criteria initially set by users’ parameters—a potential downside especially during highly volatile periods where rapid swings could generate valuable profit chances if captured timely through other analytical methods alongside Renko tools.
Practical Applications & Trading Strategies
Renko charts have found widespread use across various markets due primarily to their simplicity and effectiveness at trend detection:
- Trend Following: Traders often use them as primary indicators for identifying sustained directional moves.
- Breakout Trading: Clear breakout points emerge from pattern formations like triangles or channels visible on Bricks.
- Reversal Signals: Reversal patterns such as double tops/bottoms become easier discernible once noise is minimized.
Many practitioners combine renown technical indicators—including moving averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), MACD—with reno-based visuals for confirmation purposes before executing trades — enhancing robustness against false signals inherent in single-indicator approaches.
Recent Trends & Adoption
In recent years notably within cryptocurrency markets—which tend toward high volatility—Renko charting has gained popularity among retail investors seeking clearer insights amid chaotic price action environments . Many advanced trading platforms now incorporate customizable reno tools directly into their suite offerings enabling seamless integration with other technical indicators .
Online communities dedicated specifically towards technical analysis frequently discuss best practices involving reno setups—sharing templates optimized for different assets—and strategies designed around breakout confirmation combined with volume analysis . These developments reflect growing recognition of Reno’s utility beyond traditional equities into fast-moving digital assets.
Risks & Considerations When Using Renko Charts
While advantageous features make Renovation appealing , overreliance poses risks:
- Traders may overlook important short-term opportunities due solely to threshold settings filtering out smaller movements.
- Subjectivity involved in selecting Brick Sizes could lead analysts down divergent paths even analyzing identical data sets.
- Lack of temporal information complicates precise timing decisions essential during rapid-market conditions typical with scalping strategies .
Therefore , it remains crucial for users combining Renovation with other analytical methods—including volume studies , oscillators , fundamental news—to mitigate potential blind spots .
Final Thoughts
Renko charts serve as powerful tools offering unique perspectives focused on significant market moves rather than fleeting fluctuations tied strictly to clock timeframes . Their abilityto clarify complex trends makes them invaluable components within comprehensive technical analysis frameworks—but they should complement rather than replace traditional methods given inherent limitations regarding timing precisionand subjective parameter choices . Proper understanding coupled with disciplined application ensures maximum benefit from incorporating Renovation into your overall strategy toolbox.
Note: Always tailor your use case based on your specific asset class volatility profileand risk management preferences while experimenting with different Brick Sizes until optimal settings are identified.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are MEV Bots and How Do They Extract Value?
Understanding MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) in Blockchain
MEV, or Maximal Extractable Value, refers to the additional profit that miners or validators can extract from blockchain transactions beyond standard block rewards and fees. In the context of decentralized finance (DeFi), MEV bots are specialized software programs designed to identify and capitalize on opportunities within blockchain networks—particularly on platforms like Ethereum—to maximize their earnings. These bots operate by analyzing transaction data, smart contract states, and network conditions to execute strategic actions that generate extra value.
The concept of MEV has gained prominence because it highlights how certain actors can influence transaction ordering for financial gain. While miners traditionally prioritized transactions based on gas fees, MEV bots go a step further by actively manipulating transaction sequences to their advantage. This practice raises important questions about fairness, network security, and market integrity within decentralized ecosystems.
How Do MEV Bots Work?
MEV bots employ sophisticated algorithms that scan blockchain mempools—the pool of pending transactions—and smart contract states for profitable opportunities. Once identified, these bots execute specific strategies such as frontrunning or transaction reordering to extract maximum value.
Key Strategies Used by MEV Bots
Frontrunning Transactions: This involves detecting high-value trades or arbitrage opportunities before they are confirmed in a block. The bot then submits its own transaction with a higher gas fee so it gets processed first—allowing it to buy assets at lower prices before the original trade executes.
Gas Price Manipulation: By increasing the gas price offered for their transactions, MEV bots can incentivize miners or validators to prioritize their actions over others'. This ensures they secure favorable execution orderings.
Transaction Reordering: Some advanced bots reorder pending transactions within a block after they've been submitted but before final confirmation. This allows them to optimize profit extraction—for example, executing arbitrage trades between different exchanges or protocols based on real-time price discrepancies.
Exploiting Smart Contract Logic
Smart contracts often contain complex conditional logic that can be exploited if understood correctly. For instance, during liquidity provision or token swaps in DeFi protocols like Uniswap or SushiSwap, small timing advantages can lead to significant gains when executed via automated scripts—these are precisely what many MEV bots target.
Recent Developments Impacting MEV Bot Operations
The evolution of Ethereum’s protocol upgrades has influenced how MEV bots operate:
Ethereum's London Hard Fork & EIP-1559: Implemented in August 2021, this upgrade introduced a new fee mechanism aimed at making gas costs more predictable and reducing spam attacks. While beneficial for regular users by lowering costs during high congestion periods, it also changed how profitable some arbitrage strategies could be for MEV bots.
Emergence of Arbitrage Opportunities: As DeFi protocols grow more complex with multiple exchanges offering slightly different prices for assets—a phenomenon known as price discrepancies—MEV bots increasingly exploit these gaps through arbitrage trading across platforms.
Regulatory Attention: Governments and regulatory bodies have started scrutinizing activities related to blockchain manipulation—including those carried out by MEV robots—as concerns about market fairness intensify.
Risks Associated With Mev Bots
While these automated systems enable significant profit generation for operators—they also introduce several risks:
Network Congestion
The rapid execution of multiple high-gas transactions by numerous MEV bot operators can congest networks like Ethereum during peak times. Increased congestion leads not only to higher transaction fees but also slower confirmation times affecting all users’ experience.
Market Manipulation
Frontrunning capabilities allow certain actors using these tools to gain unfair advantages over regular traders—potentially leading toward market manipulation scenarios where prices are distorted due to strategic order placements rather than genuine supply-demand dynamics.
Security Concerns
Complexity in deploying effective yet secure bot algorithms means vulnerabilities may exist within the codebase itself; malicious actors could exploit poorly secured systems leading either directly—or indirectly—to financial losses across participants involved in DeFi activities.
The Future Outlook of Mev Bots
As DeFi continues expanding rapidly—with innovations such as layer 2 scaling solutions—the landscape around Maximal Extractable Value is expectedly evolving too:
Developers are working on solutions like Flashbots—a research organization dedicated specifically toward mitigating negative impacts caused by Mev extraction while still allowing legitimate use cases.
Protocol-level changes aim at reducing front-running possibilities—for example through randomized transaction ordering mechanisms—that make exploitation harder without compromising decentralization principles.
Regulatory frameworks may emerge globally requiring transparency around bot operations; this could influence how future versions of blockchain networks handle Maximal Extractable Value activities altogether.
Understanding how these developments unfold will be crucial both for developers designing fairer protocols and traders seeking safer environments free from manipulative practices associated with aggressive automation tools like MevBots.
By grasping what makes up an MEV bot’s operation—from its core strategies such as frontrunning and reordering—to its broader implications on network health and market fairness—you gain insight into one of the most dynamic aspects shaping modern blockchain ecosystems today. As technology advances alongside regulatory efforts worldwide, ongoing dialogue remains essential in balancing innovation with integrity within decentralized finance markets.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-14 11:41
What are MEV bots and how do they extract value?
What Are MEV Bots and How Do They Extract Value?
Understanding MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) in Blockchain
MEV, or Maximal Extractable Value, refers to the additional profit that miners or validators can extract from blockchain transactions beyond standard block rewards and fees. In the context of decentralized finance (DeFi), MEV bots are specialized software programs designed to identify and capitalize on opportunities within blockchain networks—particularly on platforms like Ethereum—to maximize their earnings. These bots operate by analyzing transaction data, smart contract states, and network conditions to execute strategic actions that generate extra value.
The concept of MEV has gained prominence because it highlights how certain actors can influence transaction ordering for financial gain. While miners traditionally prioritized transactions based on gas fees, MEV bots go a step further by actively manipulating transaction sequences to their advantage. This practice raises important questions about fairness, network security, and market integrity within decentralized ecosystems.
How Do MEV Bots Work?
MEV bots employ sophisticated algorithms that scan blockchain mempools—the pool of pending transactions—and smart contract states for profitable opportunities. Once identified, these bots execute specific strategies such as frontrunning or transaction reordering to extract maximum value.
Key Strategies Used by MEV Bots
Frontrunning Transactions: This involves detecting high-value trades or arbitrage opportunities before they are confirmed in a block. The bot then submits its own transaction with a higher gas fee so it gets processed first—allowing it to buy assets at lower prices before the original trade executes.
Gas Price Manipulation: By increasing the gas price offered for their transactions, MEV bots can incentivize miners or validators to prioritize their actions over others'. This ensures they secure favorable execution orderings.
Transaction Reordering: Some advanced bots reorder pending transactions within a block after they've been submitted but before final confirmation. This allows them to optimize profit extraction—for example, executing arbitrage trades between different exchanges or protocols based on real-time price discrepancies.
Exploiting Smart Contract Logic
Smart contracts often contain complex conditional logic that can be exploited if understood correctly. For instance, during liquidity provision or token swaps in DeFi protocols like Uniswap or SushiSwap, small timing advantages can lead to significant gains when executed via automated scripts—these are precisely what many MEV bots target.
Recent Developments Impacting MEV Bot Operations
The evolution of Ethereum’s protocol upgrades has influenced how MEV bots operate:
Ethereum's London Hard Fork & EIP-1559: Implemented in August 2021, this upgrade introduced a new fee mechanism aimed at making gas costs more predictable and reducing spam attacks. While beneficial for regular users by lowering costs during high congestion periods, it also changed how profitable some arbitrage strategies could be for MEV bots.
Emergence of Arbitrage Opportunities: As DeFi protocols grow more complex with multiple exchanges offering slightly different prices for assets—a phenomenon known as price discrepancies—MEV bots increasingly exploit these gaps through arbitrage trading across platforms.
Regulatory Attention: Governments and regulatory bodies have started scrutinizing activities related to blockchain manipulation—including those carried out by MEV robots—as concerns about market fairness intensify.
Risks Associated With Mev Bots
While these automated systems enable significant profit generation for operators—they also introduce several risks:
Network Congestion
The rapid execution of multiple high-gas transactions by numerous MEV bot operators can congest networks like Ethereum during peak times. Increased congestion leads not only to higher transaction fees but also slower confirmation times affecting all users’ experience.
Market Manipulation
Frontrunning capabilities allow certain actors using these tools to gain unfair advantages over regular traders—potentially leading toward market manipulation scenarios where prices are distorted due to strategic order placements rather than genuine supply-demand dynamics.
Security Concerns
Complexity in deploying effective yet secure bot algorithms means vulnerabilities may exist within the codebase itself; malicious actors could exploit poorly secured systems leading either directly—or indirectly—to financial losses across participants involved in DeFi activities.
The Future Outlook of Mev Bots
As DeFi continues expanding rapidly—with innovations such as layer 2 scaling solutions—the landscape around Maximal Extractable Value is expectedly evolving too:
Developers are working on solutions like Flashbots—a research organization dedicated specifically toward mitigating negative impacts caused by Mev extraction while still allowing legitimate use cases.
Protocol-level changes aim at reducing front-running possibilities—for example through randomized transaction ordering mechanisms—that make exploitation harder without compromising decentralization principles.
Regulatory frameworks may emerge globally requiring transparency around bot operations; this could influence how future versions of blockchain networks handle Maximal Extractable Value activities altogether.
Understanding how these developments unfold will be crucial both for developers designing fairer protocols and traders seeking safer environments free from manipulative practices associated with aggressive automation tools like MevBots.
By grasping what makes up an MEV bot’s operation—from its core strategies such as frontrunning and reordering—to its broader implications on network health and market fairness—you gain insight into one of the most dynamic aspects shaping modern blockchain ecosystems today. As technology advances alongside regulatory efforts worldwide, ongoing dialogue remains essential in balancing innovation with integrity within decentralized finance markets.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Memecoins Gain Traction Despite Having No Utility?
Understanding the Popularity of Memecoins in Cryptocurrency Markets
Memecoins have become a notable phenomenon within the cryptocurrency landscape, attracting widespread attention despite their lack of inherent utility. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, memecoins are primarily driven by community support, social media hype, and speculative trading rather than technological innovation or real-world applications. This raises an important question: how do these coins manage to gain significant traction and even reach impressive market valuations without offering practical use cases?
The Power of Community and Social Media Influence
One of the primary factors behind the rapid rise of memecoins is their ability to mobilize communities online. Platforms like Twitter, Reddit, TikTok, and Discord serve as hubs where enthusiasts share memes, news updates, and hype around specific coins like Dogecoin (DOGE) or Shiba Inu (SHIB). These communities often develop a sense of identity and belonging that fuels ongoing engagement.
Celebrity endorsements also play a crucial role in amplifying memecoin popularity. When high-profile figures publicly endorse or mention certain coins—such as Elon Musk’s tweets about DOGE—they can trigger massive price surges almost instantaneously. Such endorsements act as social proof that attracts new investors eager to capitalize on potential gains.
Market Sentiment Drives Speculative Investment
Since memecoins lack fundamental value propositions—like utility functions or technological advantages—their prices are predominantly influenced by market sentiment rather than intrinsic worth. Investors often buy memecoins with the hope that they can sell at higher prices later—a classic example of speculative trading.
This speculative nature leads to extreme volatility; prices can skyrocket during periods of hype but also plummet rapidly when enthusiasm wanes or negative news emerges. The fear-of-missing-out (FOMO) effect further accelerates buying activity during bullish phases.
Hype Cycles and Viral Trends
Memecoin popularity is frequently fueled by viral trends on social media platforms where memes spread rapidly across audiences worldwide. These viral moments create short-term demand spikes that push prices upward regardless of any underlying utility—or lack thereof.
For example:
- Meme-based campaigns
- Influencer promotions
- Community-driven challenges
All contribute to creating buzz around specific tokens temporarily elevating their market value before corrections occur.
Speculative Trading Strategies & FOMO Effect
Many retail investors are attracted to memecoins because they offer quick profit opportunities through short-term trading strategies such as day trading or swing trading based on hype cycles. The allure lies in low entry barriers—many memecoins have low per-token prices—and the potential for exponential gains during bull runs driven by social media momentum.
However, this approach carries significant risks due to high volatility; traders may experience substantial losses if market sentiment shifts unexpectedly.
Regulatory Environment & Market Dynamics
Despite their popularity among retail investors, memecoins operate within an uncertain regulatory landscape globally. Authorities are increasingly scrutinizing these assets for potential manipulation schemes or fraudulent activities—especially those resembling Ponzi schemes where early investors profit at others’ expense.
Regulatory crackdowns can lead to sudden drops in valuation and increased skepticism from institutional players who typically prefer assets with clear utility frameworks and compliance standards.
Environmental Considerations Impacting Traction
Some critics highlight environmental concerns related to energy-intensive mining processes associated with certain cryptocurrencies—even if many memecoin projects utilize less resource-heavy mechanisms compared to proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin. Nonetheless, environmental debates influence public perception which indirectly affects investor confidence in some cases.
Why Do Investors Still Support Memecoins?
Despite lacking tangible utility features such as smart contract capabilities or real-world applications like payments processing—which characterize more established cryptocurrencies—memecoin supporters remain optimistic due to several reasons:
- Community Loyalty: Strong online communities foster loyalty beyond financial motives.
- Speculative Gains: Potential for quick profits motivates traders.
- Cultural Relevance: Memes resonate culturally across diverse audiences.
- Low Entry Barriers: Affordable initial investment encourages participation from new users.
These factors combine into a self-reinforcing cycle: community engagement fuels hype which drives price increases attracting more participants seeking similar gains—all despite limited functional value underpinning these assets.
Monitoring Future Trends in Memecoin Adoption
As awareness grows about both risks and opportunities associated with memcoins—and regulatory scrutiny intensifies—their future trajectory remains uncertain yet intriguing for market observers:
- Will mainstream adoption increase through integration into payment systems?
- Could innovative tokenomics sustain long-term interest?
- How will regulatory measures shape their development?
Investors should approach this space cautiously while recognizing its unique blend of entertainment-driven speculation intertwined with genuine community passion.
Key Takeaways
Memecoins gain traction mainly through community support fueled by social media trends rather than intrinsic utility.
Celebrity endorsements significantly amplify visibility but do not guarantee long-term sustainability.
Market sentiment heavily influences price fluctuations due to their speculative nature.
Viral memes create short-lived demand spikes that propel prices temporarily upward.
Regulatory uncertainty poses risks but has yet to dampen overall enthusiasm significantly.
Understanding why people invest in meme-based cryptocurrencies despite no practical use highlights broader themes about investor psychology—including FOMO—and demonstrates how digital culture shapes modern financial markets.
By recognizing these dynamics alongside ongoing developments within regulation and technology sectors, stakeholders can better navigate this volatile yet fascinating segment of cryptocurrency markets while making informed decisions aligned with risk tolerance levels.
Keywords: how do memecoins gain traction?, meme coin popularity reasons?, cryptocurrency hype cycles?, social media influence on crypto investing?, retail investor behavior crypto


Lo
2025-05-09 20:06
How do memecoins gain traction despite having no utility?
How Do Memecoins Gain Traction Despite Having No Utility?
Understanding the Popularity of Memecoins in Cryptocurrency Markets
Memecoins have become a notable phenomenon within the cryptocurrency landscape, attracting widespread attention despite their lack of inherent utility. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, memecoins are primarily driven by community support, social media hype, and speculative trading rather than technological innovation or real-world applications. This raises an important question: how do these coins manage to gain significant traction and even reach impressive market valuations without offering practical use cases?
The Power of Community and Social Media Influence
One of the primary factors behind the rapid rise of memecoins is their ability to mobilize communities online. Platforms like Twitter, Reddit, TikTok, and Discord serve as hubs where enthusiasts share memes, news updates, and hype around specific coins like Dogecoin (DOGE) or Shiba Inu (SHIB). These communities often develop a sense of identity and belonging that fuels ongoing engagement.
Celebrity endorsements also play a crucial role in amplifying memecoin popularity. When high-profile figures publicly endorse or mention certain coins—such as Elon Musk’s tweets about DOGE—they can trigger massive price surges almost instantaneously. Such endorsements act as social proof that attracts new investors eager to capitalize on potential gains.
Market Sentiment Drives Speculative Investment
Since memecoins lack fundamental value propositions—like utility functions or technological advantages—their prices are predominantly influenced by market sentiment rather than intrinsic worth. Investors often buy memecoins with the hope that they can sell at higher prices later—a classic example of speculative trading.
This speculative nature leads to extreme volatility; prices can skyrocket during periods of hype but also plummet rapidly when enthusiasm wanes or negative news emerges. The fear-of-missing-out (FOMO) effect further accelerates buying activity during bullish phases.
Hype Cycles and Viral Trends
Memecoin popularity is frequently fueled by viral trends on social media platforms where memes spread rapidly across audiences worldwide. These viral moments create short-term demand spikes that push prices upward regardless of any underlying utility—or lack thereof.
For example:
- Meme-based campaigns
- Influencer promotions
- Community-driven challenges
All contribute to creating buzz around specific tokens temporarily elevating their market value before corrections occur.
Speculative Trading Strategies & FOMO Effect
Many retail investors are attracted to memecoins because they offer quick profit opportunities through short-term trading strategies such as day trading or swing trading based on hype cycles. The allure lies in low entry barriers—many memecoins have low per-token prices—and the potential for exponential gains during bull runs driven by social media momentum.
However, this approach carries significant risks due to high volatility; traders may experience substantial losses if market sentiment shifts unexpectedly.
Regulatory Environment & Market Dynamics
Despite their popularity among retail investors, memecoins operate within an uncertain regulatory landscape globally. Authorities are increasingly scrutinizing these assets for potential manipulation schemes or fraudulent activities—especially those resembling Ponzi schemes where early investors profit at others’ expense.
Regulatory crackdowns can lead to sudden drops in valuation and increased skepticism from institutional players who typically prefer assets with clear utility frameworks and compliance standards.
Environmental Considerations Impacting Traction
Some critics highlight environmental concerns related to energy-intensive mining processes associated with certain cryptocurrencies—even if many memecoin projects utilize less resource-heavy mechanisms compared to proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin. Nonetheless, environmental debates influence public perception which indirectly affects investor confidence in some cases.
Why Do Investors Still Support Memecoins?
Despite lacking tangible utility features such as smart contract capabilities or real-world applications like payments processing—which characterize more established cryptocurrencies—memecoin supporters remain optimistic due to several reasons:
- Community Loyalty: Strong online communities foster loyalty beyond financial motives.
- Speculative Gains: Potential for quick profits motivates traders.
- Cultural Relevance: Memes resonate culturally across diverse audiences.
- Low Entry Barriers: Affordable initial investment encourages participation from new users.
These factors combine into a self-reinforcing cycle: community engagement fuels hype which drives price increases attracting more participants seeking similar gains—all despite limited functional value underpinning these assets.
Monitoring Future Trends in Memecoin Adoption
As awareness grows about both risks and opportunities associated with memcoins—and regulatory scrutiny intensifies—their future trajectory remains uncertain yet intriguing for market observers:
- Will mainstream adoption increase through integration into payment systems?
- Could innovative tokenomics sustain long-term interest?
- How will regulatory measures shape their development?
Investors should approach this space cautiously while recognizing its unique blend of entertainment-driven speculation intertwined with genuine community passion.
Key Takeaways
Memecoins gain traction mainly through community support fueled by social media trends rather than intrinsic utility.
Celebrity endorsements significantly amplify visibility but do not guarantee long-term sustainability.
Market sentiment heavily influences price fluctuations due to their speculative nature.
Viral memes create short-lived demand spikes that propel prices temporarily upward.
Regulatory uncertainty poses risks but has yet to dampen overall enthusiasm significantly.
Understanding why people invest in meme-based cryptocurrencies despite no practical use highlights broader themes about investor psychology—including FOMO—and demonstrates how digital culture shapes modern financial markets.
By recognizing these dynamics alongside ongoing developments within regulation and technology sectors, stakeholders can better navigate this volatile yet fascinating segment of cryptocurrency markets while making informed decisions aligned with risk tolerance levels.
Keywords: how do memecoins gain traction?, meme coin popularity reasons?, cryptocurrency hype cycles?, social media influence on crypto investing?, retail investor behavior crypto
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that enhances the protection of online accounts by requiring users to verify their identity through two distinct methods. Unlike traditional password-only systems, 2FA adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly more difficult for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access. This method is especially vital in safeguarding sensitive information and digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies.
In essence, 2FA combines something you know—like a password or PIN—with something you have or are. The secondary factor could be a physical device like a hardware token, an app-generated code, or biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition. By requiring these two different forms of verification, 2FA minimizes the risk posed by stolen passwords and other common attack vectors.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work?
The operation of 2FA involves a straightforward but effective process during user login:
Primary Verification: The user enters their username and password.
Secondary Challenge: If the primary credentials are correct, the system prompts for an additional verification step.
Second Factor Submission: The user provides this second piece of evidence—such as entering a code from an authenticator app or scanning their fingerprint.
This layered approach ensures that even if one factor (like your password) is compromised, unauthorized access remains unlikely without the second factor.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
Different methods exist for implementing 2FA depending on security needs and convenience:
- SMS-Based One-Time Passwords (OTPs): A code sent via SMS to your mobile device that expires after use.
- Authenticator Apps: Applications like Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-sensitive codes on your smartphone without needing internet connectivity.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices such as YubiKey display changing codes when plugged into your computer.
- Biometric Verification: Uses unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial scans for authentication.
Each type offers varying levels of security and usability; choosing the right one depends on individual preferences and threat models.
Why Is 2FA Critical in Cryptocurrency Security?
Cryptocurrency platforms handle high-value assets that are attractive targets for hackers. Implementing robust security measures like 2FA is essential to protect users’ digital wallets from theft and unauthorized transactions.
Protecting Against Common Cyber Threats
Crypto users face several prevalent threats where 2FA plays a crucial role:
Phishing Attacks: Attackers often create fake login pages mimicking legitimate exchanges to steal credentials. While phishing can trick users into revealing passwords, they typically cannot bypass secondary verification steps enabled by 2FA.
Keylogger Malware: Malicious software records keystrokes—including passwords—but cannot intercept OTPs generated by authenticator apps unless malware also compromises those apps directly.
Brute Force Attacks: Repeatedly trying different password combinations becomes less effective when accounts require additional verification steps after multiple failed attempts due to rate limiting enforced by many platforms with integrated 2FA systems.
Regulatory Compliance & User Trust
Many financial institutions now mandate two-factor authentication because it aligns with regulatory standards aimed at protecting customer data and financial transactions. In crypto environments where assets can be worth thousands—or even millions—of dollars per account, employing strong multi-layered defenses builds trust among users while complying with evolving legal requirements.
Recent Innovations in Two-Factor Authentication Technology
Advancements continue shaping how we secure our digital identities through improved convenience and enhanced safety features:
QR Code-Based Setup & Use
Many services now utilize QR codes during setup processes; users scan these with authenticator apps to quickly link their accounts securely without manually entering secret keys—a process reducing setup errors while improving ease-of-use.
Behavioral Biometrics & Passive Authentication
Emerging techniques analyze behavioral patterns—such as typing rhythm or mouse movements—to verify identity passively during interactions without interrupting workflow. Location-based checks also add context-aware layers that detect suspicious activities based on geographic anomalies.
Challenges & Risks in Implementation
Despite technological progress, challenges remain:
- Some users find multi-step setups cumbersome leading to lower adoption rates
- Costs associated with deploying advanced solutions may deter smaller organizations
- Improper implementation can introduce vulnerabilities—for example, SMS interception attacks exploiting weaknesses in cellular networks
Ensuring proper deployment aligned with best practices remains critical for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
Historical Milestones in Two-Factor Authentication Development
Understanding the evolution of 2FA helps appreciate its current significance:
In the late 1970s, Leslie Lamport proposed concepts related to multi-factor authentication within his research papers focusing on secure communication protocols.
During the early-to-mid-2000s, SMS-based OTP systems gained popularity among banks due to widespread mobile phone adoption.
The rise of smartphone applications like Google Authenticator marked a shift toward more secure time-based OTP generation methods around the early-to-mid2010s.
Recently developed biometric options such as facial recognition have become mainstream thanks to improvements in hardware sensors integrated into smartphones.
Implementing Effective Two-Factor Authentication Strategies
For individuals using cryptocurrencies—and organizations managing crypto exchanges—the key lies not only in adopting but also properly configuring robust MFA solutions:
Choose reputable providers offering hardware tokens or trusted authenticator apps over less secure options like SMS alone whenever possible.
Educate yourself about potential vulnerabilities associated with certain methods (e.g., SIM swapping attacks targeting SMS).
Regularly review account activity logs for suspicious behavior indicating possible breaches despite active MFA measures.
By staying informed about technological advancements and best practices surrounding two-factor authentication strategies tailored specifically towards crypto security needs—and maintaining vigilance—you significantly enhance your defenses against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats targeting digital assets today.
This comprehensive overview aims at empowering both individual cryptocurrency holders and institutional stakeholders with clear insights into what makes two-factor authentication indispensable today—and how leveraging its latest innovations can help safeguard valuable digital investments effectively across evolving cybersecurity landscapes


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-22 06:15
What is two-factor authentication (2FA), and why is it essential for crypto security?
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that enhances the protection of online accounts by requiring users to verify their identity through two distinct methods. Unlike traditional password-only systems, 2FA adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly more difficult for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access. This method is especially vital in safeguarding sensitive information and digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies.
In essence, 2FA combines something you know—like a password or PIN—with something you have or are. The secondary factor could be a physical device like a hardware token, an app-generated code, or biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition. By requiring these two different forms of verification, 2FA minimizes the risk posed by stolen passwords and other common attack vectors.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work?
The operation of 2FA involves a straightforward but effective process during user login:
Primary Verification: The user enters their username and password.
Secondary Challenge: If the primary credentials are correct, the system prompts for an additional verification step.
Second Factor Submission: The user provides this second piece of evidence—such as entering a code from an authenticator app or scanning their fingerprint.
This layered approach ensures that even if one factor (like your password) is compromised, unauthorized access remains unlikely without the second factor.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
Different methods exist for implementing 2FA depending on security needs and convenience:
- SMS-Based One-Time Passwords (OTPs): A code sent via SMS to your mobile device that expires after use.
- Authenticator Apps: Applications like Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-sensitive codes on your smartphone without needing internet connectivity.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices such as YubiKey display changing codes when plugged into your computer.
- Biometric Verification: Uses unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial scans for authentication.
Each type offers varying levels of security and usability; choosing the right one depends on individual preferences and threat models.
Why Is 2FA Critical in Cryptocurrency Security?
Cryptocurrency platforms handle high-value assets that are attractive targets for hackers. Implementing robust security measures like 2FA is essential to protect users’ digital wallets from theft and unauthorized transactions.
Protecting Against Common Cyber Threats
Crypto users face several prevalent threats where 2FA plays a crucial role:
Phishing Attacks: Attackers often create fake login pages mimicking legitimate exchanges to steal credentials. While phishing can trick users into revealing passwords, they typically cannot bypass secondary verification steps enabled by 2FA.
Keylogger Malware: Malicious software records keystrokes—including passwords—but cannot intercept OTPs generated by authenticator apps unless malware also compromises those apps directly.
Brute Force Attacks: Repeatedly trying different password combinations becomes less effective when accounts require additional verification steps after multiple failed attempts due to rate limiting enforced by many platforms with integrated 2FA systems.
Regulatory Compliance & User Trust
Many financial institutions now mandate two-factor authentication because it aligns with regulatory standards aimed at protecting customer data and financial transactions. In crypto environments where assets can be worth thousands—or even millions—of dollars per account, employing strong multi-layered defenses builds trust among users while complying with evolving legal requirements.
Recent Innovations in Two-Factor Authentication Technology
Advancements continue shaping how we secure our digital identities through improved convenience and enhanced safety features:
QR Code-Based Setup & Use
Many services now utilize QR codes during setup processes; users scan these with authenticator apps to quickly link their accounts securely without manually entering secret keys—a process reducing setup errors while improving ease-of-use.
Behavioral Biometrics & Passive Authentication
Emerging techniques analyze behavioral patterns—such as typing rhythm or mouse movements—to verify identity passively during interactions without interrupting workflow. Location-based checks also add context-aware layers that detect suspicious activities based on geographic anomalies.
Challenges & Risks in Implementation
Despite technological progress, challenges remain:
- Some users find multi-step setups cumbersome leading to lower adoption rates
- Costs associated with deploying advanced solutions may deter smaller organizations
- Improper implementation can introduce vulnerabilities—for example, SMS interception attacks exploiting weaknesses in cellular networks
Ensuring proper deployment aligned with best practices remains critical for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
Historical Milestones in Two-Factor Authentication Development
Understanding the evolution of 2FA helps appreciate its current significance:
In the late 1970s, Leslie Lamport proposed concepts related to multi-factor authentication within his research papers focusing on secure communication protocols.
During the early-to-mid-2000s, SMS-based OTP systems gained popularity among banks due to widespread mobile phone adoption.
The rise of smartphone applications like Google Authenticator marked a shift toward more secure time-based OTP generation methods around the early-to-mid2010s.
Recently developed biometric options such as facial recognition have become mainstream thanks to improvements in hardware sensors integrated into smartphones.
Implementing Effective Two-Factor Authentication Strategies
For individuals using cryptocurrencies—and organizations managing crypto exchanges—the key lies not only in adopting but also properly configuring robust MFA solutions:
Choose reputable providers offering hardware tokens or trusted authenticator apps over less secure options like SMS alone whenever possible.
Educate yourself about potential vulnerabilities associated with certain methods (e.g., SIM swapping attacks targeting SMS).
Regularly review account activity logs for suspicious behavior indicating possible breaches despite active MFA measures.
By staying informed about technological advancements and best practices surrounding two-factor authentication strategies tailored specifically towards crypto security needs—and maintaining vigilance—you significantly enhance your defenses against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats targeting digital assets today.
This comprehensive overview aims at empowering both individual cryptocurrency holders and institutional stakeholders with clear insights into what makes two-factor authentication indispensable today—and how leveraging its latest innovations can help safeguard valuable digital investments effectively across evolving cybersecurity landscapes
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is VWAP? A Complete Guide for Traders and Investors
Understanding market indicators is essential for making informed trading decisions. One such powerful tool is the Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP). This technical indicator provides a nuanced view of the average price at which a security has traded throughout a specific period, factoring in trade volume. Whether you're involved in stock trading, options, futures, or cryptocurrencies, grasping VWAP can significantly enhance your market analysis.
What Does VWAP Mean?
VWAP stands for Volume-Weighted Average Price. Unlike simple moving averages that consider only price data over time, VWAP incorporates both price and volume data to give a more accurate picture of the market's true average trading price during a session or over a specified period. It essentially answers the question: "At what average price did most of the trading occur today?"
This indicator helps traders identify whether the current market sentiment leans bullish or bearish by comparing current prices with VWAP levels. When prices are above VWAP, it often indicates buying pressure; when below, selling pressure may dominate.
How Is VWAP Calculated?
The calculation of VWAP involves summing up all traded values (price multiplied by volume) and dividing this total by the total traded volume within the chosen timeframe. The formula looks like this:
VWAP = Σ(Price × Volume) / Σ(Volume)In practice, this calculation updates continuously during trading hours as new trades occur. Modern trading platforms automate this process in real-time so traders can access live data without manual computation.
Why Do Traders Use VWAP?
Traders utilize VWAP across various strategies because it offers insights into market behavior that other indicators might miss:
- Market Sentiment Analysis: Comparing current prices to VWAP helps determine if buyers or sellers are dominant.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Since many institutional traders use VWAP as an execution benchmark, its levels often act as support or resistance zones.
- Trade Entry and Exit Points: Buying when prices dip below the VWap or selling when they rise above can optimize trade timing.
- Order Execution Strategy: Large orders executed near or at the day's average price help minimize market impact.
These applications make VWap particularly valuable for day traders aiming for quick profits and institutional investors managing large portfolios.
Practical Applications of VWap
Day Trading
In day trading scenarios where timing is critical, traders monitor how current prices relate to daily Vwap levels to gauge short-term momentum. For example:
- If an asset's price crosses above its intraday Vwap after being below it earlier in the session—this could signal upward momentum.
Swing Trading
Swing traders look at longer-term trends involving multiple days' worth of data:
- Consistent positioning above Vwap suggests an uptrend.
- Conversely, sustained movement below indicates potential downtrends or reversals.
Long-Term Investing
While primarily used in shorter timeframes, some long-term investors incorporate Vwap into their broader analysis framework to confirm trend directions before making significant investment decisions.
Using Support & Resistance with Volkswagen Price Data
One key benefit of using Vwap is its role as dynamic support and resistance level:
During bullish phases where prices stay above Vwap,
- The level acts as support; dips toward it may be seen as buying opportunities.
In bearish markets,
- The same level functions as resistance; rallies toward it could be opportunities to sell or short-sell assets.
This characteristic makes Vwap especially useful during volatile periods where traditional static support/resistance lines might not suffice.
Trend Identification Through Vwap Comparison
By observing how asset prices move relative to their Vwap:
- An upward trending asset typically stays consistently above its Vwap.
- A downward trend shows persistent movement below it.
- Crossovers—where price moves from below to above (or vice versa)—can signal potential trend reversals worth noting for entry/exit points.
Such comparisons assist traders in aligning their strategies with prevailing momentum rather than reacting solely on raw price movements alone.
Limitations & Challenges of Using VWap
Despite its usefulness, there are limitations:
- Market Volatility: During highly volatile periods—such as earnings releases or macroeconomic news—the reliability diminishes because rapid swings distort true sentiment signals.
- Liquidity Concerns: In illiquid markets like certain cryptocurrencies or thinly traded stocks,
- Low volumes can cause erratic shifts in Wvap readings that do not reflect genuine supply/demand dynamics accurately.
- Timeframe Dependency: Different trader goals require different periods (intraday vs daily), so selecting appropriate settings is crucial but sometimes subjective.
Evolution & Modern Trends Surrounding Volkswagen Price Indicator
Since its inception in the 1980s by NYSE traders seeking better execution benchmarks,
the use of Wvap has expanded significantly:
Adoption Across Markets
It’s now widely employed beyond equities—including options contracts,futures markets,and increasingly popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum due to their high volatility profiles.
Integration With Advanced Technologies
Modern platforms leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms alongside real-time Wvap calculations:
- These integrations enable more precise predictions
- Allow dynamic adjustments based on evolving conditions
Regulatory bodies also promote transparency standards encouraging broader adoption among institutional players.
Impact on Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic systems frequently incorporate Wvap metrics within complex models designed for optimal order placement while minimizing slippage—a crucial factor given today's fast-paced electronic markets.
Final Thoughts on Using Volkswagen Weighted Average Price
VWap remains one of those indispensable tools that bridge fundamental insights with technical analysis—helping both novice investors learn about typical trade ranges while empowering experienced professionals with actionable signals based on real-time data flow.
Its ability to adapt across various assets—from stocks through crypto—and integrate seamlessly into automated systems underscores its relevance today more than ever before.
While no indicator guarantees success—especially amid unpredictable volatility—the strategic application of Wvap enhances decision-making processes significantly.
By understanding how Wvap reflects overall market activity—and combining it with other analytical tools—you position yourself better within competitive financial landscapes.
Whether you’re executing quick day trades—or planning longer-term investments—keeping an eye on your security’s volume-weighted average can provide clarity amidst chaos—and guide you toward smarter trades every step along your journey


Lo
2025-05-19 20:46
What's VWAP?
What is VWAP? A Complete Guide for Traders and Investors
Understanding market indicators is essential for making informed trading decisions. One such powerful tool is the Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP). This technical indicator provides a nuanced view of the average price at which a security has traded throughout a specific period, factoring in trade volume. Whether you're involved in stock trading, options, futures, or cryptocurrencies, grasping VWAP can significantly enhance your market analysis.
What Does VWAP Mean?
VWAP stands for Volume-Weighted Average Price. Unlike simple moving averages that consider only price data over time, VWAP incorporates both price and volume data to give a more accurate picture of the market's true average trading price during a session or over a specified period. It essentially answers the question: "At what average price did most of the trading occur today?"
This indicator helps traders identify whether the current market sentiment leans bullish or bearish by comparing current prices with VWAP levels. When prices are above VWAP, it often indicates buying pressure; when below, selling pressure may dominate.
How Is VWAP Calculated?
The calculation of VWAP involves summing up all traded values (price multiplied by volume) and dividing this total by the total traded volume within the chosen timeframe. The formula looks like this:
VWAP = Σ(Price × Volume) / Σ(Volume)In practice, this calculation updates continuously during trading hours as new trades occur. Modern trading platforms automate this process in real-time so traders can access live data without manual computation.
Why Do Traders Use VWAP?
Traders utilize VWAP across various strategies because it offers insights into market behavior that other indicators might miss:
- Market Sentiment Analysis: Comparing current prices to VWAP helps determine if buyers or sellers are dominant.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Since many institutional traders use VWAP as an execution benchmark, its levels often act as support or resistance zones.
- Trade Entry and Exit Points: Buying when prices dip below the VWap or selling when they rise above can optimize trade timing.
- Order Execution Strategy: Large orders executed near or at the day's average price help minimize market impact.
These applications make VWap particularly valuable for day traders aiming for quick profits and institutional investors managing large portfolios.
Practical Applications of VWap
Day Trading
In day trading scenarios where timing is critical, traders monitor how current prices relate to daily Vwap levels to gauge short-term momentum. For example:
- If an asset's price crosses above its intraday Vwap after being below it earlier in the session—this could signal upward momentum.
Swing Trading
Swing traders look at longer-term trends involving multiple days' worth of data:
- Consistent positioning above Vwap suggests an uptrend.
- Conversely, sustained movement below indicates potential downtrends or reversals.
Long-Term Investing
While primarily used in shorter timeframes, some long-term investors incorporate Vwap into their broader analysis framework to confirm trend directions before making significant investment decisions.
Using Support & Resistance with Volkswagen Price Data
One key benefit of using Vwap is its role as dynamic support and resistance level:
During bullish phases where prices stay above Vwap,
- The level acts as support; dips toward it may be seen as buying opportunities.
In bearish markets,
- The same level functions as resistance; rallies toward it could be opportunities to sell or short-sell assets.
This characteristic makes Vwap especially useful during volatile periods where traditional static support/resistance lines might not suffice.
Trend Identification Through Vwap Comparison
By observing how asset prices move relative to their Vwap:
- An upward trending asset typically stays consistently above its Vwap.
- A downward trend shows persistent movement below it.
- Crossovers—where price moves from below to above (or vice versa)—can signal potential trend reversals worth noting for entry/exit points.
Such comparisons assist traders in aligning their strategies with prevailing momentum rather than reacting solely on raw price movements alone.
Limitations & Challenges of Using VWap
Despite its usefulness, there are limitations:
- Market Volatility: During highly volatile periods—such as earnings releases or macroeconomic news—the reliability diminishes because rapid swings distort true sentiment signals.
- Liquidity Concerns: In illiquid markets like certain cryptocurrencies or thinly traded stocks,
- Low volumes can cause erratic shifts in Wvap readings that do not reflect genuine supply/demand dynamics accurately.
- Timeframe Dependency: Different trader goals require different periods (intraday vs daily), so selecting appropriate settings is crucial but sometimes subjective.
Evolution & Modern Trends Surrounding Volkswagen Price Indicator
Since its inception in the 1980s by NYSE traders seeking better execution benchmarks,
the use of Wvap has expanded significantly:
Adoption Across Markets
It’s now widely employed beyond equities—including options contracts,futures markets,and increasingly popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum due to their high volatility profiles.
Integration With Advanced Technologies
Modern platforms leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms alongside real-time Wvap calculations:
- These integrations enable more precise predictions
- Allow dynamic adjustments based on evolving conditions
Regulatory bodies also promote transparency standards encouraging broader adoption among institutional players.
Impact on Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic systems frequently incorporate Wvap metrics within complex models designed for optimal order placement while minimizing slippage—a crucial factor given today's fast-paced electronic markets.
Final Thoughts on Using Volkswagen Weighted Average Price
VWap remains one of those indispensable tools that bridge fundamental insights with technical analysis—helping both novice investors learn about typical trade ranges while empowering experienced professionals with actionable signals based on real-time data flow.
Its ability to adapt across various assets—from stocks through crypto—and integrate seamlessly into automated systems underscores its relevance today more than ever before.
While no indicator guarantees success—especially amid unpredictable volatility—the strategic application of Wvap enhances decision-making processes significantly.
By understanding how Wvap reflects overall market activity—and combining it with other analytical tools—you position yourself better within competitive financial landscapes.
Whether you’re executing quick day trades—or planning longer-term investments—keeping an eye on your security’s volume-weighted average can provide clarity amidst chaos—and guide you toward smarter trades every step along your journey
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is an Earnings Surprise Chart?
An earnings surprise chart is a vital financial visualization tool that helps investors, analysts, and market participants understand how a company's actual earnings per share (EPS) compare to what was expected. This chart provides a clear snapshot of whether a company has exceeded or fallen short of analyst forecasts during earnings reporting periods. By illustrating these deviations, the chart offers insights into company performance and potential future trends in stock prices.
Earnings surprises are significant because they often trigger immediate market reactions. When actual EPS surpasses expectations (a positive surprise), it can lead to stock price increases as investors interpret this as a sign of strong financial health. Conversely, negative surprises—where actual EPS falls below forecasts—may result in declines in stock value due to concerns over the company's prospects.
How Does an Earnings Surprise Chart Work?
The core components of an earnings surprise chart include three key elements:
- Actual EPS: The real earnings per share reported by the company for a specific period.
- Forecasted EPS: The projected earnings per share based on analyst estimates before the report is released.
- Surprise: The numerical difference between actual and forecasted EPS, which can be positive or negative.
Typically presented as bar graphs or line charts, these visuals allow users to quickly assess how well companies are performing relative to expectations over time. A positive deviation indicates better-than-expected performance; negative deviations suggest underperformance.
Interpreting these charts involves understanding market sentiment and investor psychology. Consistent positive surprises often boost investor confidence and may lead to sustained upward momentum in stock prices. Conversely, frequent negative surprises could signal underlying issues within the company or industry challenges.
Why Are Earnings Surprises Important for Investors?
Earnings surprises play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions because they reflect real-time assessments of corporate health versus market expectations. For traders and long-term investors alike, understanding when companies beat or miss estimates helps gauge management effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Moreover, stocks with consistent positive surprises tend to outperform their peers over time due to increased investor trust and perceived growth potential. On the other hand, recurrent negative surprises might prompt reevaluation of valuation models or risk assessments associated with particular stocks.
In addition to influencing individual securities’ prices, widespread patterns of earnings surprises can impact broader indices like the S&P 500 or NASDAQ by shifting overall market sentiment temporarily or sustainably depending on macroeconomic conditions.
Recent Trends in Earnings Surprises (2023)
The 2023 earnings season highlighted notable trends across various sectors:
Technology Sector: Major players such as Apple and Amazon reported higher-than-expected profits driven by robust consumer demand for electronics and cloud services.
Retail Industry: Retail giants like Walmart and Target experienced positive surprises fueled by resilient consumer spending despite economic uncertainties.
These unexpected results contributed significantly to short-term gains for individual stocks but also increased volatility across markets as traders reacted swiftly post-reporting.
Furthermore, recent developments have seen increasing integration between traditional financial metrics like earnings reports and emerging asset classes such as cryptocurrencies. For example:
- During periods when tech firms announced strong quarterly results leading to substantial earning beats, related cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin experienced heightened activity.
This crossover underscores how traditional corporate performance indicators influence broader investment landscapes beyond equities alone—highlighting diversification strategies that blend stocks with digital assets are gaining popularity among savvy investors seeking balanced portfolios.
Impact on Stock Market Dynamics
Earnings surprise data directly influences stock price movements through immediate reactions from traders reacting emotionally or strategically based on new information. Positive surprises typically cause sharp upward swings due to increased buying interest; meanwhile negative ones may trigger sell-offs amid fears about declining profitability.
Market volatility tends also increase around earning report dates because uncertainty about whether results will beat expectations creates rapid trading activity — especially if multiple companies within an index report simultaneously with mixed outcomes. Such fluctuations underscore why monitoring earning surprise charts is essential for active traders aiming at short-term gains while maintaining awareness of overall market stability risks linked with sudden shifts caused by unexpected corporate news releases.
Risks Associated With Overreliance
While tracking earnings surprises offers valuable insights into corporate performance trends—and can inform strategic decision-making—it’s important not to rely solely on this metric for investment choices:
Short-Term Focus Risks: Overemphasizing quarterly results might lead investors away from long-term fundamentals such as sustainable growth strategies or competitive advantages.
Market Manipulation Concerns: Companies might attempt accounting maneuvers aimed at beating estimates temporarily rather than improving genuine operational efficiency—a practice known as "earnings management."
Regulatory Oversight: Regulatory bodies like the SEC continuously monitor disclosures related to earning reports; however, discrepancies still occur which could mislead uninformed investors if they focus only on surprise figures without considering broader context.
Regulatory Environment
To mitigate risks stemming from misleading disclosures tied closely with earning beats/misses:
- The U.S Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) enforces strict guidelines requiring transparency around financial reporting practices.
- International standards such as IFRS aim at harmonizing accounting rules globally so that comparisons across markets remain fairer—and less susceptible manipulation.
How Investors Can Use Earnings Surprise Charts Effectively
For both retail investors seeking informed decisions—and professional analysts aiming at precise forecasting—the key lies in integrating these charts within comprehensive research frameworks:
- Combine historical patterns observed through past surpluses/shortfalls with macroeconomic data
- Analyze sector-specific factors influencing profitability
- Consider qualitative aspects such as management commentary during quarterly calls
- Use technical analysis tools alongside fundamental metrics
By doing so, one enhances their ability not just reactively responding after reports but proactively positioning investments ahead based on anticipated trends indicated by consistent patterns visible through detailed visualizations like earning surprise charts.
Final Thoughts
An understanding of what constitutes an earnings surprise chart unlocks deeper insights into corporate health beyond raw numbers alone—serving both short-term trading strategies and long-term portfolio planning effectively. As markets evolve—with increasing complexity from global economic shifts—the importance of accurately interpreting these visual cues remains paramount for making informed investment choices rooted in transparency standards upheld worldwide.


kai
2025-05-19 07:38
What is Earnings Surprise Chart?
What Is an Earnings Surprise Chart?
An earnings surprise chart is a vital financial visualization tool that helps investors, analysts, and market participants understand how a company's actual earnings per share (EPS) compare to what was expected. This chart provides a clear snapshot of whether a company has exceeded or fallen short of analyst forecasts during earnings reporting periods. By illustrating these deviations, the chart offers insights into company performance and potential future trends in stock prices.
Earnings surprises are significant because they often trigger immediate market reactions. When actual EPS surpasses expectations (a positive surprise), it can lead to stock price increases as investors interpret this as a sign of strong financial health. Conversely, negative surprises—where actual EPS falls below forecasts—may result in declines in stock value due to concerns over the company's prospects.
How Does an Earnings Surprise Chart Work?
The core components of an earnings surprise chart include three key elements:
- Actual EPS: The real earnings per share reported by the company for a specific period.
- Forecasted EPS: The projected earnings per share based on analyst estimates before the report is released.
- Surprise: The numerical difference between actual and forecasted EPS, which can be positive or negative.
Typically presented as bar graphs or line charts, these visuals allow users to quickly assess how well companies are performing relative to expectations over time. A positive deviation indicates better-than-expected performance; negative deviations suggest underperformance.
Interpreting these charts involves understanding market sentiment and investor psychology. Consistent positive surprises often boost investor confidence and may lead to sustained upward momentum in stock prices. Conversely, frequent negative surprises could signal underlying issues within the company or industry challenges.
Why Are Earnings Surprises Important for Investors?
Earnings surprises play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions because they reflect real-time assessments of corporate health versus market expectations. For traders and long-term investors alike, understanding when companies beat or miss estimates helps gauge management effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Moreover, stocks with consistent positive surprises tend to outperform their peers over time due to increased investor trust and perceived growth potential. On the other hand, recurrent negative surprises might prompt reevaluation of valuation models or risk assessments associated with particular stocks.
In addition to influencing individual securities’ prices, widespread patterns of earnings surprises can impact broader indices like the S&P 500 or NASDAQ by shifting overall market sentiment temporarily or sustainably depending on macroeconomic conditions.
Recent Trends in Earnings Surprises (2023)
The 2023 earnings season highlighted notable trends across various sectors:
Technology Sector: Major players such as Apple and Amazon reported higher-than-expected profits driven by robust consumer demand for electronics and cloud services.
Retail Industry: Retail giants like Walmart and Target experienced positive surprises fueled by resilient consumer spending despite economic uncertainties.
These unexpected results contributed significantly to short-term gains for individual stocks but also increased volatility across markets as traders reacted swiftly post-reporting.
Furthermore, recent developments have seen increasing integration between traditional financial metrics like earnings reports and emerging asset classes such as cryptocurrencies. For example:
- During periods when tech firms announced strong quarterly results leading to substantial earning beats, related cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin experienced heightened activity.
This crossover underscores how traditional corporate performance indicators influence broader investment landscapes beyond equities alone—highlighting diversification strategies that blend stocks with digital assets are gaining popularity among savvy investors seeking balanced portfolios.
Impact on Stock Market Dynamics
Earnings surprise data directly influences stock price movements through immediate reactions from traders reacting emotionally or strategically based on new information. Positive surprises typically cause sharp upward swings due to increased buying interest; meanwhile negative ones may trigger sell-offs amid fears about declining profitability.
Market volatility tends also increase around earning report dates because uncertainty about whether results will beat expectations creates rapid trading activity — especially if multiple companies within an index report simultaneously with mixed outcomes. Such fluctuations underscore why monitoring earning surprise charts is essential for active traders aiming at short-term gains while maintaining awareness of overall market stability risks linked with sudden shifts caused by unexpected corporate news releases.
Risks Associated With Overreliance
While tracking earnings surprises offers valuable insights into corporate performance trends—and can inform strategic decision-making—it’s important not to rely solely on this metric for investment choices:
Short-Term Focus Risks: Overemphasizing quarterly results might lead investors away from long-term fundamentals such as sustainable growth strategies or competitive advantages.
Market Manipulation Concerns: Companies might attempt accounting maneuvers aimed at beating estimates temporarily rather than improving genuine operational efficiency—a practice known as "earnings management."
Regulatory Oversight: Regulatory bodies like the SEC continuously monitor disclosures related to earning reports; however, discrepancies still occur which could mislead uninformed investors if they focus only on surprise figures without considering broader context.
Regulatory Environment
To mitigate risks stemming from misleading disclosures tied closely with earning beats/misses:
- The U.S Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) enforces strict guidelines requiring transparency around financial reporting practices.
- International standards such as IFRS aim at harmonizing accounting rules globally so that comparisons across markets remain fairer—and less susceptible manipulation.
How Investors Can Use Earnings Surprise Charts Effectively
For both retail investors seeking informed decisions—and professional analysts aiming at precise forecasting—the key lies in integrating these charts within comprehensive research frameworks:
- Combine historical patterns observed through past surpluses/shortfalls with macroeconomic data
- Analyze sector-specific factors influencing profitability
- Consider qualitative aspects such as management commentary during quarterly calls
- Use technical analysis tools alongside fundamental metrics
By doing so, one enhances their ability not just reactively responding after reports but proactively positioning investments ahead based on anticipated trends indicated by consistent patterns visible through detailed visualizations like earning surprise charts.
Final Thoughts
An understanding of what constitutes an earnings surprise chart unlocks deeper insights into corporate health beyond raw numbers alone—serving both short-term trading strategies and long-term portfolio planning effectively. As markets evolve—with increasing complexity from global economic shifts—the importance of accurately interpreting these visual cues remains paramount for making informed investment choices rooted in transparency standards upheld worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Replace-by-Fee (RBF) Transactions Work?
Understanding Replace-by-Fee (RBF) in Cryptocurrency Transactions
Replace-by-Fee (RBF) is a feature integrated into Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies that enhances transaction flexibility and prioritization. Essentially, RBF allows users to replace an unconfirmed transaction with a new one that offers a higher fee, incentivizing miners to include it in the next block. This mechanism addresses common issues related to network congestion and slow confirmation times, especially during periods of high demand.
The core idea behind RBF is straightforward: when you create a transaction, you attach a certain fee based on current network conditions. If your transaction remains unconfirmed after some time—perhaps due to low fees—you can opt to replace it with an updated version that includes a higher fee. Miners are then more likely to prioritize this new transaction because they earn more from the increased fee.
The Step-by-Step Process of RBF Transactions
Understanding how RBF transactions work involves several key steps:
Initial Transaction Creation:
A user creates and broadcasts their original transaction with an initial fee estimate suitable for current network conditions.Broadcasting the Transaction:
The transaction propagates through the Bitcoin network where miners see it but may not include it immediately if competing transactions offer higher fees or if the network is congested.Monitoring Confirmation Status:
If after some time the user notices delays or wants faster confirmation, they can decide whether to replace their pending transaction.Creating a Replacement Transaction:
To do this, the user constructs a new version of their original transaction but increases its fee significantly—often by adjusting inputs or outputs while maintaining valid cryptographic signatures.Broadcasting the Replacement:
The replacement transaction is broadcasted across the network with specific signaling indicating it's intended as an update rather than an entirely new payment request.Miner Selection & Confirmation:
Miners evaluate available transactions based on various criteria such as fees offered, size, and complexity. They typically prefer transactions offering higher rewards; thus, they are more inclined to include your replacement over earlier versions if it offers better compensation.
This process relies heavily on adherence to protocols like BIP 125—a Bitcoin Improvement Proposal—that standardizes how RBF signals are communicated within transactions for compatibility across nodes and miners worldwide.
Why Is RBF Important for Users?
The primary benefit of RBF lies in its ability to improve user experience by reducing waiting times for confirmations during busy periods without needing external interventions like double-spending or complex off-chain solutions. It provides flexibility for users who might initially set lower fees but later realize they need faster processing due to urgent circumstances such as business payments or time-sensitive transfers.
Moreover, RBF aligns well with best practices around dynamic fee estimation—where users adjust their fees based on real-time network congestion data—to optimize costs while ensuring timely confirmation when necessary.
Potential Risks & Controversies Surrounding RBF
While beneficial in many scenarios, implementing RBF has sparked debate within cryptocurrency communities:
Disruption of Original Sender's Intent:
Since users can replace unconfirmed transactions at will before final settlement—a feature designed for flexibility—it raises concerns about potential malicious use cases like double-spending attacks or confusion among recipients expecting stable payment records.Security Concerns:
Malicious actors could flood networks with high-fee replacement transactions aimed at overwhelming legitimate ones or manipulating miner priorities—especially if proper safeguards aren’t enforced through protocol standards like BIP 125.Network Congestion:
During peak times when many users employ RBF simultaneously by replacing low-fee transactions with even higher ones, overall blockchain congestion could worsen temporarily until these replacements settle into confirmed blocks.
Recent Developments Enhancing Understanding & Adoption
Since its introduction via BIP 125 in 2017—which standardized signaling mechanisms—RBF has seen widespread adoption among wallets and services seeking greater control over unconfirmed payments. Notably:
- The activation of Segregated Witness (SegWit) in August 2018 improved overall efficiency by reducing data size per transaction; this indirectly lessened reliance on aggressive use of RBF since lower fees often sufficed under optimized conditions.
- Forks like Bitcoin Cash have also incorporated similar mechanisms inspired by Bitcoin’s design principles aimed at improving throughput without compromising security.
- Industry discussions continue around balancing flexibility provided by RBF against potential misuse risks; some wallets now allow optional enabling/disabling features depending on user preferences.
How Does SegWit Impact Replace-by-Fee?
Segregated Witness (SegWit), introduced as part of Bitcoin’s scaling upgrades in 2018, plays an indirect yet significant role concerning RBF functionality:
- By separating signature data from transactional information stored within blocks—which reduces overall size—it enables quicker propagation and confirmation times.
- As smaller-sized transactions become cheaper per byte due to SegWit's efficiencies, users may feel less compelled initially toward replacing low-fee transactions via R BF unless urgent needs arise.
However—as both features aim at optimizing blockchain performance—they complement each other rather than compete directly.
Final Thoughts
Replace-by-Fee remains an essential tool within modern cryptocurrency ecosystems that balances cost efficiency against timely processing demands amid fluctuating network traffic levels. Its implementation underscores ongoing efforts toward making blockchain technology more adaptable while highlighting challenges related to security risks and protocol standardization issues that require continuous community oversight.
By understanding how these mechanisms operate—from creation through replacement—and recognizing recent technological advancements influencing their effectiveness—you gain valuable insights into managing digital assets efficiently amidst evolving blockchain landscapes.
References


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 10:35
How do replace-by-fee (RBF) transactions work?
How Do Replace-by-Fee (RBF) Transactions Work?
Understanding Replace-by-Fee (RBF) in Cryptocurrency Transactions
Replace-by-Fee (RBF) is a feature integrated into Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies that enhances transaction flexibility and prioritization. Essentially, RBF allows users to replace an unconfirmed transaction with a new one that offers a higher fee, incentivizing miners to include it in the next block. This mechanism addresses common issues related to network congestion and slow confirmation times, especially during periods of high demand.
The core idea behind RBF is straightforward: when you create a transaction, you attach a certain fee based on current network conditions. If your transaction remains unconfirmed after some time—perhaps due to low fees—you can opt to replace it with an updated version that includes a higher fee. Miners are then more likely to prioritize this new transaction because they earn more from the increased fee.
The Step-by-Step Process of RBF Transactions
Understanding how RBF transactions work involves several key steps:
Initial Transaction Creation:
A user creates and broadcasts their original transaction with an initial fee estimate suitable for current network conditions.Broadcasting the Transaction:
The transaction propagates through the Bitcoin network where miners see it but may not include it immediately if competing transactions offer higher fees or if the network is congested.Monitoring Confirmation Status:
If after some time the user notices delays or wants faster confirmation, they can decide whether to replace their pending transaction.Creating a Replacement Transaction:
To do this, the user constructs a new version of their original transaction but increases its fee significantly—often by adjusting inputs or outputs while maintaining valid cryptographic signatures.Broadcasting the Replacement:
The replacement transaction is broadcasted across the network with specific signaling indicating it's intended as an update rather than an entirely new payment request.Miner Selection & Confirmation:
Miners evaluate available transactions based on various criteria such as fees offered, size, and complexity. They typically prefer transactions offering higher rewards; thus, they are more inclined to include your replacement over earlier versions if it offers better compensation.
This process relies heavily on adherence to protocols like BIP 125—a Bitcoin Improvement Proposal—that standardizes how RBF signals are communicated within transactions for compatibility across nodes and miners worldwide.
Why Is RBF Important for Users?
The primary benefit of RBF lies in its ability to improve user experience by reducing waiting times for confirmations during busy periods without needing external interventions like double-spending or complex off-chain solutions. It provides flexibility for users who might initially set lower fees but later realize they need faster processing due to urgent circumstances such as business payments or time-sensitive transfers.
Moreover, RBF aligns well with best practices around dynamic fee estimation—where users adjust their fees based on real-time network congestion data—to optimize costs while ensuring timely confirmation when necessary.
Potential Risks & Controversies Surrounding RBF
While beneficial in many scenarios, implementing RBF has sparked debate within cryptocurrency communities:
Disruption of Original Sender's Intent:
Since users can replace unconfirmed transactions at will before final settlement—a feature designed for flexibility—it raises concerns about potential malicious use cases like double-spending attacks or confusion among recipients expecting stable payment records.Security Concerns:
Malicious actors could flood networks with high-fee replacement transactions aimed at overwhelming legitimate ones or manipulating miner priorities—especially if proper safeguards aren’t enforced through protocol standards like BIP 125.Network Congestion:
During peak times when many users employ RBF simultaneously by replacing low-fee transactions with even higher ones, overall blockchain congestion could worsen temporarily until these replacements settle into confirmed blocks.
Recent Developments Enhancing Understanding & Adoption
Since its introduction via BIP 125 in 2017—which standardized signaling mechanisms—RBF has seen widespread adoption among wallets and services seeking greater control over unconfirmed payments. Notably:
- The activation of Segregated Witness (SegWit) in August 2018 improved overall efficiency by reducing data size per transaction; this indirectly lessened reliance on aggressive use of RBF since lower fees often sufficed under optimized conditions.
- Forks like Bitcoin Cash have also incorporated similar mechanisms inspired by Bitcoin’s design principles aimed at improving throughput without compromising security.
- Industry discussions continue around balancing flexibility provided by RBF against potential misuse risks; some wallets now allow optional enabling/disabling features depending on user preferences.
How Does SegWit Impact Replace-by-Fee?
Segregated Witness (SegWit), introduced as part of Bitcoin’s scaling upgrades in 2018, plays an indirect yet significant role concerning RBF functionality:
- By separating signature data from transactional information stored within blocks—which reduces overall size—it enables quicker propagation and confirmation times.
- As smaller-sized transactions become cheaper per byte due to SegWit's efficiencies, users may feel less compelled initially toward replacing low-fee transactions via R BF unless urgent needs arise.
However—as both features aim at optimizing blockchain performance—they complement each other rather than compete directly.
Final Thoughts
Replace-by-Fee remains an essential tool within modern cryptocurrency ecosystems that balances cost efficiency against timely processing demands amid fluctuating network traffic levels. Its implementation underscores ongoing efforts toward making blockchain technology more adaptable while highlighting challenges related to security risks and protocol standardization issues that require continuous community oversight.
By understanding how these mechanisms operate—from creation through replacement—and recognizing recent technological advancements influencing their effectiveness—you gain valuable insights into managing digital assets efficiently amidst evolving blockchain landscapes.
References
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
HODL – the dream of diamond hands 💎 turned into pocket change 🪙. He held through every pump 📈 and dump 📉, but forgot to take profits 💸. Now he’s counting coins at the counter 🧾 — proof that sometimes you need more than just strong hands 👐. Take profits along the way folks! ✅
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#CryptoHumor #CryptoMeme #HODLForever #CryptoSkits


JuCoin Media
2025-08-04 08:49
HODL: When Diamond Hands Become Loose Change 💎
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does a Liquidity Pool Work?
Understanding how liquidity pools operate is essential for anyone interested in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology. These pools are the backbone of many decentralized exchanges (DEXs), enabling seamless trading without traditional order books. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanics behind liquidity pools, their benefits, risks, and recent innovations.
What Is a Liquidity Pool?
A liquidity pool is a smart contract-based reserve of cryptocurrencies that facilitates trading on decentralized platforms. Instead of relying on centralized order books where buyers and sellers match directly, liquidity pools allow users to deposit pairs of tokens into a shared pool. These deposits enable other users to trade against the pooled assets instantly, with prices determined algorithmically.
In essence, liquidity pools democratize access to trading by allowing anyone to contribute assets and earn passive income through transaction fees. They also eliminate the need for large capital reserves traditionally required by centralized exchanges.
How Do Users Contribute to Liquidity Pools?
Creating or participating in a liquidity pool involves depositing specific cryptocurrency pairs into a smart contract. For example, on Uniswap or SushiSwap, users might deposit equal values of ETH and USDT into the pool. Once deposited:
- The user becomes a liquidity provider.
- The deposited assets are stored securely within the smart contract.
- In return for providing liquidity, they receive liquidity tokens, representing their share in the pool.
These tokens can be redeemed later for their proportional share of the underlying assets plus any earned fees.
How Are Trades Executed in Liquidity Pools?
When traders want to swap one token for another—say ETH for DAI—they interact directly with the smart contract rather than placing an order on an exchange’s order book. The platform uses an algorithmic formula—most notably Uniswap's constant product formula—to determine prices dynamically based on current reserves:
[ x \times y = k ]
Where:
- ( x ) = amount of token A
- ( y ) = amount of token B
- ( k ) = constant
This formula ensures that as someone trades against the pool (buying or selling tokens), it adjusts prices automatically while maintaining balance within the pool.
The trade executes immediately at this calculated price, providing instant settlement without intermediaries or centralized matching engines.
Earning Through Trading Fees
Every time someone makes a trade involving your pooled assets:
- A small fee (typically 0.3%) is charged.
- This fee is distributed proportionally among all liquidity providers based on their share.
Over time, these accumulated fees can generate significant passive income—especially during periods with high trading volume—making participation attractive for investors seeking yield from their crypto holdings.
Types of Liquidity Pools
Different DeFi platforms have tailored approaches suited to various asset types:
- Uniswap: Uses constant product formulas suitable for volatile cryptocurrencies.
- SushiSwap: Similar mechanics but emphasizes community governance and additional features like staking.
- Curve Finance: Focuses exclusively on stablecoins such as USDC, DAI, and USDT; optimized for low slippage during stablecoin swaps.
- Balancer: Allows multi-token pools with customizable weightings beyond simple 50/50 ratios.
Each type caters to different user needs—from high-volatility asset swaps to stablecoin transactions requiring minimal price impact.
Benefits Offered by Liquidity Pools
Providing assets to these pools offers multiple advantages:
Passive Income Generation: Earn part of transaction fees without active management.
Portfolio Diversification: Gain exposure across various cryptocurrencies through pooled investments rather than direct holdings alone.
Decentralized Access & Control: Anyone globally can participate without intermediaries or traditional banking restrictions; this promotes financial inclusion within DeFi ecosystems.
Furthermore, some platforms incentivize participation through governance tokens or yield farming strategies that amplify potential returns beyond standard fee sharing.
Risks Associated With Liquidity Pools
Despite numerous benefits, participating in liquidity pools carries inherent risks that must be carefully considered:
Impermanent Loss
This occurs when relative prices between paired tokens change significantly after deposit — potentially leading LPs (liquidity providers) to realize less value upon withdrawal compared to simply holding onto their original assets outside the pool—a phenomenon known as impermanent loss due to market volatility affecting asset ratios over time.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are complex codebases susceptible sometimes vulnerable exploits or bugs which malicious actors could exploit resulting in loss of funds from pooled reserves if security measures aren’t robust enough.
Market Volatility Impact
Crypto markets are highly volatile; sudden price swings can affect both asset values within pools and potential earnings from trading fees—sometimes leading LPs into losses if not managed properly.
Recent Innovations & Trends in Liquidity Pool Technology
The DeFi space continues evolving rapidly with technological advancements aimed at reducing risks while enhancing profitability:
Optimized Algorithms
- New formulas aim at minimizing impermanent loss—for instance: dynamic rebalancing mechanisms or hybrid models combining different mathematical approaches improve stability during volatile periods.
Cross-chain Pools
- Interoperability solutions now enable pooling across multiple blockchains like Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain (BSC). This expands opportunities but also introduces new complexities related to security standards across networks.
Governance & Community Participation
- Many platforms issue governance tokens allowing holders voting rights over protocol upgrades—including adjustments related directly to fee structures or risk mitigation strategies—which fosters community-driven development.
Yield Farming & Incentives
- Yield farming involves locking up LP tokens temporarily across multiple protocols simultaneously—for higher yields—but increases exposure complexity requiring careful risk assessment.
Regulatory Developments
- As governments worldwide scrutinize DeFi activities more closely—including those involving liquidity provision—the regulatory landscape may influence how these systems evolve moving forward.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Modern Decentralized Trading Ecosystems
Liquidity pools form an integral part of modern decentralized finance infrastructure by enabling continuous market activity without traditional intermediaries’ constraints.. They offer lucrative opportunities such as earning passive income while supporting open financial systems accessible globally.. However—and crucially—they come with notable risks including impermanent loss and potential vulnerabilities inherent in smart contracts..
As technology advances—with cross-chain compatibility becoming more prevalent—and regulatory frameworks develop around DeFi activities—it’s vital that participants stay informed about best practices regarding security measures and risk management strategies when engaging with these innovative financial tools.. By understanding how they work under-the hood—and keeping abreast with ongoing innovations—you can better position yourself within this rapidly evolving landscape toward responsible investment decisions aligned with your financial goals.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-29 07:43
How does a liquidity pool work?
How Does a Liquidity Pool Work?
Understanding how liquidity pools operate is essential for anyone interested in decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology. These pools are the backbone of many decentralized exchanges (DEXs), enabling seamless trading without traditional order books. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanics behind liquidity pools, their benefits, risks, and recent innovations.
What Is a Liquidity Pool?
A liquidity pool is a smart contract-based reserve of cryptocurrencies that facilitates trading on decentralized platforms. Instead of relying on centralized order books where buyers and sellers match directly, liquidity pools allow users to deposit pairs of tokens into a shared pool. These deposits enable other users to trade against the pooled assets instantly, with prices determined algorithmically.
In essence, liquidity pools democratize access to trading by allowing anyone to contribute assets and earn passive income through transaction fees. They also eliminate the need for large capital reserves traditionally required by centralized exchanges.
How Do Users Contribute to Liquidity Pools?
Creating or participating in a liquidity pool involves depositing specific cryptocurrency pairs into a smart contract. For example, on Uniswap or SushiSwap, users might deposit equal values of ETH and USDT into the pool. Once deposited:
- The user becomes a liquidity provider.
- The deposited assets are stored securely within the smart contract.
- In return for providing liquidity, they receive liquidity tokens, representing their share in the pool.
These tokens can be redeemed later for their proportional share of the underlying assets plus any earned fees.
How Are Trades Executed in Liquidity Pools?
When traders want to swap one token for another—say ETH for DAI—they interact directly with the smart contract rather than placing an order on an exchange’s order book. The platform uses an algorithmic formula—most notably Uniswap's constant product formula—to determine prices dynamically based on current reserves:
[ x \times y = k ]
Where:
- ( x ) = amount of token A
- ( y ) = amount of token B
- ( k ) = constant
This formula ensures that as someone trades against the pool (buying or selling tokens), it adjusts prices automatically while maintaining balance within the pool.
The trade executes immediately at this calculated price, providing instant settlement without intermediaries or centralized matching engines.
Earning Through Trading Fees
Every time someone makes a trade involving your pooled assets:
- A small fee (typically 0.3%) is charged.
- This fee is distributed proportionally among all liquidity providers based on their share.
Over time, these accumulated fees can generate significant passive income—especially during periods with high trading volume—making participation attractive for investors seeking yield from their crypto holdings.
Types of Liquidity Pools
Different DeFi platforms have tailored approaches suited to various asset types:
- Uniswap: Uses constant product formulas suitable for volatile cryptocurrencies.
- SushiSwap: Similar mechanics but emphasizes community governance and additional features like staking.
- Curve Finance: Focuses exclusively on stablecoins such as USDC, DAI, and USDT; optimized for low slippage during stablecoin swaps.
- Balancer: Allows multi-token pools with customizable weightings beyond simple 50/50 ratios.
Each type caters to different user needs—from high-volatility asset swaps to stablecoin transactions requiring minimal price impact.
Benefits Offered by Liquidity Pools
Providing assets to these pools offers multiple advantages:
Passive Income Generation: Earn part of transaction fees without active management.
Portfolio Diversification: Gain exposure across various cryptocurrencies through pooled investments rather than direct holdings alone.
Decentralized Access & Control: Anyone globally can participate without intermediaries or traditional banking restrictions; this promotes financial inclusion within DeFi ecosystems.
Furthermore, some platforms incentivize participation through governance tokens or yield farming strategies that amplify potential returns beyond standard fee sharing.
Risks Associated With Liquidity Pools
Despite numerous benefits, participating in liquidity pools carries inherent risks that must be carefully considered:
Impermanent Loss
This occurs when relative prices between paired tokens change significantly after deposit — potentially leading LPs (liquidity providers) to realize less value upon withdrawal compared to simply holding onto their original assets outside the pool—a phenomenon known as impermanent loss due to market volatility affecting asset ratios over time.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are complex codebases susceptible sometimes vulnerable exploits or bugs which malicious actors could exploit resulting in loss of funds from pooled reserves if security measures aren’t robust enough.
Market Volatility Impact
Crypto markets are highly volatile; sudden price swings can affect both asset values within pools and potential earnings from trading fees—sometimes leading LPs into losses if not managed properly.
Recent Innovations & Trends in Liquidity Pool Technology
The DeFi space continues evolving rapidly with technological advancements aimed at reducing risks while enhancing profitability:
Optimized Algorithms
- New formulas aim at minimizing impermanent loss—for instance: dynamic rebalancing mechanisms or hybrid models combining different mathematical approaches improve stability during volatile periods.
Cross-chain Pools
- Interoperability solutions now enable pooling across multiple blockchains like Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain (BSC). This expands opportunities but also introduces new complexities related to security standards across networks.
Governance & Community Participation
- Many platforms issue governance tokens allowing holders voting rights over protocol upgrades—including adjustments related directly to fee structures or risk mitigation strategies—which fosters community-driven development.
Yield Farming & Incentives
- Yield farming involves locking up LP tokens temporarily across multiple protocols simultaneously—for higher yields—but increases exposure complexity requiring careful risk assessment.
Regulatory Developments
- As governments worldwide scrutinize DeFi activities more closely—including those involving liquidity provision—the regulatory landscape may influence how these systems evolve moving forward.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Modern Decentralized Trading Ecosystems
Liquidity pools form an integral part of modern decentralized finance infrastructure by enabling continuous market activity without traditional intermediaries’ constraints.. They offer lucrative opportunities such as earning passive income while supporting open financial systems accessible globally.. However—and crucially—they come with notable risks including impermanent loss and potential vulnerabilities inherent in smart contracts..
As technology advances—with cross-chain compatibility becoming more prevalent—and regulatory frameworks develop around DeFi activities—it’s vital that participants stay informed about best practices regarding security measures and risk management strategies when engaging with these innovative financial tools.. By understanding how they work under-the hood—and keeping abreast with ongoing innovations—you can better position yourself within this rapidly evolving landscape toward responsible investment decisions aligned with your financial goals.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What is XRP (XRP) Primarily Used For?
Understanding the Core Function of XRP in the Financial Ecosystem
XRP, often referred to as Ripple, is a digital asset designed with a specific purpose within the global financial system. Unlike many cryptocurrencies that serve primarily as stores of value or speculative assets, XRP’s main role revolves around facilitating fast and cost-effective cross-border transactions. Its unique technology and strategic positioning make it an essential tool for financial institutions seeking to optimize international payments.
At its core, XRP acts as a bridge currency that enables seamless transfer of funds across different fiat currencies and banking systems. This capability addresses longstanding issues in international finance—namely high transaction costs, delays, and inefficiencies associated with traditional methods like SWIFT. By leveraging its blockchain technology and consensus protocol, XRP can process transactions in seconds at a fraction of the cost compared to conventional banking channels.
How XRP Enhances Cross-Border Payments
The primary use case for XRP is within cross-border payment corridors between banks and financial institutions. These entities often face challenges such as lengthy settlement times—sometimes taking several days—and hefty fees due to intermediary banks and currency conversions. Ripple’s platform aims to streamline this process by providing a decentralized network where transactions are validated quickly without relying on centralized clearinghouses.
Financial institutions adopting Ripple’s solutions utilize XRP either directly or indirectly to facilitate liquidity management during international transfers. For example:
- Liquidity Optimization: Banks can hold minimal reserves in multiple currencies by using XRP for instant liquidity when needed.
- Reduced Settlement Times: Transactions that traditionally take days are completed within seconds.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Eliminating intermediaries reduces fees significantly.
This efficiency not only benefits banks but also enhances customer experience by enabling faster fund transfers across borders.
The Role of RippleNet and Institutional Adoption
Ripple has developed an extensive network called RippleNet that connects various financial institutions globally. Within this network, XRP serves as an on-demand liquidity (ODL) solution—allowing participants to settle cross-border payments swiftly without pre-funding accounts in foreign currencies.
Several major players have explored or integrated XRP into their operations:
- American Express
- Bank of America
- Santander
These collaborations demonstrate how institutional adoption leverages XRPs’ speed and low-cost features for practical use cases rather than mere speculation.
Regulatory Environment Impacting Usage
Despite its technological advantages, the primary challenge facing XRP's widespread adoption stems from regulatory uncertainties. The ongoing lawsuit filed by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) alleges that XRPL tokens were sold unregistered securities—a claim that has created hesitation among some potential users.
If regulators classify XRP as a security rather than a commodity or utility token, it could impose restrictions on its use within certain jurisdictions or require additional compliance measures from participating institutions. Conversely, if courts determine it qualifies as a commodity like gold or oil—which are not subject to securities laws—it could pave the way for broader acceptance across global markets.
Future Potential: Disrupting Traditional Banking Systems
Looking ahead, if regulatory hurdles are addressed favorably—or if legal rulings clarify XRPs’ status—the cryptocurrency could significantly reshape how international payments are processed worldwide. Its ability to deliver near-instantaneous settlements at minimal costs makes it attractive not only for large banks but also emerging fintech companies aiming to democratize access to efficient remittance services.
Furthermore, ongoing technological developments aim at increasing scalability while maintaining security standards—ensuring XRPs' relevance amid evolving market demands.
Summary: Key Uses of XRP in Finance Today
To summarize:
- Facilitates fast cross-border money transfers
- Acts as bridge currency between different fiat systems
- Enables real-time settlement through RippleNet
- Reduces transaction costs compared to traditional methods
- Supports liquidity management for financial institutions
By focusing on these core functionalities—and navigating regulatory landscapes—XRP continues positioning itself as an innovative solution capable of transforming global remittance infrastructure while offering transparency through blockchain technology.
Why Understanding XRPs Use Cases Matters
For investors and industry stakeholders alike, grasping what makes XRPs valuable helps inform strategic decisions about participation in crypto markets or integration into existing payment frameworks. As regulation evolves alongside technological advancements—and with increasing institutional interest—the role of XRP may expand further beyond current applications into broader areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), digital asset custody solutions, or even central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
In essence: knowing how ripple's native token functions provides insight into both its current utility landscape—and future potential—as part of the ongoing evolution toward more efficient global finance systems.
Keywords: what is xrp used for | xrp cross border payments | ripple cryptocurrency uses | ripple net | institutional adoption xrp | xrp regulation impact


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-15 00:16
What is XRP (XRP) primarily used for?
What is XRP (XRP) Primarily Used For?
Understanding the Core Function of XRP in the Financial Ecosystem
XRP, often referred to as Ripple, is a digital asset designed with a specific purpose within the global financial system. Unlike many cryptocurrencies that serve primarily as stores of value or speculative assets, XRP’s main role revolves around facilitating fast and cost-effective cross-border transactions. Its unique technology and strategic positioning make it an essential tool for financial institutions seeking to optimize international payments.
At its core, XRP acts as a bridge currency that enables seamless transfer of funds across different fiat currencies and banking systems. This capability addresses longstanding issues in international finance—namely high transaction costs, delays, and inefficiencies associated with traditional methods like SWIFT. By leveraging its blockchain technology and consensus protocol, XRP can process transactions in seconds at a fraction of the cost compared to conventional banking channels.
How XRP Enhances Cross-Border Payments
The primary use case for XRP is within cross-border payment corridors between banks and financial institutions. These entities often face challenges such as lengthy settlement times—sometimes taking several days—and hefty fees due to intermediary banks and currency conversions. Ripple’s platform aims to streamline this process by providing a decentralized network where transactions are validated quickly without relying on centralized clearinghouses.
Financial institutions adopting Ripple’s solutions utilize XRP either directly or indirectly to facilitate liquidity management during international transfers. For example:
- Liquidity Optimization: Banks can hold minimal reserves in multiple currencies by using XRP for instant liquidity when needed.
- Reduced Settlement Times: Transactions that traditionally take days are completed within seconds.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Eliminating intermediaries reduces fees significantly.
This efficiency not only benefits banks but also enhances customer experience by enabling faster fund transfers across borders.
The Role of RippleNet and Institutional Adoption
Ripple has developed an extensive network called RippleNet that connects various financial institutions globally. Within this network, XRP serves as an on-demand liquidity (ODL) solution—allowing participants to settle cross-border payments swiftly without pre-funding accounts in foreign currencies.
Several major players have explored or integrated XRP into their operations:
- American Express
- Bank of America
- Santander
These collaborations demonstrate how institutional adoption leverages XRPs’ speed and low-cost features for practical use cases rather than mere speculation.
Regulatory Environment Impacting Usage
Despite its technological advantages, the primary challenge facing XRP's widespread adoption stems from regulatory uncertainties. The ongoing lawsuit filed by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) alleges that XRPL tokens were sold unregistered securities—a claim that has created hesitation among some potential users.
If regulators classify XRP as a security rather than a commodity or utility token, it could impose restrictions on its use within certain jurisdictions or require additional compliance measures from participating institutions. Conversely, if courts determine it qualifies as a commodity like gold or oil—which are not subject to securities laws—it could pave the way for broader acceptance across global markets.
Future Potential: Disrupting Traditional Banking Systems
Looking ahead, if regulatory hurdles are addressed favorably—or if legal rulings clarify XRPs’ status—the cryptocurrency could significantly reshape how international payments are processed worldwide. Its ability to deliver near-instantaneous settlements at minimal costs makes it attractive not only for large banks but also emerging fintech companies aiming to democratize access to efficient remittance services.
Furthermore, ongoing technological developments aim at increasing scalability while maintaining security standards—ensuring XRPs' relevance amid evolving market demands.
Summary: Key Uses of XRP in Finance Today
To summarize:
- Facilitates fast cross-border money transfers
- Acts as bridge currency between different fiat systems
- Enables real-time settlement through RippleNet
- Reduces transaction costs compared to traditional methods
- Supports liquidity management for financial institutions
By focusing on these core functionalities—and navigating regulatory landscapes—XRP continues positioning itself as an innovative solution capable of transforming global remittance infrastructure while offering transparency through blockchain technology.
Why Understanding XRPs Use Cases Matters
For investors and industry stakeholders alike, grasping what makes XRPs valuable helps inform strategic decisions about participation in crypto markets or integration into existing payment frameworks. As regulation evolves alongside technological advancements—and with increasing institutional interest—the role of XRP may expand further beyond current applications into broader areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), digital asset custody solutions, or even central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
In essence: knowing how ripple's native token functions provides insight into both its current utility landscape—and future potential—as part of the ongoing evolution toward more efficient global finance systems.
Keywords: what is xrp used for | xrp cross border payments | ripple cryptocurrency uses | ripple net | institutional adoption xrp | xrp regulation impact
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📈 Top Coins by Bullish Period & Performance
3m % and Bullish Period:
• $TROLL $37.1 +1,004% (44d)
$ENA/USDT $0.49 +107.2% (36d)
$LDO/USDT $1.34 +39.8% (34d)
• $SYRUP $0.22 +17.1% (34d)
This metric shows how often a coin has been bullish in the last 100 days. Daily growth above 5% taken only.
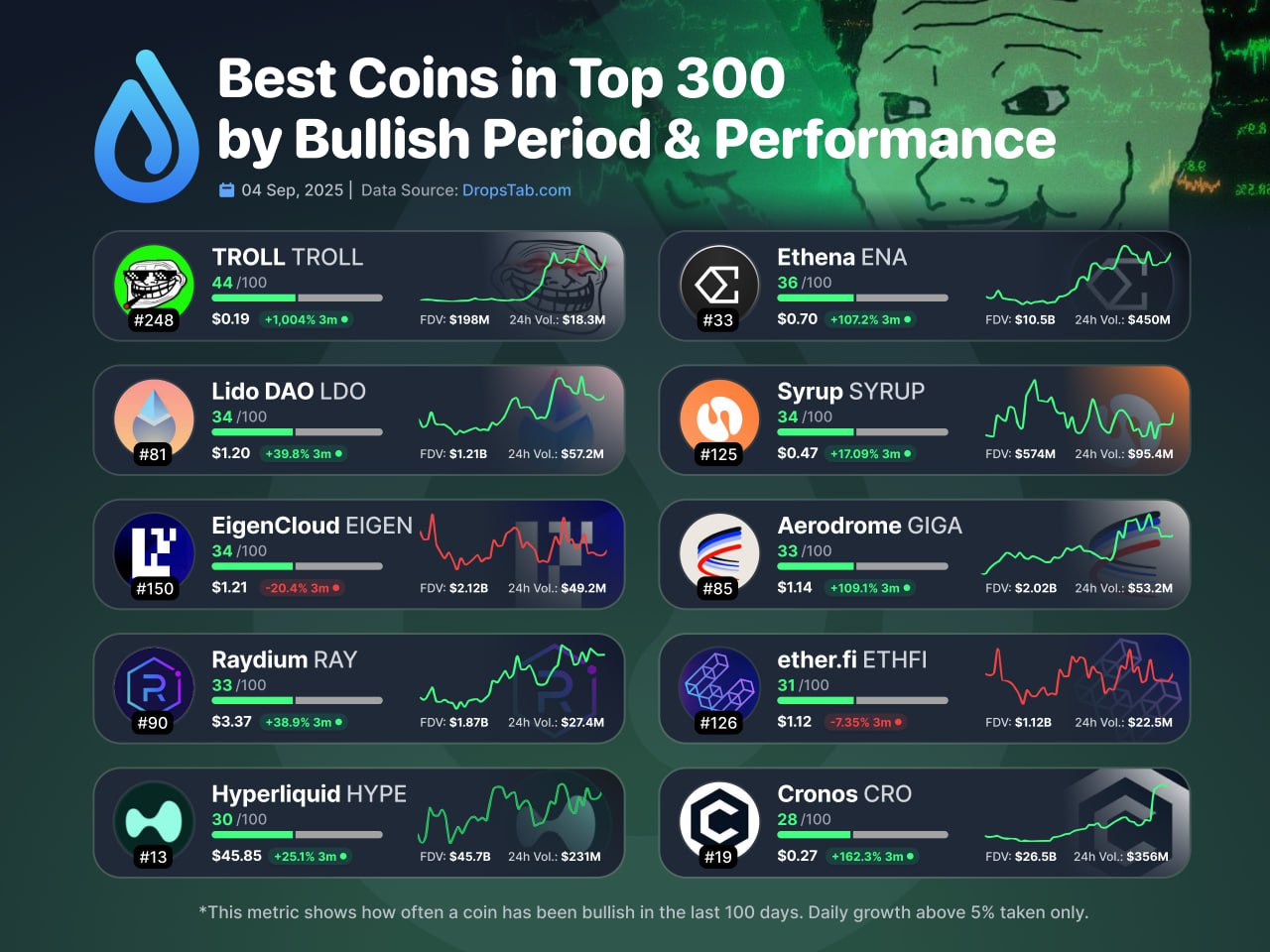


JioCoins
2025-09-04 12:12
Top Coins by Bullish Period & Performance
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Understanding How Bollinger Bands Work in Technical Analysis
Bollinger Bands are a popular and versatile tool used by traders and analysts to assess market volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, this indicator has stood the test of time due to its simplicity and effectiveness across various financial markets, including stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities, ETFs, and index funds. To fully grasp how Bollinger Bands function, it’s essential to understand their components and the underlying principles that drive their signals.
What Are the Components of Bollinger Bands?
At its core, a Bollinger Band consists of three key elements:
Middle Band (Simple Moving Average): Typically set at 20 periods (days), this moving average serves as a baseline representing the average price over that period. It smooths out short-term fluctuations to reveal the overall trend.
Upper Band: Calculated by adding two standard deviations to the middle band. This creates an upper boundary that adapts dynamically based on recent price volatility.
Lower Band: Derived by subtracting two standard deviations from the middle band. Like the upper band, it adjusts according to market volatility.
The use of standard deviation ensures that these bands expand during periods of high volatility when prices fluctuate widely and contract during calmer phases with less price movement.
How Do Bollinger Bands Measure Market Volatility?
The primary purpose of Bollinger Bands is to quantify market volatility visually. When prices are stable or trending steadily within narrow ranges, the bands tend to tighten or "pinch" together—indicating low volatility conditions. Conversely, when markets become more turbulent with rapid price swings, these bands widen apart significantly.
This dynamic adjustment makes Bollinger Bands particularly useful for traders seeking insights into current market states without relying solely on raw price data. The distance between upper and lower bands acts as an intuitive gauge; wider gaps suggest increased uncertainty or heightened trading activity while narrower gaps imply consolidation phases where breakout opportunities may arise.
Using Price Movements Relative to Bollinger Bands
One common approach among traders is observing how prices interact with these bands:
Price Touches or Crosses Upper Band: Often interpreted as overbought territory—potentially signaling a reversal or pullback if confirmed with other indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index). However, in strong trending markets, prices can remain near or above this level longer than expected.
Price Touches or Crosses Lower Band: Seen as oversold conditions—possibly indicating a buying opportunity if supported by other signals such as bullish divergence on momentum indicators.
These interactions alone do not guarantee reversals but serve as valuable cues for further analysis rather than standalone signals.
Generating Trading Signals Using Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are frequently combined with additional technical tools like RSI for more reliable trade entries:
Bullish Signals:
- When prices touch or dip below the lower band
- Confirmed by oversold RSI levels (below 30)
- Potential indication of an upcoming upward move
Bearish Signals:
- When prices reach or cross above the upper band
- Supported by overbought RSI readings (above 70)
- Suggesting possible downward correction
It’s important for traders not to rely solely on these signals but instead incorporate them into broader strategies involving trend analysis and volume confirmation.
The Role of Overbought/Oversold Conditions
Overbought and oversold states provide context about potential reversals but should be interpreted cautiously:
- An asset might remain overbought during strong uptrends
- Oversold conditions can persist in downtrends
Therefore, combining Bollinger Band signals with momentum oscillators like RSI enhances decision-making accuracy — helping avoid false alarms caused by temporary extremes in pricing behavior.
Recent Trends & Applications Across Markets
In recent years, especially within volatile sectors such as cryptocurrencies—including Bitcoin—and commodities like gold or oil—Bollinger Bands have gained renewed popularity among retail traders due to their ability to adapt quickly amid rapid price swings. Their visual nature allows quick assessment even amidst complex charts filled with multiple indicators.
Moreover, institutional investors utilize these bands within ETF portfolios and index fund strategies for macro-level market monitoring — identifying periods where broad indices may be overheated or undervalued based on volatility patterns observed through these tools.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Bollinger Bands
Despite their usefulness; however,
They can generate false signals when markets experience sudden spikes without clear trend reversals.
Overreliance on them alone may lead traders astray; integrating other technical analysis methods reduces risk exposure.
False positives occur especially when bands become too tight—a phenomenon known as "squeeze"—which often precedes significant breakouts but does not specify directionality without additional confirmation tools such as volume analysis or candlestick patterns.
Practical Tips for Using Bollinger Bands Effectively
To maximize their effectiveness:
- Use them alongside other indicators like RSI®, MACD®, moving averages—or fundamental factors—to confirm trade setups.
- Watch for "band squeezes," which signal low-volatility periods likely followed by sharp moves.
- Be cautious during sideways consolidations where false breakouts are common.
- Adjust parameters based on specific asset characteristics—for example; shorter periods might suit highly volatile assets like cryptocurrencies whereas longer ones could better fit stable equities.
Final Thoughts on How Do Bollingers Work?
BollINGER BANDS serve as an insightful window into market dynamics through measuring real-time volatility levels while providing actionable trading cues based on how asset prices interact with dynamic boundaries around a central moving average line. Their adaptability across different assets makes them invaluable both for short-term trading strategies aiming at capturing quick moves—and long-term investors assessing overall risk environments—but always remember they work best when combined thoughtfully within comprehensive analytical frameworks rather than used in isolation.
By understanding how they measure market fluctuations through adaptive boundaries created via simple statistical concepts—the moving average plus/minus standard deviations—traders gain powerful insights into potential entry points while managing risk effectively.


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-29 04:52
How do Bollinger Bands work?
Understanding How Bollinger Bands Work in Technical Analysis
Bollinger Bands are a popular and versatile tool used by traders and analysts to assess market volatility and identify potential trading opportunities. Developed by John Bollinger in the 1980s, this indicator has stood the test of time due to its simplicity and effectiveness across various financial markets, including stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities, ETFs, and index funds. To fully grasp how Bollinger Bands function, it’s essential to understand their components and the underlying principles that drive their signals.
What Are the Components of Bollinger Bands?
At its core, a Bollinger Band consists of three key elements:
Middle Band (Simple Moving Average): Typically set at 20 periods (days), this moving average serves as a baseline representing the average price over that period. It smooths out short-term fluctuations to reveal the overall trend.
Upper Band: Calculated by adding two standard deviations to the middle band. This creates an upper boundary that adapts dynamically based on recent price volatility.
Lower Band: Derived by subtracting two standard deviations from the middle band. Like the upper band, it adjusts according to market volatility.
The use of standard deviation ensures that these bands expand during periods of high volatility when prices fluctuate widely and contract during calmer phases with less price movement.
How Do Bollinger Bands Measure Market Volatility?
The primary purpose of Bollinger Bands is to quantify market volatility visually. When prices are stable or trending steadily within narrow ranges, the bands tend to tighten or "pinch" together—indicating low volatility conditions. Conversely, when markets become more turbulent with rapid price swings, these bands widen apart significantly.
This dynamic adjustment makes Bollinger Bands particularly useful for traders seeking insights into current market states without relying solely on raw price data. The distance between upper and lower bands acts as an intuitive gauge; wider gaps suggest increased uncertainty or heightened trading activity while narrower gaps imply consolidation phases where breakout opportunities may arise.
Using Price Movements Relative to Bollinger Bands
One common approach among traders is observing how prices interact with these bands:
Price Touches or Crosses Upper Band: Often interpreted as overbought territory—potentially signaling a reversal or pullback if confirmed with other indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index). However, in strong trending markets, prices can remain near or above this level longer than expected.
Price Touches or Crosses Lower Band: Seen as oversold conditions—possibly indicating a buying opportunity if supported by other signals such as bullish divergence on momentum indicators.
These interactions alone do not guarantee reversals but serve as valuable cues for further analysis rather than standalone signals.
Generating Trading Signals Using Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are frequently combined with additional technical tools like RSI for more reliable trade entries:
Bullish Signals:
- When prices touch or dip below the lower band
- Confirmed by oversold RSI levels (below 30)
- Potential indication of an upcoming upward move
Bearish Signals:
- When prices reach or cross above the upper band
- Supported by overbought RSI readings (above 70)
- Suggesting possible downward correction
It’s important for traders not to rely solely on these signals but instead incorporate them into broader strategies involving trend analysis and volume confirmation.
The Role of Overbought/Oversold Conditions
Overbought and oversold states provide context about potential reversals but should be interpreted cautiously:
- An asset might remain overbought during strong uptrends
- Oversold conditions can persist in downtrends
Therefore, combining Bollinger Band signals with momentum oscillators like RSI enhances decision-making accuracy — helping avoid false alarms caused by temporary extremes in pricing behavior.
Recent Trends & Applications Across Markets
In recent years, especially within volatile sectors such as cryptocurrencies—including Bitcoin—and commodities like gold or oil—Bollinger Bands have gained renewed popularity among retail traders due to their ability to adapt quickly amid rapid price swings. Their visual nature allows quick assessment even amidst complex charts filled with multiple indicators.
Moreover, institutional investors utilize these bands within ETF portfolios and index fund strategies for macro-level market monitoring — identifying periods where broad indices may be overheated or undervalued based on volatility patterns observed through these tools.
Limitations & Risks Associated With Bollinger Bands
Despite their usefulness; however,
They can generate false signals when markets experience sudden spikes without clear trend reversals.
Overreliance on them alone may lead traders astray; integrating other technical analysis methods reduces risk exposure.
False positives occur especially when bands become too tight—a phenomenon known as "squeeze"—which often precedes significant breakouts but does not specify directionality without additional confirmation tools such as volume analysis or candlestick patterns.
Practical Tips for Using Bollinger Bands Effectively
To maximize their effectiveness:
- Use them alongside other indicators like RSI®, MACD®, moving averages—or fundamental factors—to confirm trade setups.
- Watch for "band squeezes," which signal low-volatility periods likely followed by sharp moves.
- Be cautious during sideways consolidations where false breakouts are common.
- Adjust parameters based on specific asset characteristics—for example; shorter periods might suit highly volatile assets like cryptocurrencies whereas longer ones could better fit stable equities.
Final Thoughts on How Do Bollingers Work?
BollINGER BANDS serve as an insightful window into market dynamics through measuring real-time volatility levels while providing actionable trading cues based on how asset prices interact with dynamic boundaries around a central moving average line. Their adaptability across different assets makes them invaluable both for short-term trading strategies aiming at capturing quick moves—and long-term investors assessing overall risk environments—but always remember they work best when combined thoughtfully within comprehensive analytical frameworks rather than used in isolation.
By understanding how they measure market fluctuations through adaptive boundaries created via simple statistical concepts—the moving average plus/minus standard deviations—traders gain powerful insights into potential entry points while managing risk effectively.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are Currency Translation Adjustments and Why Do They Matter?
Currency translation adjustments (CTAs) are essential components of financial reporting for multinational companies. They arise when a business operates across different countries with varying currencies, requiring the translation of financial statements from one currency to another—typically from the functional currency to the reporting currency. These adjustments are necessary because exchange rates fluctuate over time, impacting how assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses are valued on financial statements.
The core purpose of CTAs is to ensure that a company's reported financial position accurately reflects its economic reality despite these currency fluctuations. Without proper adjustments, companies risk presenting distorted financial results that could mislead investors or regulators. For example, if a U.S.-based multinational reports in USD but operates in Europe using euros as its functional currency, changes in EUR/USD exchange rates can significantly alter the reported figures when translated into USD.
How Do Currency Translation Adjustments Work?
Currency translation involves converting foreign operations' financial data into the parent company's reporting currency. This process depends on two main methods:
Temporal Method: This approach uses historical exchange rates for non-monetary items like inventory and fixed assets while applying current rates for monetary items such as cash or receivables. It tends to reflect more closely the actual costs at specific points in time but can lead to mismatches during periods of significant exchange rate volatility.
Current Rate Method: Under this method, all assets and liabilities are translated at current exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are also translated at average rates during the period. This method provides a more up-to-date reflection of foreign operations but can introduce volatility into reported earnings due to fluctuating exchange rates.
Both methods aim to align with accounting standards set by bodies like FASB (Financial Accounting Standards Board) under ASC 830 and IASB (International Accounting Standards Board) under IAS 21.
Challenges Posed by Exchange Rate Volatility
Exchange rate fluctuations create several complexities for companies engaged in international trade:
Financial Statement Volatility: Rapid changes in currencies can cause significant swings in reported earnings and asset values from period to period. For instance, during Brexit or COVID-19 disruptions, currencies like GBP or EUR experienced sharp declines against USD—necessitating frequent CTAs that could obscure underlying business performance.
Accounting Complexity: Applying different translation methods requires expertise; choosing between temporal or current rate approaches impacts how gains or losses appear on income statements versus other comprehensive income sections.
Regulatory Compliance: Companies must adhere strictly to standards such as IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) or US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). Misapplication can lead not only to inaccurate reporting but also regulatory penalties.
Operational Risks: Fluctuations affect cash flow management since revenue streams denominated in foreign currencies may diminish unexpectedly when converted back into home country currency—a challenge especially relevant during times of heightened market uncertainty like pandemics or geopolitical events.
Impact on Investor Perception: Investors rely heavily on transparent disclosures; inconsistent CTAs might raise concerns about management’s ability to handle foreign operations effectively—potentially affecting stock prices and credit ratings.
Recent Developments Increasing CTA Complexities
Recent global events have intensified challenges related to currency translation:
The COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented economic disruptions worldwide leading many currencies—including emerging market ones—to experience extreme volatility.
Political developments such as Brexit created persistent uncertainty around GBP valuation against major currencies like USD and EUR.
The rise of cryptocurrencies has introduced new layers of complexity; firms holding digital assets face difficulties translating these holdings into traditional fiat currencies due to regulatory ambiguities and market instability—as highlighted by recent cases where tech firms struggled with cryptocurrency valuation adjustments amid volatile markets[Reuters 2023].
These factors demand more sophisticated approaches toward managing CTAs—often requiring advanced forecasting models and real-time data analysis tools—to maintain accurate financial disclosures while complying with evolving standards.
How Companies Manage Currency Translation Risks
To mitigate risks associated with fluctuating exchange rates—and thus reduce unexpected impacts from CTAs—companies employ various strategies:
Hedging through forward contracts helps lock-in future conversion rates.
Diversifying operational bases across multiple countries spreads exposure.
Regularly updating forecasts based on macroeconomic indicators ensures timely adjustment strategies.
Additionally, adopting robust internal controls around foreign currency transactions ensures compliance with accounting standards while providing transparency for stakeholders about potential risks involved due to FX movements[IFRS Foundation].
The Impact of Inaccurate Currency Translation Adjustments
Incorrect application or neglecting proper CTA procedures can have serious repercussions:
Financial misstatement: Overstated profits may attract unwarranted investor confidence while understated liabilities could hide potential risks.
Regulatory sanctions: Non-compliance with IFRS/GAAP guidelines might result in fines or reputational damage.
Strategic misjudgments: Poor understanding of FX impacts hampers decision-making regarding investments abroad or supply chain planning.
4.. Investor mistrust: Transparency issues stemming from unreliable translations erode stakeholder confidence over time[Perplexity Finance 2025].
Hence, maintaining accuracy through diligent application of accounting principles is vital for sustaining corporate integrity amid complex international environments.
In summary, understanding what constitutes a currency translation adjustment involves recognizing both its necessity within global finance practices—and its inherent complexities driven by volatile markets, evolving regulations, technological innovations like cryptocurrencies—and operational challenges faced by multinational corporations today.[#] Proper management ensures transparent reporting that accurately reflects an enterprise’s true economic standing despite ongoing forex fluctuations.[#]


Lo
2025-05-19 16:19
What complexities arise from currency translation adjustments?
What Are Currency Translation Adjustments and Why Do They Matter?
Currency translation adjustments (CTAs) are essential components of financial reporting for multinational companies. They arise when a business operates across different countries with varying currencies, requiring the translation of financial statements from one currency to another—typically from the functional currency to the reporting currency. These adjustments are necessary because exchange rates fluctuate over time, impacting how assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses are valued on financial statements.
The core purpose of CTAs is to ensure that a company's reported financial position accurately reflects its economic reality despite these currency fluctuations. Without proper adjustments, companies risk presenting distorted financial results that could mislead investors or regulators. For example, if a U.S.-based multinational reports in USD but operates in Europe using euros as its functional currency, changes in EUR/USD exchange rates can significantly alter the reported figures when translated into USD.
How Do Currency Translation Adjustments Work?
Currency translation involves converting foreign operations' financial data into the parent company's reporting currency. This process depends on two main methods:
Temporal Method: This approach uses historical exchange rates for non-monetary items like inventory and fixed assets while applying current rates for monetary items such as cash or receivables. It tends to reflect more closely the actual costs at specific points in time but can lead to mismatches during periods of significant exchange rate volatility.
Current Rate Method: Under this method, all assets and liabilities are translated at current exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are also translated at average rates during the period. This method provides a more up-to-date reflection of foreign operations but can introduce volatility into reported earnings due to fluctuating exchange rates.
Both methods aim to align with accounting standards set by bodies like FASB (Financial Accounting Standards Board) under ASC 830 and IASB (International Accounting Standards Board) under IAS 21.
Challenges Posed by Exchange Rate Volatility
Exchange rate fluctuations create several complexities for companies engaged in international trade:
Financial Statement Volatility: Rapid changes in currencies can cause significant swings in reported earnings and asset values from period to period. For instance, during Brexit or COVID-19 disruptions, currencies like GBP or EUR experienced sharp declines against USD—necessitating frequent CTAs that could obscure underlying business performance.
Accounting Complexity: Applying different translation methods requires expertise; choosing between temporal or current rate approaches impacts how gains or losses appear on income statements versus other comprehensive income sections.
Regulatory Compliance: Companies must adhere strictly to standards such as IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) or US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). Misapplication can lead not only to inaccurate reporting but also regulatory penalties.
Operational Risks: Fluctuations affect cash flow management since revenue streams denominated in foreign currencies may diminish unexpectedly when converted back into home country currency—a challenge especially relevant during times of heightened market uncertainty like pandemics or geopolitical events.
Impact on Investor Perception: Investors rely heavily on transparent disclosures; inconsistent CTAs might raise concerns about management’s ability to handle foreign operations effectively—potentially affecting stock prices and credit ratings.
Recent Developments Increasing CTA Complexities
Recent global events have intensified challenges related to currency translation:
The COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented economic disruptions worldwide leading many currencies—including emerging market ones—to experience extreme volatility.
Political developments such as Brexit created persistent uncertainty around GBP valuation against major currencies like USD and EUR.
The rise of cryptocurrencies has introduced new layers of complexity; firms holding digital assets face difficulties translating these holdings into traditional fiat currencies due to regulatory ambiguities and market instability—as highlighted by recent cases where tech firms struggled with cryptocurrency valuation adjustments amid volatile markets[Reuters 2023].
These factors demand more sophisticated approaches toward managing CTAs—often requiring advanced forecasting models and real-time data analysis tools—to maintain accurate financial disclosures while complying with evolving standards.
How Companies Manage Currency Translation Risks
To mitigate risks associated with fluctuating exchange rates—and thus reduce unexpected impacts from CTAs—companies employ various strategies:
Hedging through forward contracts helps lock-in future conversion rates.
Diversifying operational bases across multiple countries spreads exposure.
Regularly updating forecasts based on macroeconomic indicators ensures timely adjustment strategies.
Additionally, adopting robust internal controls around foreign currency transactions ensures compliance with accounting standards while providing transparency for stakeholders about potential risks involved due to FX movements[IFRS Foundation].
The Impact of Inaccurate Currency Translation Adjustments
Incorrect application or neglecting proper CTA procedures can have serious repercussions:
Financial misstatement: Overstated profits may attract unwarranted investor confidence while understated liabilities could hide potential risks.
Regulatory sanctions: Non-compliance with IFRS/GAAP guidelines might result in fines or reputational damage.
Strategic misjudgments: Poor understanding of FX impacts hampers decision-making regarding investments abroad or supply chain planning.
4.. Investor mistrust: Transparency issues stemming from unreliable translations erode stakeholder confidence over time[Perplexity Finance 2025].
Hence, maintaining accuracy through diligent application of accounting principles is vital for sustaining corporate integrity amid complex international environments.
In summary, understanding what constitutes a currency translation adjustment involves recognizing both its necessity within global finance practices—and its inherent complexities driven by volatile markets, evolving regulations, technological innovations like cryptocurrencies—and operational challenges faced by multinational corporations today.[#] Proper management ensures transparent reporting that accurately reflects an enterprise’s true economic standing despite ongoing forex fluctuations.[#]
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Are MEV Bots and How Do They Extract Value?
Understanding the role of MEV bots in the Ethereum ecosystem is essential for anyone interested in decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain technology, or cryptocurrency trading. These sophisticated algorithms have become a significant part of how transactions are processed and profits are made within DeFi platforms. This article aims to provide a clear, comprehensive overview of what MEV bots are, how they operate, and their impact on the Ethereum network.
What Is Maximal Extractable Value (MEV)?
Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) refers to the maximum amount of profit that can be extracted from a set of blockchain transactions by reordering, inserting, or censoring them. On Ethereum and similar blockchains that support smart contracts, miners or validators have control over transaction ordering within blocks. This control creates opportunities for extracting additional value beyond standard transaction fees.
In simple terms, MEV is about finding ways to profit from transaction sequencing—whether by front-running trades or manipulating gas prices—by exploiting knowledge about pending transactions before they are confirmed on-chain.
How Do MEV Bots Work?
MEV bots leverage advanced algorithms and real-time data analysis to identify profitable opportunities within the mempool—the pool of unconfirmed transactions waiting to be included in blocks. These bots monitor pending transactions continuously and execute strategies designed to maximize returns through specific manipulations:
Front-Running: The bot detects large trades or arbitrage opportunities before they are executed publicly. It then submits its own transaction with higher gas fees so it gets prioritized ahead of others.
Sandwich Attacks: The bot places one transaction just before a target trade (to buy low) and another immediately after (to sell high), capturing profit from price movements caused by the initial trade.
Gas Price Manipulation: By adjusting gas prices dynamically, these bots influence which transactions get prioritized during block creation.
These techniques require rapid decision-making capabilities because delays can result in missed opportunities due to network congestion or other competing bots.
Types of MEV Bots
There are several categories based on their primary strategies:
- Front-Running Bots: These execute trades ahead of large market-moving orders detected in the mempool.
- Sandwiching Bots: They insert themselves between two related transactions—buying just before a big trade and selling immediately afterward—to capitalize on price swings.
- Gas Price Manipulation Bots: These adjust their gas bids strategically to influence transaction ordering without necessarily executing specific trades directly related to market movements.
Each type exploits different vulnerabilities inherent in blockchain mechanics but all aim at maximizing extractable value during each block's formation process.
Impact on Ethereum Network Performance
While MEV bots can generate significant profits for their operators, their activities also introduce notable challenges for network health:
Network Congestion: Because many MEV strategies involve rapid-fire multiple transactions executed almost simultaneously, they increase overall network load.
Higher Gas Fees: Increased competition among traders—including those using MEV bots—drives up gas prices for regular users trying to interact with DeFi protocols like lending platforms or decentralized exchanges.
This congestion not only raises costs but can also slow down legitimate user activity—a concern especially during periods of high market volatility when demand surges unexpectedly.
Recent Developments in Addressing MEV Challenges
The rise of MEV has prompted both community-led innovations and efforts from organizations like the Ethereum Foundation:
2021: Growing Awareness & Initial Responses
High-profile incidents such as hacks exploiting DeFi vulnerabilities brought attention to how malicious actors could leverage MEV techniques maliciously or exploit protocol flaws intentionally. In response, developers proposed solutions like "MEV-boost," an upgrade allowing users’ transactions to be bundled off-chain with validators choosing which bundles get included based on certain criteria—aimed at reducing harmful front-running while maintaining decentralization principles.
2022: Regulatory Scrutiny & Industry Discussions
Regulators such as the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission began scrutinizing activities associated with some forms of arbitrage enabled by these bots under anti-market manipulation laws. Meanwhile, industry participants debated balancing innovation-driven profit mechanisms against fairness concerns; some projects explored implementing “fair ordering” protocols designed explicitly against front-running tactics used by certain types of MEV extraction tools.
Risks Associated With Growing Use Of BEVs
As more entities develop sophisticated tools around these practices:
There’s potential centralization risk — larger players with more resources may dominate extraction activities.
Market integrity could suffer if manipulative practices distort asset prices unfairly.
Additionally, regulatory bodies might impose restrictions if perceived unfair advantages threaten broader financial stability or consumer protection standards within crypto markets.
By understanding what makes up an effective strategy for extracting value via blockchain manipulation—and recognizing its implications—you gain insight into ongoing debates around fairness versus profitability within DeFi ecosystems. As this landscape continues evolving rapidly through technological innovation and regulatory responses alike, staying informed remains crucial for participants across all levels—from casual traders through institutional investors seeking transparency amid complex dynamics driven largely by automated systems like MEV bots.


kai
2025-05-09 18:17
What are MEV bots and how do they extract value?
What Are MEV Bots and How Do They Extract Value?
Understanding the role of MEV bots in the Ethereum ecosystem is essential for anyone interested in decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain technology, or cryptocurrency trading. These sophisticated algorithms have become a significant part of how transactions are processed and profits are made within DeFi platforms. This article aims to provide a clear, comprehensive overview of what MEV bots are, how they operate, and their impact on the Ethereum network.
What Is Maximal Extractable Value (MEV)?
Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) refers to the maximum amount of profit that can be extracted from a set of blockchain transactions by reordering, inserting, or censoring them. On Ethereum and similar blockchains that support smart contracts, miners or validators have control over transaction ordering within blocks. This control creates opportunities for extracting additional value beyond standard transaction fees.
In simple terms, MEV is about finding ways to profit from transaction sequencing—whether by front-running trades or manipulating gas prices—by exploiting knowledge about pending transactions before they are confirmed on-chain.
How Do MEV Bots Work?
MEV bots leverage advanced algorithms and real-time data analysis to identify profitable opportunities within the mempool—the pool of unconfirmed transactions waiting to be included in blocks. These bots monitor pending transactions continuously and execute strategies designed to maximize returns through specific manipulations:
Front-Running: The bot detects large trades or arbitrage opportunities before they are executed publicly. It then submits its own transaction with higher gas fees so it gets prioritized ahead of others.
Sandwich Attacks: The bot places one transaction just before a target trade (to buy low) and another immediately after (to sell high), capturing profit from price movements caused by the initial trade.
Gas Price Manipulation: By adjusting gas prices dynamically, these bots influence which transactions get prioritized during block creation.
These techniques require rapid decision-making capabilities because delays can result in missed opportunities due to network congestion or other competing bots.
Types of MEV Bots
There are several categories based on their primary strategies:
- Front-Running Bots: These execute trades ahead of large market-moving orders detected in the mempool.
- Sandwiching Bots: They insert themselves between two related transactions—buying just before a big trade and selling immediately afterward—to capitalize on price swings.
- Gas Price Manipulation Bots: These adjust their gas bids strategically to influence transaction ordering without necessarily executing specific trades directly related to market movements.
Each type exploits different vulnerabilities inherent in blockchain mechanics but all aim at maximizing extractable value during each block's formation process.
Impact on Ethereum Network Performance
While MEV bots can generate significant profits for their operators, their activities also introduce notable challenges for network health:
Network Congestion: Because many MEV strategies involve rapid-fire multiple transactions executed almost simultaneously, they increase overall network load.
Higher Gas Fees: Increased competition among traders—including those using MEV bots—drives up gas prices for regular users trying to interact with DeFi protocols like lending platforms or decentralized exchanges.
This congestion not only raises costs but can also slow down legitimate user activity—a concern especially during periods of high market volatility when demand surges unexpectedly.
Recent Developments in Addressing MEV Challenges
The rise of MEV has prompted both community-led innovations and efforts from organizations like the Ethereum Foundation:
2021: Growing Awareness & Initial Responses
High-profile incidents such as hacks exploiting DeFi vulnerabilities brought attention to how malicious actors could leverage MEV techniques maliciously or exploit protocol flaws intentionally. In response, developers proposed solutions like "MEV-boost," an upgrade allowing users’ transactions to be bundled off-chain with validators choosing which bundles get included based on certain criteria—aimed at reducing harmful front-running while maintaining decentralization principles.
2022: Regulatory Scrutiny & Industry Discussions
Regulators such as the U.S Securities and Exchange Commission began scrutinizing activities associated with some forms of arbitrage enabled by these bots under anti-market manipulation laws. Meanwhile, industry participants debated balancing innovation-driven profit mechanisms against fairness concerns; some projects explored implementing “fair ordering” protocols designed explicitly against front-running tactics used by certain types of MEV extraction tools.
Risks Associated With Growing Use Of BEVs
As more entities develop sophisticated tools around these practices:
There’s potential centralization risk — larger players with more resources may dominate extraction activities.
Market integrity could suffer if manipulative practices distort asset prices unfairly.
Additionally, regulatory bodies might impose restrictions if perceived unfair advantages threaten broader financial stability or consumer protection standards within crypto markets.
By understanding what makes up an effective strategy for extracting value via blockchain manipulation—and recognizing its implications—you gain insight into ongoing debates around fairness versus profitability within DeFi ecosystems. As this landscape continues evolving rapidly through technological innovation and regulatory responses alike, staying informed remains crucial for participants across all levels—from casual traders through institutional investors seeking transparency amid complex dynamics driven largely by automated systems like MEV bots.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
